Codeforces Round #432 (Div. 2, based on IndiaHacks Final Round 2017) C
You are given set of n points in 5-dimensional space. The points are labeled from 1 to n. No two points coincide.
We will call point a bad if there are different points b and c, not equal to a, from the given set such that angle between vectors 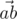 and
and 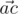 is acute (i.e. strictly less than
is acute (i.e. strictly less than 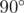 ). Otherwise, the point is called good.
). Otherwise, the point is called good.
The angle between vectors 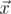 and
and 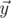 in 5-dimensional space is defined as
in 5-dimensional space is defined as 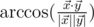 , where
, where 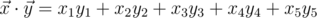 is the scalar product and
is the scalar product and 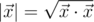 is length of
is length of 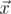 .
.
Given the list of points, print the indices of the good points in ascending order.
The first line of input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 103) — the number of points.
The next n lines of input contain five integers ai, bi, ci, di, ei (|ai|, |bi|, |ci|, |di|, |ei| ≤ 103) — the coordinates of the i-th point. All points are distinct.
First, print a single integer k — the number of good points.
Then, print k integers, each on their own line — the indices of the good points in ascending order.
6
0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1
1
1
3
0 0 1 2 0
0 0 9 2 0
0 0 5 9 0
0
In the first sample, the first point forms exactly a 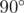 angle with all other pairs of points, so it is good.
angle with all other pairs of points, so it is good.
In the second sample, along the cd plane, we can see the points look as follows:
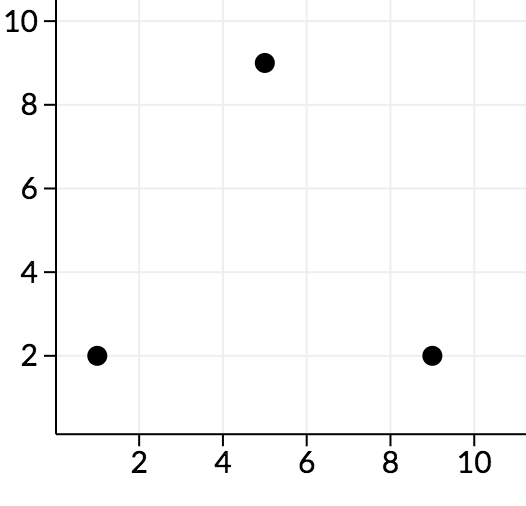
We can see that all angles here are acute, so no points are good.
题意:坏点:一个点和它周围的点形成的角度有一个小于90,问有多少好点,五维的环境下哦
解法:
1 二维的环境下 一个点周围是4个点,三维的环境下,一个点周围是6个点,那么..五维的环境应该是10个点,包括本身是11点,超过11点都不算
2 然后暴力计算
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int x[1230][6]; int y[1230][6]; int n; vector<int>Ve; int main(){ cin>>n; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ for(int j=1;j<=5;j++){ cin>>x[i][j]; } } if(n>=12){ cout<<"0"<<endl; return 0; } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ memset(y,0,sizeof(y)); int flag=0; for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){ if(i==j) continue; for(int k=1;k<=5;k++){ y[j][k]=x[j][k]-x[i][k]; // cout<<y[j][k]<<"A"<<endl; } for(int k=1;k<j;k++){ int sum=0; if(k==i) continue; for(int l=1;l<=5;l++){ sum+=y[k][l]*y[j][l]; } if(sum>0){ flag=1; break; } } if(flag){ break; } } if(flag==0){ Ve.push_back(i); } } int Size=Ve.size(); cout<<Size<<endl; for(int i=0;i<Size;i++){ cout<<Ve[i]<<endl; } return 0; }





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 从HTTP原因短语缺失研究HTTP/2和HTTP/3的设计差异
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~