JavaScript各种继承方式和优缺点
好久没写博客啦,嘻嘻,这个月是2017年的最后一个月啦,大家应该都开始忙着写年终总结了吧,嘻嘻,小颖今天给大家分享下Javascript中的几种继承方式以及他们的优缺点。
1.借助构造函数实现继承
原理:通过call()函数修改 this 指向,从而实现将父类属性挂载到子类实例中。
function parent1() { this.name = 'parent1'; } function child1() { parent1.call(this); this.type = 'child1'; } console.log(new child1);
打印结果:
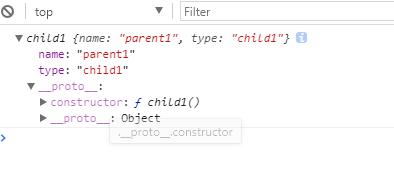
当我们给父类 parent1 的 prototype 属性添加say方法后,但是在 child1 中是获取不到的。
function parent1() { this.name = 'parent1'; } parent1.prototype.say = function() { console.log('hello'); }; function child1() { parent1.call(this); this.type = 'child1'; } console.log(new child1, new child1().say());
打印结果:
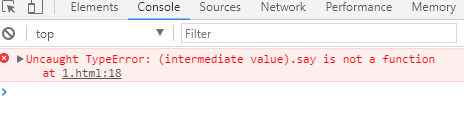
所以.借助构造函数实现继承,只能实现部分继承;如果父类属性都在构造函数中,则能够实现全部继承,如果父类原型对象上还有方法,则子类是继承不到的。
总结:
优点:
1.只调用一次父类的构造函数,避免了在子类原型上创建不必要的,多余的属性 。
2.原型链保持不变。
缺点:只能实现部分继承;如果父类属性都在构造函数中,则能够实现全部继承,如果父类原型对象上还有方法,则子类是继承不到的。
2.借助原型链实现继承(最通用的方式)
原理:将子类的prototype属性赋值为父类实例对象,则子类的_proto_属性继承父类。
function parent2() { this.name = 'parent2'; this.play = [1, 2, 3]; } parent2.prototype.say = function() { console.log('hello'); }; function child2() { this.type = 'child2'; } child2.prototype = new parent2(); console.log(new child2); var p1 = new child2(); var p2 = new child2(); console.log(p1.say()); console.log(p1.play, p2.play); p1.play.push(4); console.log(p1, p2); console.log(p1.play, p2.play);
打印结果:
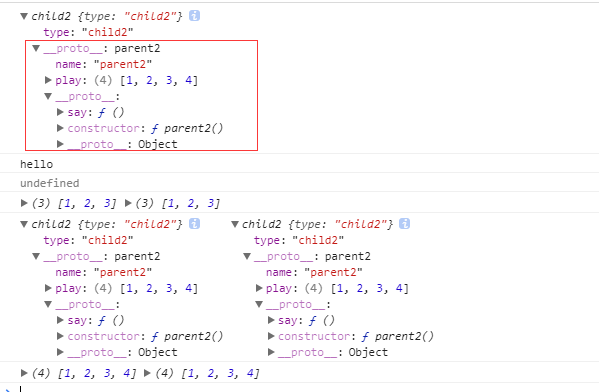
注意:
1.在第一种继承方式中,子类是继承不到父类 prototype 属性的内容的,但现在可以继承到了。
2.其实小颖只执行了 p1.play.push(4) ,然而 p2.play 的值也跟着变化了。
这其实都是因为 child2.prototype = new parent2(),他们的 __proto__ 都继承了父类parent2 的所有属性。虽然表面上 p1.play.push(4) 看起来像是只改变了 p1 的 play 属性,但其实是改变了父类 parent2 的 play 属性,而p1,p2继承了 parent2 ,所以p1,p2同时发生变化。
总结:
优点:父类的方法(getName)得到了复用。
缺点:重写子类的原型 等于 父类的一个实例,(父类的实例属性变成子类的原型属性)如果父类包含引用类型的属性,那么子类所有实例都会共享该属性 (包含引用类型的*原型*属性会被实例共享)。
3.组合方式
function parent3() { this.name = 'parent3'; this.play = [1, 2, 3]; } function child3() { parent3.call(this); this.type = 'child3'; } child3.prototype = new parent3(); var p3 = new child3(); var p4 = new child3(); console.log(p3.play, p4.play); p3.play.push(4); console.log(p3,p4); console.log(p3.play, p4.play);
打印结果:
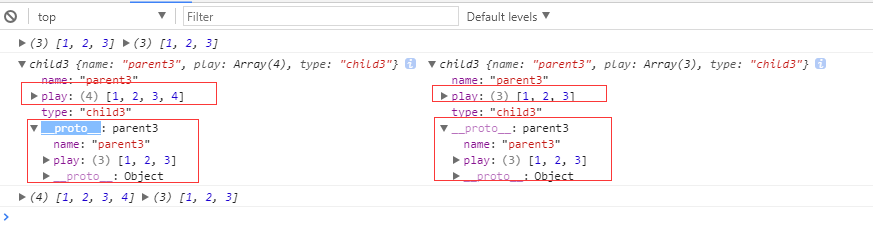
注意:
在上面的结果中,大家有没有发现,同样只给 p3.play.push(4) ,但是只有p3一个变了,但p4没有变,其实大家通过小颖用红框框起来的地方,大就会明白,为什么p3、p4的 __proto__ 都继承了父类parent2 的属性,为什么修改p3,p4,这次p4却没有变化。
总结:
优点:继承了上述两种方式的优点,摒弃了缺点,复用了方法,子类又有各自的属性。
缺点:因为父类构造函数被执行了两次,子类的原型对象(Sub.prototype)中也有一份父类的实例属性,而且这些属性会被子类实例(sub1,sub2)的属性覆盖掉,也存在内存浪费。
4.组合继承的优化1
function parent4() { this.name = 'parent4'; this.play = [1, 2, 3]; } function child4() { parent4.call(this); this.type = 'child4'; } child4.prototype = parent4.prototype; var p5 = new child4(); var p6 = new child4(); console.log(p5, p6); console.log(p5 instanceof child4, p5 instanceof parent4); console.log(p5.constructor);
打印结果:
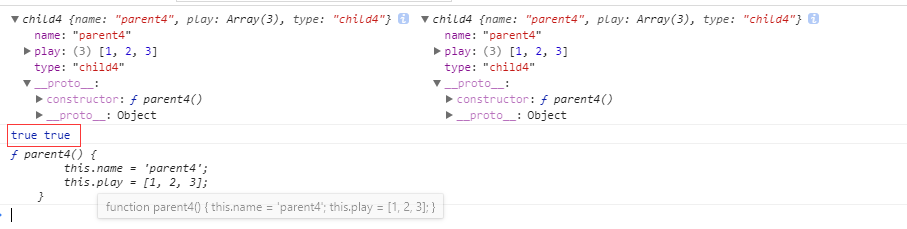
注意:
instanceof 和 constructor 都是用来判断一个实例对象是不是这个构造函数的实例的。
不同点是:用constructor 比instanceof 更严谨,例如如果 A 继承 B,B 继承 C,A 生成的实例对象,用 instanceof 判断与 A、B、C 的关系,都是 true。所以无法区分这个到底是 A、B、C 谁生成的实例。而constructor 是原型对象的一个属性,并且这个属性的值是指向创建当前实例的对象的。
console.log(p5 instanceof child4, p5 instanceof parent4); 执行结果一样,而且 p5.constructor 竟然不是 child4 而是 parent4。
5.组合继承的优化2 ——寄生组合式继承
function parent5() { this.name = 'parent5'; this.play = [1, 2, 3]; } function child5() { parent5.call(this); this.type = 'child5'; } child5.prototype = Object.create(parent5.prototype); child5.prototype.constructor = child5; var p7 = new child5(); var p8 = new child5(); console.log(p7, p8); console.log(p7.constructor);
打印结果:
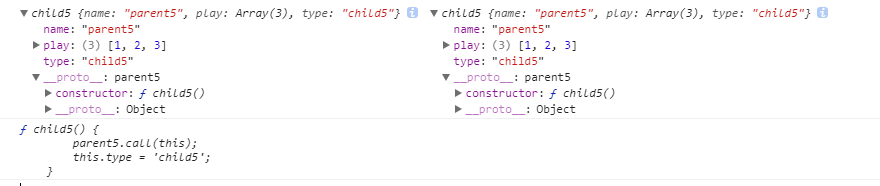
总结:
组合继承的缺点就是在继承父类方法的时候调用了父类构造函数,从而造成内存浪费,并且找不到实例对象真正的 constructor 。
那在复用父类方法的时候,使用Object.create方法也可以达到目的,没有调用父类构造函数,并将子类的 prototype.constructor 属性赋值为自己本身,则问题完美解决。



