List自定义对象的排序,根据对象的某一列进行排序
在工作中,经常需要对List对象集合进行排序操作,下面总结下搞个通用排序对象,原理是使用JAVA的
Comparator 接口实现排序 不多说直接上“干货”
1、存在实体类:
1 @Data 2 @AllArgsConstructor 3 @NoArgsConstructor 4 class Book { 5 private Long id;//编号 6 private String userName;//书本名称 7 private double productPrice;//书本价格 8 private String author;//作者 9 private Integer weight;//权重 10 }
2、SortList 排序实现通用类:
1 @Data 2 @AllArgsConstructor 3 @NoArgsConstructor 4 public class SortList<T> implements Comparator<T> { 5 6 //需要比较的对象属性字段名称 7 private String propertyName; 8 //是否是升序排序 9 private boolean isAsc; 10 11 /** 12 * 需要的是:根据类中的字段对对象进行排序 13 * 14 * @return 15 */ 16 17 @Override 18 public int compare(T b1, T b2) { 19 20 Class<?> clz = b1.getClass(); 21 Method method = getPropertyMethod(clz, propertyName); 22 try { 23 24 Object objectOne = method.invoke(b1); 25 26 Object objectTwo = method.invoke(b2); 27 28 if (objectOne == null || objectTwo == null) { 29 return 0; 30 } 31 32 Comparable value1 = (Comparable) objectOne; 33 34 Comparable value2 = (Comparable) objectTwo; 35 36 if (isAsc) { 37 return value1.compareTo(value2); 38 } else { 39 return value2.compareTo(value1); 40 } 41 } catch (Exception e) { 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 } 44 return 0; 45 } 46 47 // 获取类名 48 public static Method getPropertyMethod(Class clz, String propertyName) { 49 Method method = null; 50 try { 51 method = clz.getMethod("get" + firstUpperCase(propertyName)); 52 } catch (Exception e) { 53 System.out.println("获取类名发生错误!"); 54 } 55 return method; 56 } 57 58 /** 59 * 首字母大写方法 60 * @param str 61 * @return 62 */ 63 public static String firstUpperCase(String str) { 64 char[] ch = str.toCharArray(); 65 if (ch[0] >= 'a' && ch[0] <= 'z') { 66 ch[0] = (char) (ch[0] - 32); 67 } 68 return new String(ch); 69 } 70 71 }
3、实际使用测试如下: 主要这么来使用
Collections.sort(bookList, new SortList<Book>("productPrice",true));
测试
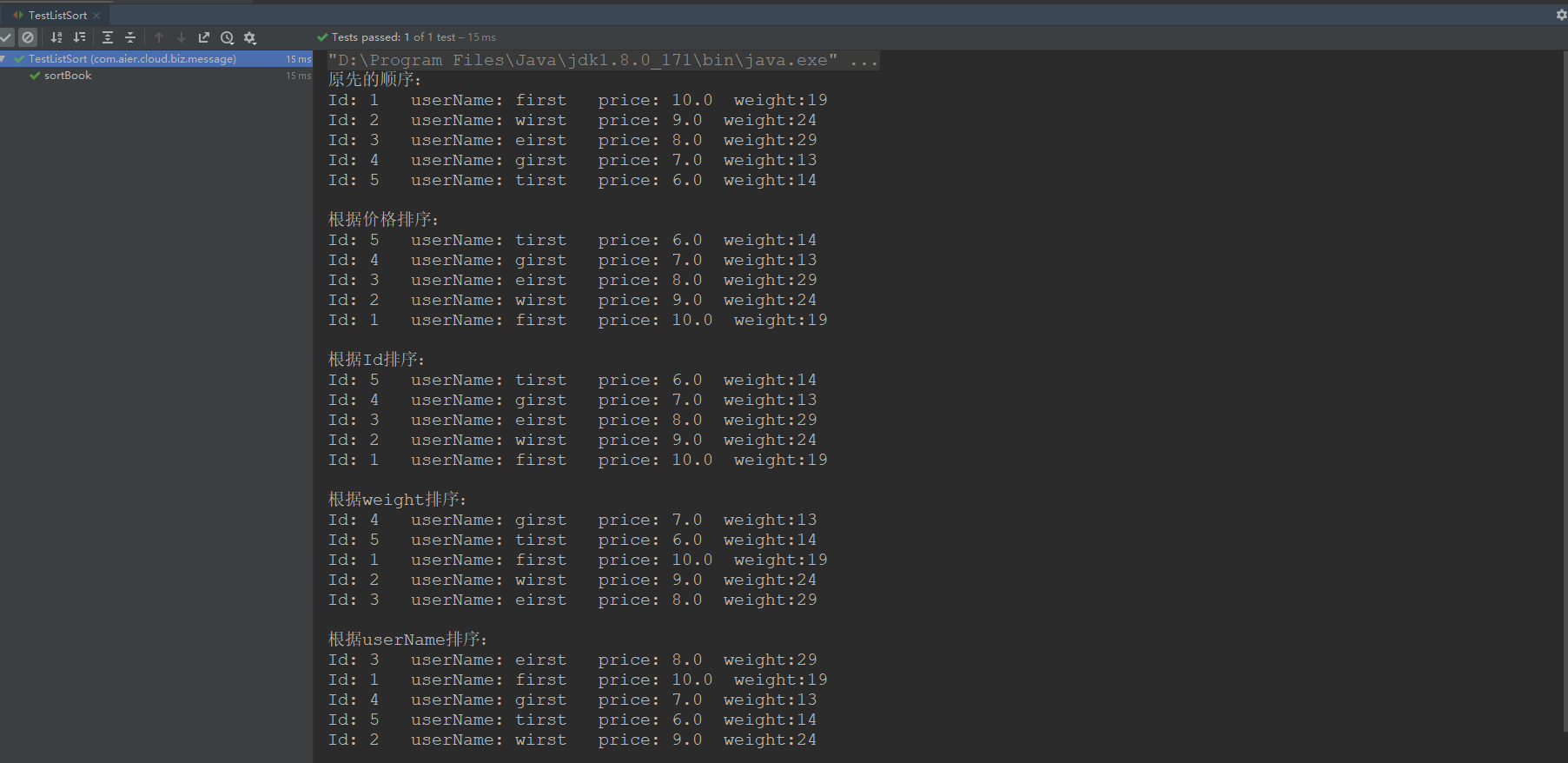
1 @Test 2 public void sortBook() { 3 List<Book> bookList = getBookList(); 4 System.out.println("原先的顺序:"); 5 printf(bookList); 6 7 System.out.println("根据价格排序:"); 8 Collections.sort(bookList, new SortList<Book>("productPrice",true)); 9 printf(bookList); 10 11 System.out.println("根据Id排序:"); 12 Collections.sort(bookList, new SortList<Book>("id",false)); 13 printf(bookList); 14 15 System.out.println("根据weight排序:"); 16 Collections.sort(bookList, new SortList<Book>("weight",true)); 17 printf(bookList); 18 19 System.out.println("根据userName排序:"); 20 Collections.sort(bookList, new SortList<Book>("userName",true)); 21 printf(bookList); 22 23 24 } 25 26 public List<Book> getBookList() { 27 List<Book> books = Lists.newArrayList(); 28 Book book1 = new Book(1L, "first", 10.00, "zhangsan", 19); 29 Book book2 = new Book(2L, "wirst", 9.00, "zhangsan", 24); 30 Book book3 = new Book(3L, "eirst", 8.00, "zhangsan", 29); 31 Book book4 = new Book(4L, "girst", 7.00, "zhangsan", 13); 32 Book book5 = new Book(5L, "tirst", 6.00, "zhangsan", 14); 33 34 books.add(book1); 35 books.add(book2); 36 books.add(book3); 37 books.add(book4); 38 books.add(book5); 39 40 return books; 41 } 42 43 /** 44 * 打印函数 45 * 46 * @param lisbk 47 */ 48 public void printf(List<Book> lisbk) { 49 if (lisbk.isEmpty() || lisbk == null) { 50 System.out.println("没有数据"); 51 return; 52 } 53 for (Book book : lisbk) { 54 System.out.println("Id: " + book.getId() + " userName: " + book.getUserName() + " price: " + book.getProductPrice() + " weight:" + book.getWeight()); 55 } 56 System.out.println(); 57 return; 58 }
执行结果如下: