Vue3
Vue3
1.Vue简介
1.Vue的特点
- 采用组件化模式,提高代码复用率、且让代码更好维护。
- 声明式编码,让编码人员无需直接操作Dom,提高开发效率。
- 使用虚拟Dom+优秀的Diff算法,尽量复用Dom节点。
2.入门案例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="../js/vue3.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="counter">
<h1> counter:{{ num }}</h1>
</div>
<script>
// const Counter={
// data(){
// return{
// num:0
// }
// }
// }
const Counter={
data:function(){
return {
num:0
}
}
}
//创建一个应用,将配置的对象counter的内容渲染到选择器#counter的元素上
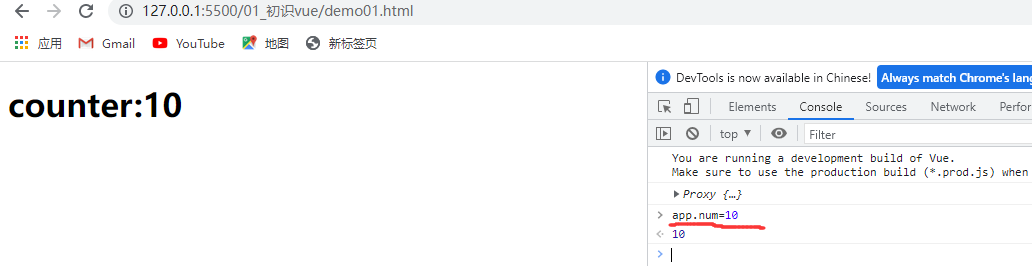
let app = Vue.createApp(Counter).mount("#counter")
console.log(app)
</script>
</body>
</html>
可以用 app.num = 10修改值
2.用 Vite来创建一个vue项目
使用 npm:(在控制台终端输入)
npm init vite-app vue3demo03 //vue3demo03 项目名称
cd vue3demo03
npm install
npm run dev
最新创建步骤
# npm 6.x
$ npm init vite@latest <project-name> --template vue
# npm 7+,需要加上额外的双短横线
$ npm init vite@latest <project-name> -- --template vue
$ cd <project-name>
$ npm install
$ npm run dev
创建好后生成:
3.Vue声明式语法与数据双向绑定(v-model)
App.vue
<template>
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png" />
<!-- <HelloWorld msg="Hello Vue 3.0 + Vite" /> -->
<h2 @click="changeMsg"> {{msg}}</h2>
<!-- v-model来进行绑定 -->
<input type="text" v-model="msg" />
</template>
<script>
import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
//命令式
//document.querySelector("h1").innerHTML="helloworld"
//声明式
export default {
name: 'App',
// components: {
// HelloWorld
// }
data(){
return{
msg:"helloword"
}
},
methods:{
changeMsg(){
this.msg = "jihu,真帅"
}
}
}
</script>
运行结果:
改变输入框的值,上面的值就会改变,这就是双向绑定

单击后,会改变值

4.模板语法常用指令
插值
1.文本 (v-once指令)
数据绑定最常见的形式就是使用“Mustache” (双大括号) 语法的文本插值:
<span>Message: {{ msg }}</span>
Mustache 标签将会被替代为对应组件实例中 msg property 的值。无论何时,绑定的组件实例上 msgproperty 发生了改变,插值处的内容都会更新。
通过使用 v-once 指令,你也能执行一次性地插值,当数据改变时,插值处的内容不会更新。但请留心这会影响到该节点上的其它数据绑定:
<span v-once>这个将不会改变: {{ msg }}</span>
<template>
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png" />
<!--双括号语法 Mustache -->
<h2 >{{msg}}</h2>
<!-- v-once指令,使得内容只渲染一次 -->
<h2 @click="changeMsg" v-once> {{msg}}</h2>
</template>
<script>
import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
//声明式
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
msg:"helloword"
}
},
methods:{
changeMsg(){
this.msg = "jihu,真帅"
}
}
}
</script>
2.原始 HTML Attribute (v-html指令 、v-bind指令)
<template>
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png" />
<!-- <HelloWorld msg="Hello Vue 3.0 + Vite" /> -->
<!--双括号语法 Mustache -->
<h2 >{{msg}}</h2>
<!-- v-once指令,使得内容只渲染一次 -->
<h2 @click="changeMsg" v-once> {{msg}}</h2>
<!-- v-html指令,使得内容插入html的代码 -->
<div>{{content}}</div>
<div v-html="content"></div>
<!-- v-bind指令,绑定属性的内容 -->
<div :id="id" :class="id"></div>
<div v-bind:id="id" v-bind:class="id"></div>
</template>
<script>
import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
//声明式
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
msg:"helloword",
content:"<h1>标题1</h1><h2 style='color:red'>标题2</h2>",
id:"d1"
}
},
methods:{
changeMsg(){
this.msg = "jihu,真帅",
this.id= "d2"
}
}
}
</script>
<style >
#d1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: red;
}
#d2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: green;
}
</style>
展示结果:

点击helloword后:

3.使用 JavaScript 表达式
<template>
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png" />
<h2 >{{msg}}</h2>
<!-- javascript表达式可以在模板语法里使用 -->
<h1>{{msg.split('')}}</h1>
<h1> {{ msg.split('').reverse() }}</h1>
<h1>{{msg.split('').reverse().join('')}}</h1>
<div v-bind:id="msg.split('').reverse().join('')" v-bind:class="id"></div>
<div>{{color=='绿色'?'开心':'难过'}}</div>
<div v-html="content" ></div>
<div :id="color1">{{msg}}</div>
</template>
<script>
//声明式
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
msg:"helloword",
color:'绿色',
color1:'color',
content:"<h1 style='color:red'>红黑树</h1>"
}
}
}
</script>
<style >
#color{
color: orange;
}
</style>
展示结果:

动态指令
<template>
<!-- 动态指令 -->
<div v-bind:[attributeName]="d1"></div>
<button @click="changeName">点击 切换颜色</button>
<button @[eventName]="changeName">点击切换颜色</button>
</template>
<script>
//声明式
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
attributeName:'class',
d1:'color',
eventName:'click'
}
},
methods:{
changeName:function(){
this.attributeName='id'
}
}
}
</script>
<style >
#color{
width: 100px;
height:100px;
background: yellow;
}
.color{
width: 100px;
height:100px;
background: blue;
}
</style>
5.计算属性和监听器
1.计算属性
<template>
<!-- 计算属性 -->
<div class="d1">{{msg.split('').reverse().join('')}}</div>
<div class="d1">{{reverseMsg}}</div>
</template>
<script>
//声明式
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
msg:'helloworld'
}
},
computed:{
reverseMsg:function(){
return this.msg.split('').reverse().join('')
}
}
}
}
</script>
<style >
.d1{
width: 100px;
height:100px;
background: blue;
}
</style>
展示结果:
2.监听器 (监听数据的变化)
<template>
<!-- 计算属性 -->
<div class="d1">{{msg.split('').reverse().join('')}}</div>
<div class="d1">{{reverseMsg}}</div>
<!-- 监听 -->
<input type="text" v-model="msg" />
<h1>{{msg}}</h1>
</template>
<script>
//声明式
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
msg:'helloworld'
}
},
computed:{
reverseMsg:function(){
return this.msg.split('').reverse().join('')
}
},
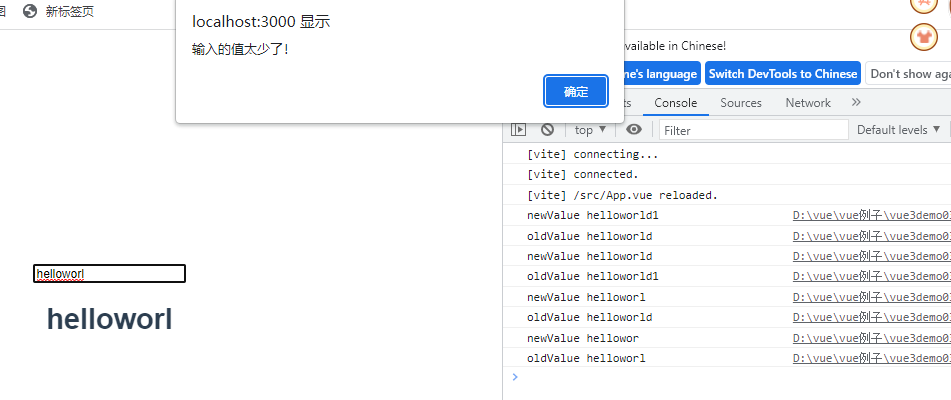
watch:{
//监听值的变化
msg:function(newValue,oldValue){
console.log('newValue',newValue)
console.log('oldValue',oldValue)
if(newValue.length<10){
alert("输入的值太少了!")
}
}
}
}
</script>
<style >
#id{
width: 100px;
height:100px;
background: yellow;
}
.d1{
width: 100px;
height:100px;
background: blue;
}
</style>
展示结果
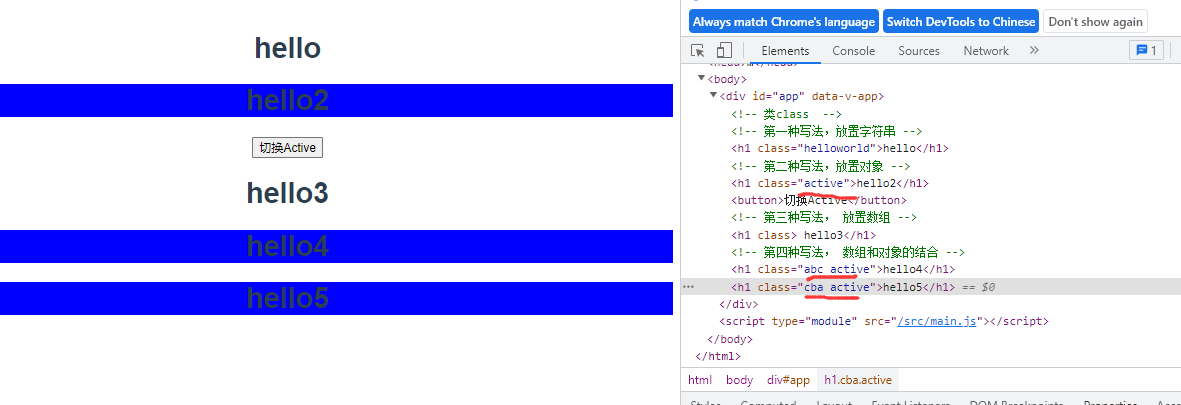
6.Class与Style绑定
1.Class类名的多种操作方式
<template>
<!-- 类class -->
<!-- 第一种写法,放置字符串 -->
<h1 :class="msg">hello</h1>
<!-- 第二种写法,放置对象 -->
<h1 :class="{active:isActive}" >hello2</h1>
<button @click="tochangeActive">切换Active</button>
<!-- 第三种写法, 放置数组 -->
<h1 :class="attr"> hello3</h1>
<!-- 第四种写法, 数组和对象的结合 -->
<h1 :class="['abc',{active:true}]">hello4</h1>
<h1 :class="[classname,{active:isActive}]">hello5</h1>
</template>
<script>
//声明式
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
msg:'helloworld',
isActive:true,
attr:['swiper','active'],
classname:'abc'
}
},
methods:{
tochangeActive:function(){
this.isActive = !this.isActive,
this.attr.pop(), //pop() 用来删除attr:['swiper','active']中的值,一次删一个,从后往前删
this.classname='cba'
}
}
}
</script>
<style >
.active{
background: blue;
}
</style>
输出结果:
2.Style样式的多种操作方式
<template>
<!-- style -->
<!-- 第一种写法,放置字符串 -->
<h1 :style="msg">hello</h1>
<!-- 第二种写法,放置对象 -->
<h1 :style="{background:'purple'}" >hello2</h1>
<button @click="tochangeActive">切换Active</button>
<!-- 第三种写法, 放置数组 -->
<h1 :style="styleObj"> hello3</h1>
<!-- 第四种写法, 数组和对象的结合 -->
<h1 :style="[styleObj,{width:'500px'}]">hello4</h1>
</template>
<script>
//声明式
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
msg:"background:yellow;",
isActive:true,
styleObj:{
//如果遇到需要多个单词组成的样式,可以使用引号 例如:'background-color':'pink'
//也可以使用驼峰命名法 例如: backgroundColor:'pink',
background:'pink',
border:'1px solid orange',
boxSizing:"border-box"
}
}
},
methods:{
tochangeActive:function(){
this.styleObj.backgroundColor='skyBlue'
}
}
}
</script>
<style >
.active{
background: blue;
}
</style>
展示效果
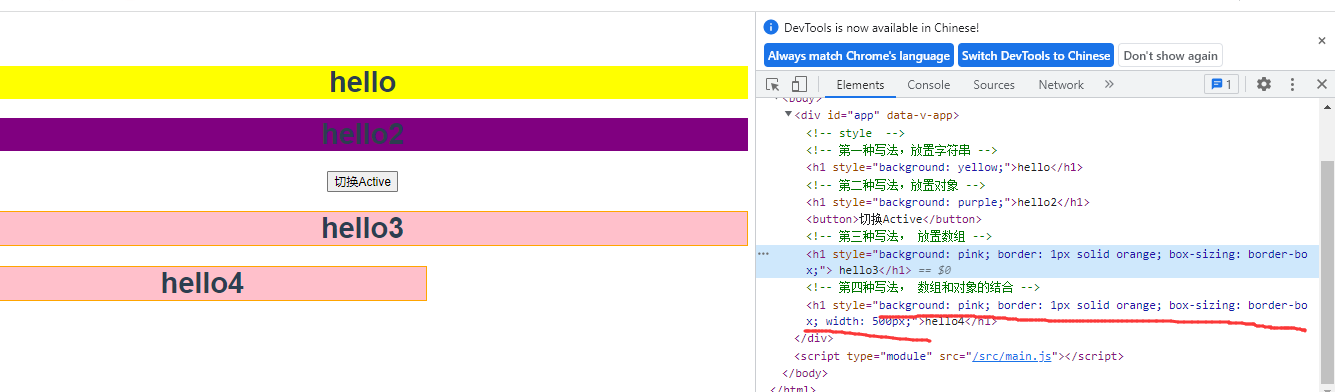
点击后

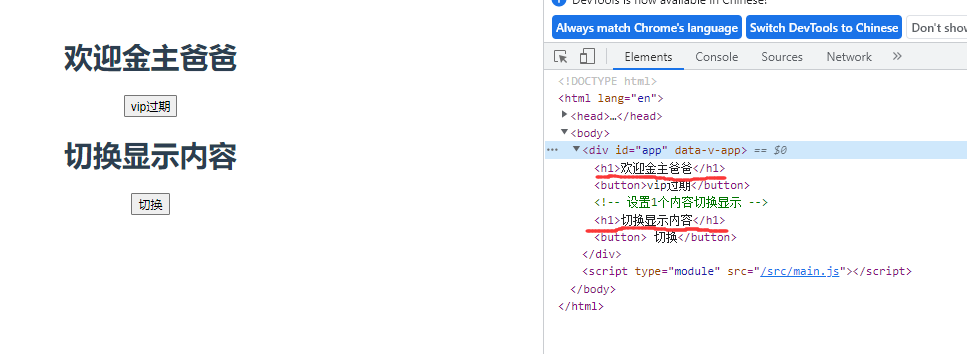
7.条件渲染 v-if 与v-show
<template>
<h1 v-if="user=='超级vip'" >欢迎金主爸爸</h1>
<h1 v-else-if="user=='vip'">欢迎会员登录</h1>
<h1 v-else>充值会让你更强大!</h1>
<button @click="changhestatus">vip过期</button>
<!-- 设置1个内容切换显示 -->
<h1 v-show="isShow">切换显示内容</h1>
<button @click="toggleShow"> 切换</button>
</template>
<script>
//声明式
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
user:'超级vip',
isShow:true
}
},
methods:{
changhestatus:function(){
this.user='普通用户'
},
toggleShow:function(){
this.isShow = !this.isShow
}
}
}
展示结果:
点击按钮后:
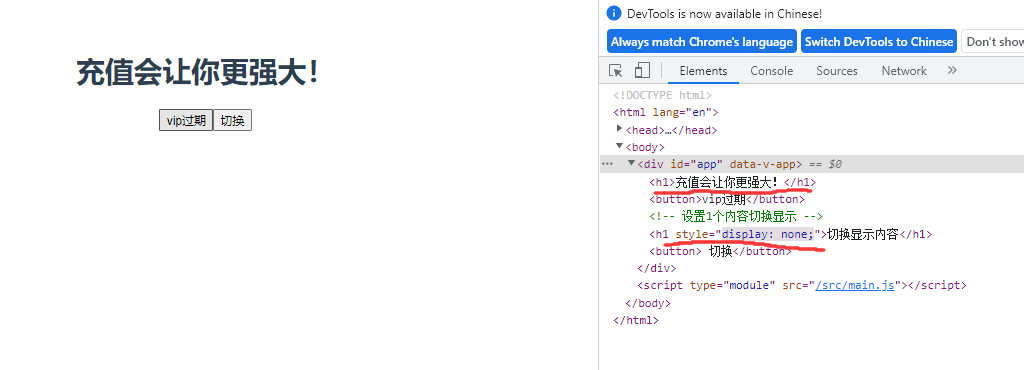
总结:v-if vs v-show
v-if 是“真正”的条件渲染,因为它会确保在切换过程中,条件块内的事件监听器和子组件适当地被销毁和重建。
v-if 也是惰性的:如果在初始渲染时条件为假,则什么也不做——直到条件第一次变为真时,才会开始渲染条件块。
相比之下,v-show 就简单得多——不管初始条件是什么,元素总是会被渲染,并且只是简单地基于 CSS 进行切换。
一般来说,v-if 有更高的切换开销,而 v-show 有更高的初始渲染开销。因此,如果需要非常频繁地切换,则使用 v-show 较好;如果在运行时条件很少改变,则使用 v-if 较好。
8.列表渲染 v-for
<template>
<div>
<ol>
<!-- item是里面一行一行的字符串 , i是它的索引值 -->
<!-- :key="i" 相当于给每个班级做上标号 不写也行 -->
<li v-for="(item,i) in news" :key="i">{{item}}-->{{i}}</li>
</ol>
<ol>
<li v-for="(item,i) in news1" :key="i">{{ item.title }}--{{item.tag}}--{{item.num}}-->{{i}}</li>
</ol>
<!-- item 是值,i相当于key -->
<ol>
<li v-for="(item,i) in jihu" :key="i">{{item}}--{{i}}</li>
</ol>
<!-- of 和in的效果一样 -->
<ol>
<li v-for="(item,i) of jihu" :key="i">{{item}}--{{i}}</li>
</ol>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//声明式
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
news:[
'2022值得期待的生活新变化',
'昨日新增本土“1860+1194”',
'吉林省15小时内增本土“1139+370”',
'乌总统:不入北约是必须承认的事实'
],
news1:[
{
title:'2022值得期待的生活新变化',
tag:"沸",
num:"450万"
},
{
title:'昨日新增本土“1860+1194”',
tag:"新",
num:"110万"
},
{
title:'吉林省15小时内增本土“1139+370”',
tag:"热",
num:"550万"
}
],
jihu:{
name:'jihu',
age:27,
type:'sport'
}
}
}
}
</script>
展示结果:

9.事件处理
我们可以使用 v-on 指令 (通常缩写为 @符号) 来监听 DOM 事件,并在触发事件时执行一些 JavaScript。用法为 v-on:click="methodName" 或使用快捷方式 @click="methodName"
1.事件与参数和事件修饰符
<template>
<div>
<!-- 绑定事件,不需要参数 -->
<h1 @click="changenumcount">{{num}}</h1>
<!-- 绑定事件,直接处理表达式 -->
<h1 @click="num+=2">{{num}}</h1>
<!-- 绑定事件,传递参数 -->
<h1 @click="addNumEvent(10)">{{num}}</h1>
<!-- 绑定事件传递事件对象和参数 -->
<h1 @click="addNumEvent1(20,$event)">{{num}}</h1>
<!-- v-on是全称指令 ,@是缩写的指令 -->
<h1 v-on:click="addNumEvent1(20,$event)">{{num}}</h1>
<!-- 一个事件绑定多个处理函数 -->
<h1 :style="{background:color}" @click="addNumEvent1(20,$event),changeColor($event)">{{num}}</h1>
<!-- 事件的修饰符 -->
<!--
常用的事件修饰:
阻止事件冒泡.stop
阻止默认事件.prevent
事件只会触发一次.once
-->
<h1 :style="{background:color}" @click.once="addNumEvent1(20,$event),changeColor($event)">{{num}}</h1>
<!--
按键修饰符
enter/tab/delete/esc/space/up/down/left/right
系统修饰符:
.ctrl/.alt/.shift/.meta
鼠标按键的修饰符
.left/.right/.middle
-->
<input type="text" @keydown.enter="searchEvent" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
//声明式
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
num:0,
color:'red'
}
},
methods:{
changenumcount:function(){
this.num += 2;
//this.num ++;
},
addNumEvent:function(number){
console.log(number);
this.num += number;
},
addNumEvent1:function(number,event){
console.log(event);
this.num += number;
},
changeColor:function(){
this.color='purple';
},
searchEvent:function(){
console.log("执行了回车的搜索事件")
}
}
}
</script>
展示结果
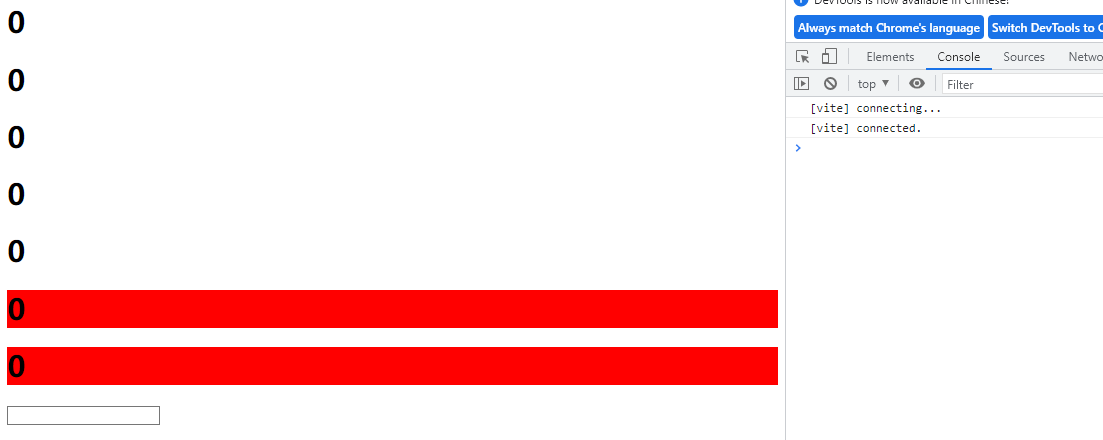

点击后
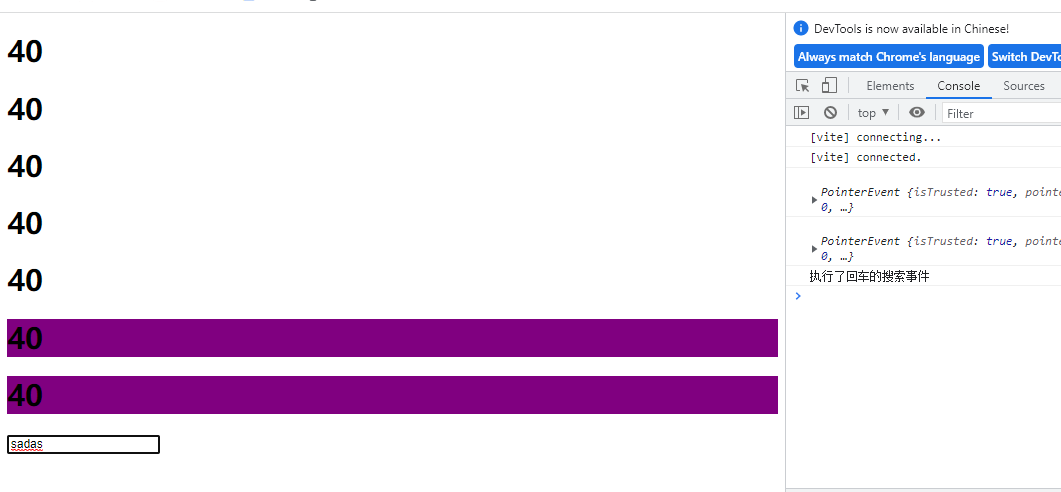

10.表单的输入绑定
基础用法
你可以用 v-model 指令在表单 <input>、<textarea> 及 <select> 元素上创建双向数据绑定。它会根据控件类型自动选取正确的方法来更新元素。尽管有些神奇,但 v-model 本质上不过是语法糖。它负责监听用户的输入事件来更新数据,并在某种极端场景下进行一些特殊处理。
1.表单的数据双向绑定 v-model与修饰符
<template>
<div>
<input v-model="searchKey" type="text" @keydown.enter="searchEvent" />
<h1>{{searchKey}}</h1>
<textarea v-model="lineText" name="textarea" id="" cols="30" rows="10"></textarea>
<h1>{{lineText}}</h1>
<!-- 表单获取的是是否选中内容 value值到时候会提交给后台-->
<input type="checkbox" name="like" v-model="checked" value="123">[true,false]
<h1>{{checked}}</h1>
<!--表单获取的是是否选中内容 -->
<input type="checkbox" name="like" v-model="checked1" true-value="喜欢" false-value="不喜欢"> [喜欢,不喜欢]
<h1>{{checked1}}</h1>
<!-- 复选框多个值的情况 -->
<input type="checkbox" name="likes" v-model="fruits" value="苹果">苹果
<input type="checkbox" name="likes" v-model="fruits" value="雪梨">雪梨
<input type="checkbox" name="likes" v-model="fruits" value="香蕉">香蕉
<h1>{{fruits}}</h1>
<!-- 单选框 -->
<input type="radio" name="sex" v-model="picked" value="man">man
<input type="radio" name="sex" v-model="picked" value="woman">woman
<h1>{{picked}}</h1>
<!-- 选项框 -->
<select name="city" v-model="city" >
<option value="广州">广州</option>
<option value="北京">北京</option>
<option value="上海">上海</option>
<option value="深圳">深圳</option>
</select>
<h1>{{city}}</h1>
<!-- 选项框 多选-->
<select name="city" v-model="cities" multiple>
<option value="广州">广州</option>
<option value="北京">北京</option>
<option value="上海">上海</option>
<option value="深圳">深圳</option>
</select>
<h1>{{cities}}</h1>
<!-- 修饰符 -->
<!-- .lazy/input变为change时间改变值 (当改变输入框的值时,searchkey的值不会自动跟着变化,只有回车 或点击外部才会改变)-->
<input v-model.lazy="searchKey" type="text" @keydown.enter="searchEvent" />
<h1>{{searchKey}}</h1>
<!-- number修饰符 转为数字 -->
<input v-model.lazy.number="searchKey" type="text" @keydown.enter="searchEvent" />
<h1>{{searchKey}}</h1>
<!-- trim修饰符 去掉空格 -->
<input v-model.trim="searchKey" type="text" @keydown.enter="searchEvent" />
<h1>{{searchKey}}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//声明式
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
searchKey:'百度一下',
lineText:"",
checked:false,
checked1:"",
fruits:[],
picked:"",
city:"",
cities:[]
}
},
methods:{
searchEvent:function(){
console.log("执行了回车的搜索事件"),
console.log(this.searchKey)
}
}
}
</script>
展示结果:


11.组件
1.组件与父组件传递数据给子组件方式props
<template>
<div>
<Header></Header>
<Main></Main>
<Main></Main>
<Footer></Footer>
<!-- 通过props传递子组件数据 -->
<News :content="newsContent"></News>
<!-- <News :content="newsContent" /> -->
</div>
</template>
<script>
//声明式
import Header from './components/Header.vue'
import Main from './components/Main.vue'
import Footer from './components/Footer.vue'
import News from './components/News.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
newsContent:'振兴中华1'
}
},
methods:{
searchEvent:function(){
console.log("执行了回车的搜索事件"),
console.log(this.searchKey)
}
},
components:{
Header, Main,Footer,News
}
}
</script>
<!-- Header.vue -->
<template>
<div>
<h1>这是头部组件</h1>
</div>
</template>
<!--Footer.vue-->
<template>
<div>
<h1>这是Footer组件</h1>
</div>
</template>
<!-- Main.vue -->
<template>
<div>
<h1> {{msg}} 这是Main组件</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return{
msg:' hello'
}
}
}
</script>
<!--News.vue-->
<template>
<div>
<h1>新闻内容是:{{content}}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props:['content']
}
</script>
2.通过自定义事件将子组件数据传递给父组件
<!-- App.vue -->
<template>
<div>
<!-- 通过props传递子组件数据 -->
<News :content="newsContent" :msg1="msg"></News>
<!-- <News :content="newsContent" /> -->
<!-- 子组件数据传递给父组件,自定义事件 -->
<Login @sendParentMsg="getChildMsg"></Login>
<h1>从子组件获取到的值: {{msg}}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//声明式
import News from './components/News.vue'
import Login from './components/Login.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
newsContent:'振兴中华1',
msg:""
}
},
methods:{
getChildMsg(value){
console.log(value);
this.msg = value;
}
},
components:{
News,Login
}
}
</script>
<!-- Login.vue -->
<template>
<div>
<input type="text" v-model="username">
<button @click="sendMsg">将数组提交给父组件</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return{
username:""
}
},
methods:{
sendMsg:function(){
//触发自定义事件, 语法: $emit(事件名称,发送的事件的参数)
this.$emit('sendParentMsg',this.username)
}
}
}
</script>
<!-- News.vue -->
<template>
<div>
<h1>新闻内容是:{{content}}</h1>
<h1>父组件获取到的数据,传递给子组件: {{msg1}}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props:['content','msg1']
}
</script>
12.vue3声明周期函数
<script setup>
// This starter template is using Vue 3 <script setup> SFCs
// Check out https://v3.vuejs.org/api/sfc-script-setup.html#sfc-script-setup
import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
</script>
<template>
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png" />
<!-- <HelloWorld msg="Hello Vue 3 + Vite" /> -->
<h1 >{{msg}}</h1>
<button @click="msg='陈陈脸皮真厚! '"> 点击修改msg值</button>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return{
msg:'陈陈真帅!'
}
},
components:{
HelloWorld
},
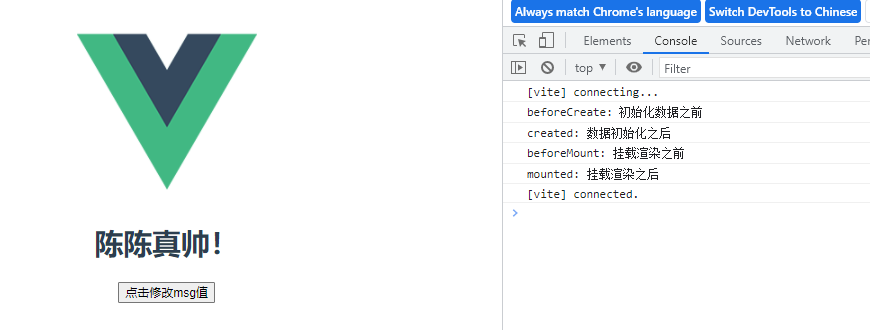
beforeCreate(){
console.log("beforeCreate: 初始化数据之前")
},
created(){
console.log("created: 数据初始化之后")
},
beforeMount(){
console.log("beforeMount: 挂载渲染之前")
},
mounted(){
console.log("mounted: 挂载渲染之后")
},
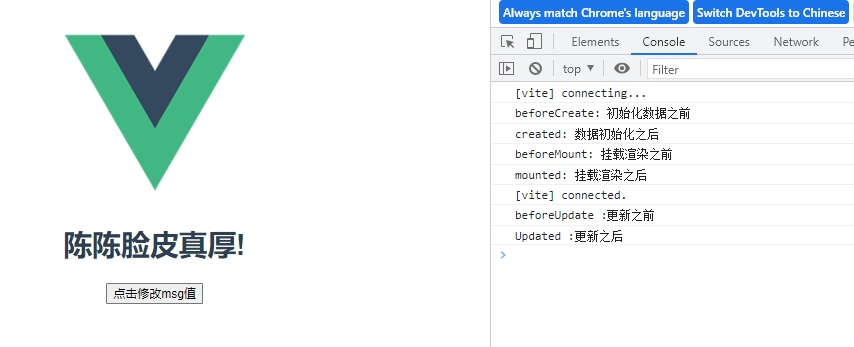
beforeUpdate(){
console.log("beforeUpdate :更新之前")
},
updated(){
console.log("Updated :更新之后")
},
beforeUnmount(){
console.log("beforeUnmount: 销毁之前")
},
unmounted(){
console.log("unmounted: 销毁之后")
}
}
</script>
展示结果:
点击后
13.vue3合成API ( setup() )
1.vue3合成API初体验 --ref
<template>
<div>
<h1 @click="changeEvent">计数: {{count}}</h1>
<h1 @click="changeNum">计数: {{num}}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {ref} from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
console.log('data')
return{
count:0
}
},
methods:{
changeEvent:function(){
this.count++;
}
},
//setup细节问题
//setup是在beforeCreate生命周期回调之前就执行了,而且就执行一次,此时组件对象还没有创建,这时就不能使用this,this为undefined,不能通过this来访问data/computed/methods/props
//其实所有的composition API相关回调函数中也都不可以
//setup中的返回值是一个对象,内部的属性和方法是给html模板使用的
//setup中的对象内部的属性和data函数中的return对象的属性都可以在html模板中使用
//setup中的对象中的属性和data函数中的对象中的属性会合并为组件对象的属性
//setup中的对象中的方法和methods对象中的方法会合并为组件对象的方法
//vue3中尽量不要混合使用data和setup及methods和setup
//setup不能是一个async函数:因为返回值不再是return的对象,而是promise,模板看不到return对象中的属性数据
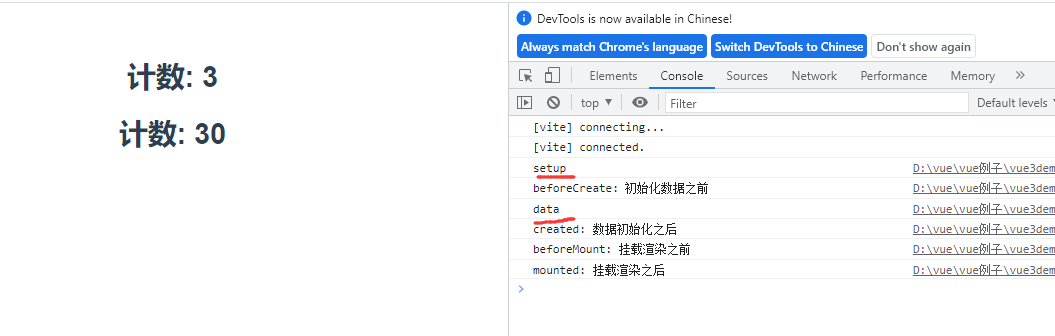
setup(){
console.log('setup')
const num = ref(0) //ref定义一个数据的响应式
function changeNum(){
num.value += 10
}
return {num,changeNum}
},
//数据初始化的生命周期回调
beforeCreate(){
console.log("beforeCreate: 初始化数据之前")
},
created(){
console.log("created: 数据初始化之后")
},
beforeMount(){
console.log("beforeMount: 挂载渲染之前")
},
//界面渲染完毕
mounted(){
console.log("mounted: 挂载渲染之后")
}
}
</script>
展示结果
2.vue3合成API详解 --reactive
<template>
<div>
<h1 @click="changeEvent">计数: {{count}}</h1>
<h1 @click="changeNum">计数: {{num}}</h1>
<h1>用户名: {{user.username}}</h1>
<h1>特点: {{user.type}}</h1>
<h1>用户名: {{username}}</h1>
<h1>特点: {{type}}</h1>
<h1 @click="changeType">特点: {{type}}</h1>
<h1>特点 翻转: {{reverseType}}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {ref,reactive,toRefs,computed,watchEffect,watch} from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
//console.log('data')
return{
count:0
}
},
methods:{
changeEvent:function(){
this.count++;
}
},
setup(){
// console.log('setup')
const num = ref(0) //ref定义一个数据的响应式
//reactive 作用: 定义多个数据的响应式
const user= reactive({
username:"老陈",
age:27,
type:'sport',
reverseType:computed(()=>{
return user.type.split('').reverse().join('');
})
})
function changeNum(){
num.value += 10
}
//vue2中的写法
function changeType(){
user.type = "超级帅!"
}
//vue3中的写法
const changeType = ()=>{
user.type="非常帅!!!"
}
watchEffect(()=>{
console.log(user.type)
console.log("当user Type改变时,会触发此函数执行")
})
//单独监听
watch(num,(newNum,preNum)=>{
console.log("newNum:"+newNum,"preNum:"+preNum)
console.log("当num改变时,会触发此函数执行")
})
//多个 监听
watch([num,user],(newNum,preNum)=>{
console.log("newNum:"+newNum,"preNum:"+preNum)
console.log("当num改变时,会触发此函数执行")
})
// ...toRefs(user) :是为了调用username时省去user.的
return {num,changeNum,user,...toRefs(user),changeType}
}
}
</script>
展示结果:
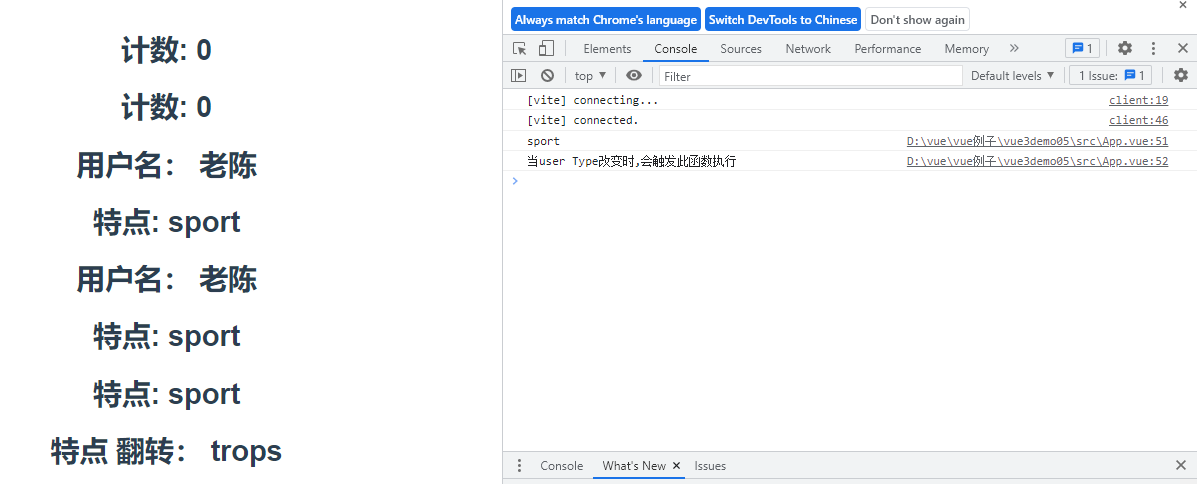
点击后
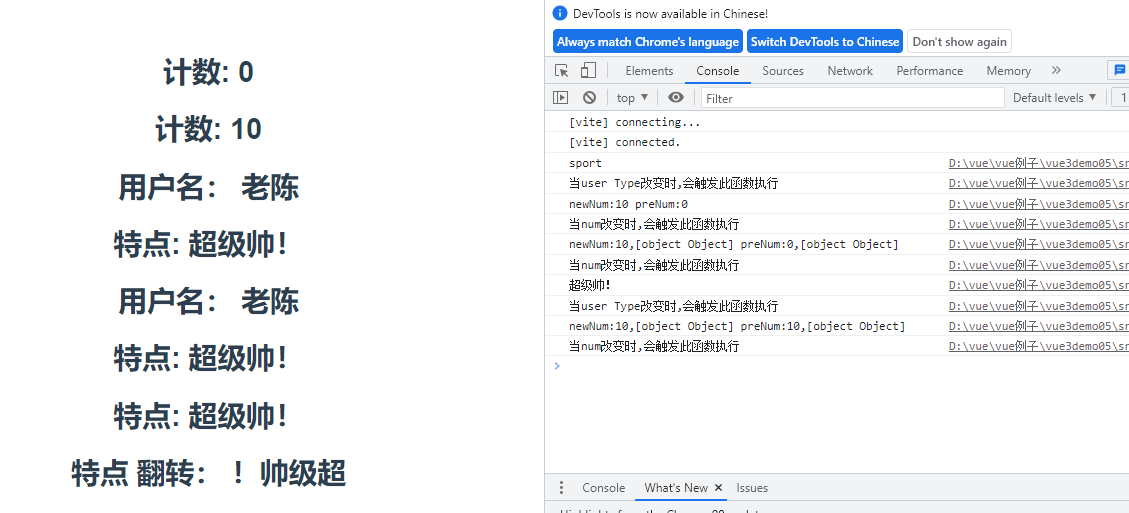
3.setup()中使用生命周期函数
<!--App.vue-->
<template>
<div>
<!-- <h1>用户名:{{username}}</h1> -->
<User :username1="username" :age="age" msg2="小米" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {reactive,toRefs} from 'vue'
import User from './components/User.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
}
},
components:{
User
},
setup(){
const user= reactive({
username:"老陈",
age:27,
type:'sport',
})
return {user,...toRefs(user)}
}
}
</script>
<!--User.vue-->
<template>
<div>
<h1>username:{{username1}}</h1>
<h1>age:{{age}}</h1>
<h1>description:{{description}}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {ref,onBeforeMount,onMounted,onBeforeUpdate,onUpdated,onBeforeUnmount,onUnmounted} from 'vue'
export default {
setup(props,content){
//props参数,是一个对象,里面有父级组件向子级组件传递的数据,并且是在子级组件中使用props接收到的所有的属性 , 包含props配置声明且传入了的所有属性的对象
//content参数是一个对象,里面有attrs对象(后去当前组件标签上的所有的属性的对象,但是该属性是在props中没有声明接收的所有的尚需要的对象),emit方法(分发事件的),slots对象(插槽)
//attrs:包含没有在props配置中声明的属性的对象,相当于 this.$attrs
//slots:包含所有掺入的插槽内容的对象,相当于this.$slots
//emit:用来分发自定义事件的函数,相当于this.$emit
//可以写成 setup(props,{attrs,slots,emit})
console.log(props)
console.log(content)
console.log(content.attrs)
console.log(content.emit)
console.log(content.attes.msg2)
const description = ref(props.username1+"年龄是"+props.age)
onBeforeMount(()=>{
console.log('onBeforeMount')
})
onBeforeMount(()=>{
console.log('onBeforeMount')
})
return {description}
},
props:['username1','age']
}
</script>
展示结果:
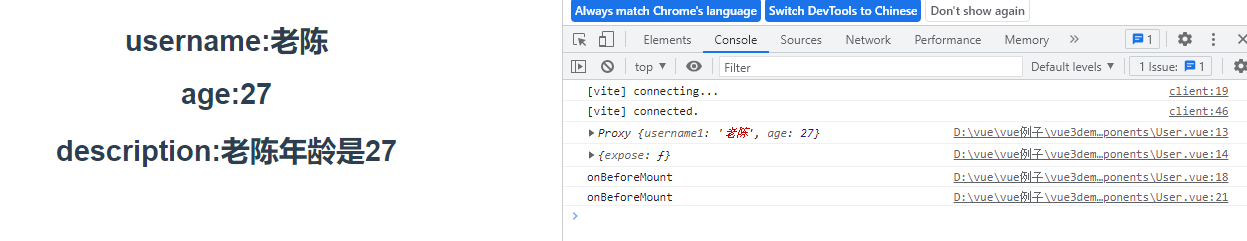
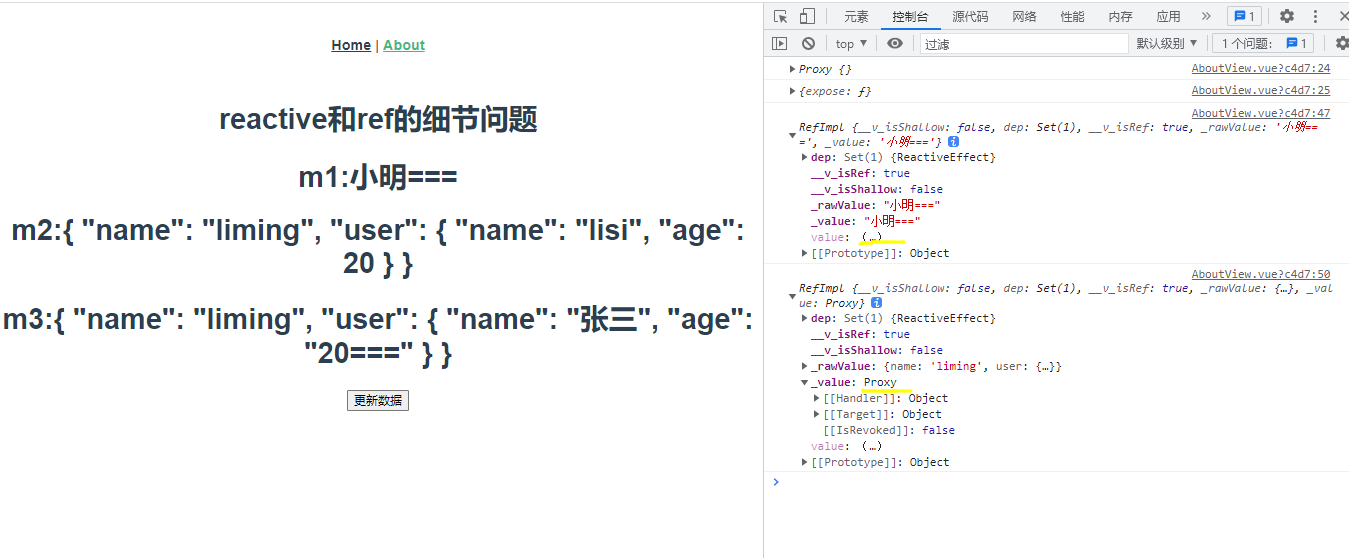
4.reactive和ref的细节问题
<template>
<div class="about">
<h1>reactive和ref的细节问题</h1>
<h1>m1:{{m1}}</h1>
<h1>m2:{{m2}}</h1>
<h1>m3:{{m3}}</h1>
<button @click="update">更新数据</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {ref,reactive} from 'vue'
export default {
//是vue3的 composition API中2个最重要的响应式API (reactive和ref)
//ref用来处理基本类型数据,reactive用来处理对象(递归深度响应式)
//如果用ref对象/数组,内部会自动将对象/数组转换为reactive的代理对象
//ref内部:通过给value属性添加getter/setter来实现对数据的劫持
//reactive内部:通过使用proxy来实现对对象内部所有数据的劫持,并通过reflect操作对象内部数据
//ref的数据操作:在js中要 .value,在模板中不需要(内部解析模板时会自动添加 .value)
setup(props,content) {
console.log(props);
console.log(content);
const m1 = ref('小明')
const m2 = reactive({
name:"liming",
user:{
name:'张三',
age:20
}
})
//ref的方式也可以传入对象
const m3 = ref({
name:"liming",
user:{
name:'张三',
age:20
}
})
function update(){
//ref中如果放入是一个对象,那么是经过了reactive的处理, 形成一个Proxy类型的对象
m1.value += "==="
console.log(m1);
m2.user.name="lisi"
m3.value.user.age += "==="
console.log(m3);
}
return{m1,m2,m3,update}
}
}
</script>
14.Provive和inject
<!--App.vue-->
<template>
<div>
<Student />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {reactive,toRefs,provide} from 'vue'
import Student from './components/Student.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
components:{
Student
},
setup(){
const student=reactive({
name:"小红",
classname:'三年级5班'
})
provide('student',student)
}
}
</script>
<!--Student.vue-->
<template>
<div>
<h1>学生</h1>
<h1>name:{{name}}</h1>
<h1>classname:{{classname}}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {ref,inject} from 'vue'
export default {
setup(){
const student=inject('student')
return {...student}
}
}
</script>
展示结果

15.路由
1.vue3路由的基本使用
<!--App.vue-->
<template>
<div>
<h1>Hello App!</h1>
<p>
<!-- use the router-link component for navigation. -->
<!-- specify the link by passing the `to` prop. -->
<!-- `<router-link>` will render an `<a>` tag with the correct `href` attribute -->
<router-link to="/">Go to Home</router-link>
<router-link to="/about">Go to About</router-link>
</p>
<!-- route outlet -->
<!-- component matched by the route will render here -->
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
HelloWorld
}
}
</script>
<!--router/index.js-->
// 导入进来
// import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import {createRouter,createWebHashHistory} from 'vue-router'
// 1. Define route components.
// These can be imported from other files
const Home = { template: '<div>Home</div>' }
const About = { template: '<div>About</div>' }
// 2. Define some routes
// Each route should map to a component.
// We'll talk about nested routes later.
const routes = [
{ path: '/', component: Home },
{ path: '/about', component: About },
]
// 3. Create the router instance and pass the `routes` option
// You can pass in additional options here, but let's
// keep it simple for now.
const router = createRouter({
// 4. Provide the history implementation to use. We are using the hash history for simplicity here.
history: createWebHashHistory(),
routes, // short for `routes: routes`
})
//导出路由
export default router
<!--main.js-->
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import router from '../router'
import App from './App.vue'
import './index.css'
const app = createApp(App)
//使用路由
app.use(router)
app.mount('#app')
2.动态路由和404NotFound
<!--App.vue-->
<template>
<div>
<!-- <h1>Hello App!</h1> -->
<!-- use the router-link component for navigation. -->
<!-- specify the link by passing the `to` prop. -->
<!-- `<router-link>` will render an `<a>` tag with the correct `href` attribute -->
<!-- <p>
<router-link to="/">Go to Home</router-link>
<router-link to="/about">Go to About</router-link>
</p> -->
<!-- route outlet -->
<!-- component matched by the route will render here -->
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
HelloWorld
}
}
</script>
<!--News.vue-->
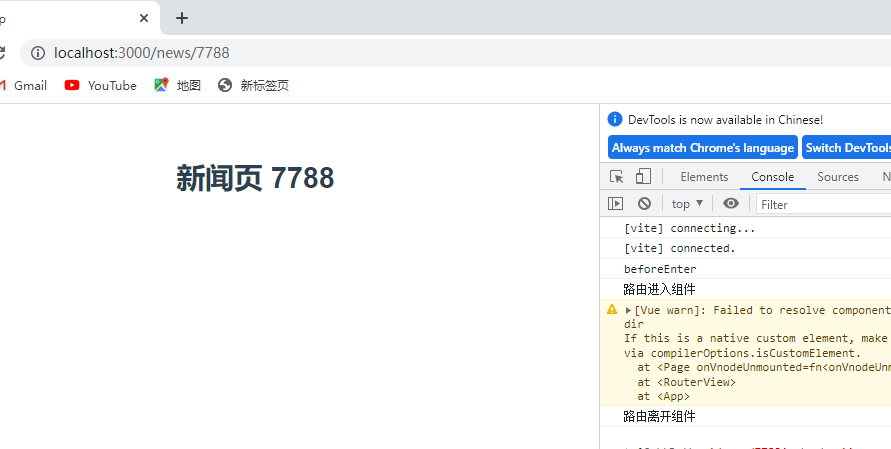
<template>
<div>
<h1>新闻页 {{$route.params.id}}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
mounted(){
console.log(this.$route)
}
}
</script>
<!--Home.vue-->
<template>
<h1>这是首页</h1>
</template>
<!--NotFound.vue-->
<template>
<h1>404,找不到页面</h1>
</template>
<!--router/index.js-->
// 导入进来
// import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import {createRouter,createWebHashHistory} from 'vue-router'
import Home from '../src/components/Home.vue'
import News from '../src/components/News.vue'
import NotFound from '../src/components/NotFound.vue'
// 1. Define route components.
// These can be imported from other files
//const Home = { template: '<div>Home</div>' }
const About = { template: '<div>About</div>' }
// 2. Define some routes
// Each route should map to a component.
// We'll talk about nested routes later.
const routes = [
{ path: '/', component: Home },
{ path: '/about', component: About },
{
path:'/news/:id',
component:News
},
{
path:'/:path(.*)',
component:NotFound
}
]
// 3. Create the router instance and pass the `routes` option
// You can pass in additional options here, but let's
// keep it simple for now.
const router = createRouter({
// 4. Provide the history implementation to use. We are using the hash history for simplicity here.
history: createWebHashHistory(),
routes, // short for `routes: routes`
})
//导出路由
export default router
3.路由正则与重复参数
/route/index.js
// 导入进来
// import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import {createRouter,createWebHashHistory} from 'vue-router'
import Home from '../src/components/Home.vue'
import News from '../src/components/News.vue'
import NotFound from '../src/components/NotFound.vue'
import Article from '../src/components/Article.vue'
import Films from '../src/components/Films.vue'
// 1. Define route components.
// These can be imported from other files
//const Home = { template: '<div>Home</div>' }
const About = { template: '<div>About</div>' }
// 2. Define some routes
// Each route should map to a component.
// We'll talk about nested routes later.
const routes = [
{ path: '/', component: Home },
{ path: '/about', component: About },
{
path:'/news/:id',
component:News
},
{
path:'/:path(.*)',
component:NotFound
},
{
path:'/article/:id(\\d+)',
component:Article
},
{
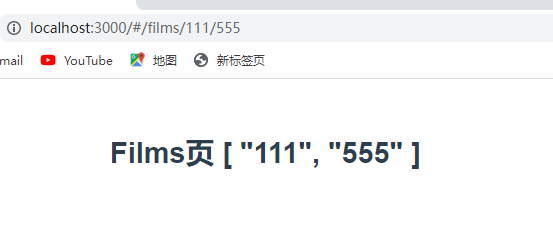
// id+ 是至少会有1个参数 例: /films/111/555
// id* 是可有可没有,也可以有任意多个 例:/films/ 或/films/111/555
// id? 是有,或者没有 ,不可以重复 例:/films/ 或/films/111
path:'/films/:id',
component:Films
}
]
// 3. Create the router instance and pass the `routes` option
// You can pass in additional options here, but let's
// keep it simple for now.
const router = createRouter({
// 4. Provide the history implementation to use. We are using the hash history for simplicity here.
history: createWebHashHistory(),
routes, // short for `routes: routes`
})
//导出路由
export default router
Films.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>Films页 {{$route.params.id}}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
mounted(){
console.log(this.$route)
}
}
</script>
Article.vue
<template>
<div>
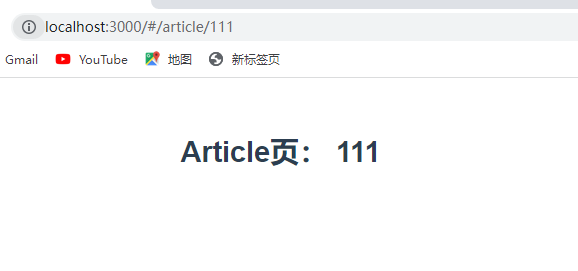
<h1>Article页: {{$route.params.id}}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
mounted(){
console.log(this.$route)
}
}
</script>
展示结果
4.路由嵌套
/route/index.js
// 导入进来
// import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import {createRouter,createWebHashHistory, useRoute} from 'vue-router'
import Home from '../src/components/Home.vue'
import News from '../src/components/News.vue'
import NotFound from '../src/components/NotFound.vue'
import Article from '../src/components/Article.vue'
import Films from '../src/components/Films.vue'
import User from '../src/components/User.vue'
import Hengban from '../src/components/Hengban.vue'
import Shuban from '../src/components/Shuban.vue'
// 1. Define route components.
// These can be imported from other files
//const Home = { template: '<div>Home</div>' }
const About = { template: '<div>About</div>' }
// 2. Define some routes
// Each route should map to a component.
// We'll talk about nested routes later.
const routes = [
{ path: '/', component: Home },
{ path: '/about', component: About },
{
path:'/news/:id',
component:News
},
{
path:'/:path(.*)',
component:NotFound
},
{
path:'/article/:id(\\d+)',
component:Article
},
{
// id+ 是至少会有1个参数 例: /films/111/555
// id* 是可有可没有,也可以有任意多个 例:/films/ 或/films/111/555
// id? 是有,或者没有 ,不可以重复 例:/films/ 或/films/111
path:'/films/:id+',
component:Films
},
{
// /user/:id 这样写的话 路径为 /user/11/hengban
// /user 这样写的话 路径为 /user/hengban
path:'/user/:id',
component:User,
children:[
{
path:'hengban',
component:Hengban
},
{
path:'shuban',
component:Shuban
}
]
}
]
// 3. Create the router instance and pass the `routes` option
// You can pass in additional options here, but let's
// keep it simple for now.
const router = createRouter({
// 4. Provide the history implementation to use. We are using the hash history for simplicity here.
history: createWebHashHistory(),
routes, // short for `routes: routes`
})
//导出路由
export default router
User.vue 、 Hengban.vue 、 Shuban.vue
<!--User.vue-->
<template>
<div>
<h1>{{$route.params.id}}:user页面</h1>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<!--Hengban.vue-->
<template>
<h1>这是横版页面</h1>
</template>
<!--Shuban.vue-->
<template>
<h1>这是竖版页面</h1>
</template>
5.使用js跳转页面
page.vue
<template>
<dir>
<h1>这是page页面,学习编程导航</h1>
<button @click="goPage">跳转页面</button>
</dir>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods:{
goPage(){
console.log("跳转到首页")
// this.$router.push("/") //跳转到首页
// this.$router.push({path:'/news/111'}) //跳转到/news/111页面
//携带参数跳转
// this.$router.push({name:"news",params:{id:7788}})
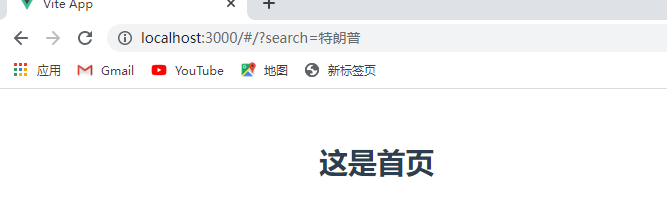
this.$router.push({path:"/",query:{search:'特朗普'}})
}
}
}
</script>
index.js
// 导入进来
// import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import {createRouter,createWebHashHistory, useRoute} from 'vue-router'
import Home from '../src/components/Home.vue'
import News from '../src/components/News.vue'
import NotFound from '../src/components/NotFound.vue'
import Article from '../src/components/Article.vue'
import Films from '../src/components/Films.vue'
import User from '../src/components/User.vue'
import Hengban from '../src/components/Hengban.vue'
import Shuban from '../src/components/Shuban.vue'
import Page from '../src/components/Page.vue'
// 1. Define route components.
// These can be imported from other files
//const Home = { template: '<div>Home</div>' }
const About = { template: '<div>About</div>' }
// 2. Define some routes
// Each route should map to a component.
// We'll talk about nested routes later.
const routes = [
{ path: '/', component: Home },
{ path: '/about', component: About },
{
name:"news",
path:'/news/:id',
component:News
},
{
path:'/:path(.*)',
component:NotFound
} ,
{
path:'/page',
component:Page
}
]
// 3. Create the router instance and pass the `routes` option
// You can pass in additional options here, but let's
// keep it simple for now.
const router = createRouter({
// 4. Provide the history implementation to use. We are using the hash history for simplicity here.
history: createWebHashHistory(),
routes, // short for `routes: routes`
})
//导出路由
export default router
News.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>新闻页 {{$route.params.id}}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
mounted(){
console.log(this.$route)
}
}
</script>
展示结果:
6.命名路由与重定向和别名
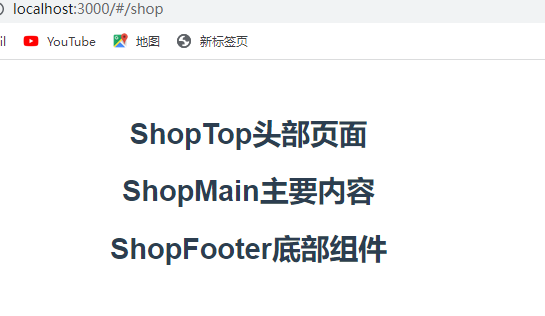
1.命名视图
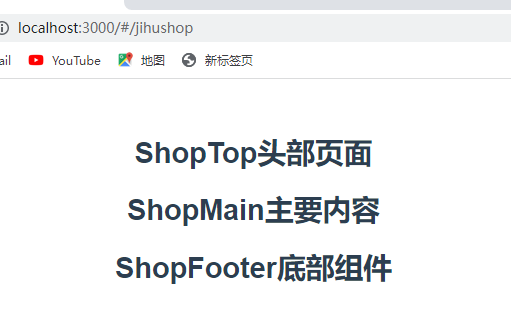
<router-view name="ShopTop"></router-view>
<router-view></router-view>
<router-view name="ShopFooter"></router-view>
import ShopMain from '../src/components/ShopMain.vue'
import ShopTop from '../src/components/ShopTop.vue'
import ShopFooter from '../src/components/ShopFooter.vue'
const routes = [
{
path:'/shop',
components:{
default:ShopMain,
ShopTop:ShopTop,
ShopFooter:ShopFooter
}
}
]
展示结果
2.重定向
{
path:'/mail',
redirect:(to)=>{return {path:'/shop'}}
// redirect:"/shop"
}
3.取别名
{
path:'/shop',
alias:"/jihushop",
//alias:["/q11","/222"],
components:{
default:ShopMain,
ShopTop:ShopTop,
ShopFooter:ShopFooter
}
}
4.replace 使用
replace : 使覆盖原来的页面,让其不能往回退
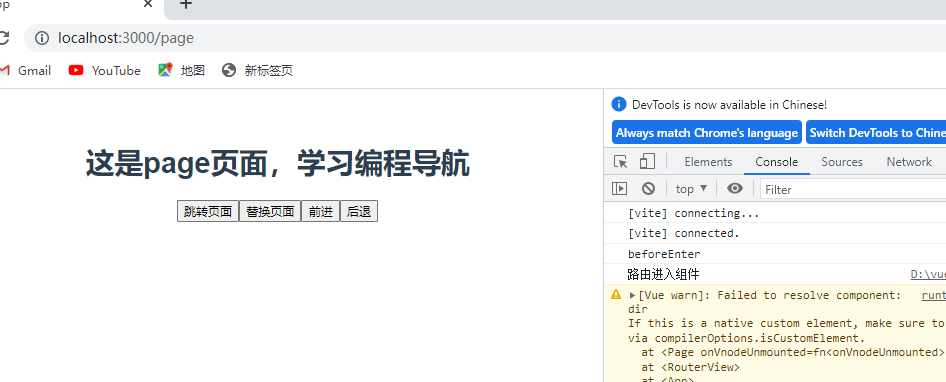
page.vue
<template>
<dir>
<h1>这是page页面,学习编程导航</h1>
<button @click="goPage">跳转页面</button>
<button @click="replacePage">替换页面</button>
<button @click="$router.go(1)">前进</button> //前进
<button @click="$router.go(-1)">后退</button> //后退
</dir>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods:{
goPage(){
console.log("跳转到首页")
// this.$router.push("/") //跳转到首页
// this.$router.push({path:'/news/111'}) //跳转到/news/111页面
//携带参数跳转
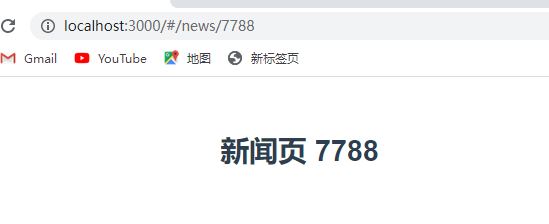
this.$router.push({name:"news",params:{id:7788}})
// this.$router.push({path:"/",query:{search:'特朗普'}})
},
replacePage(){
this.$router.replace({name:"news",params:{id:7788}})
}
}
}
</script>
5.路由模式与路由守卫
路由守卫就是 和权限差不多 没有权限进不去该页面
{
path:'/page',
component:Page,
beforeEnter:(to,from)=>{
console.log('beforeEnter')
}
},
router.beforeEach((to, from,next) => {
// ...
// explicitly return false to cancel the navigation
console.log(to)
next()
//return false
})
page.vue
<script>
export default {
methods:{
goPage(){
console.log("跳转到首页")
// this.$router.push("/") //跳转到首页
// this.$router.push({path:'/news/111'}) //跳转到/news/111页面
//携带参数跳转
this.$router.push({name:"news",params:{id:7788}})
// this.$router.push({path:"/",query:{search:'特朗普'}})
},
replacePage(){
this.$router.replace({name:"news",params:{id:7788}})
}
},
beforeRouteEnter(){
console.log('路由进入组件')
},
beforeRouteUpdate(){
console.log('路由更新组件')
},
beforeRouteLeave(){
console.log('路由离开组件')
}
}
</script>
展示结果
16.vue3中如何设置状态管理
App.vue
<template>
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png" />
<HelloWorld msg="Hello Vue 3.0 + Vite" />
</template>
<script>
import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
import store from './store/index.js'
// import {reactive} from 'vue'
// const store={
// state:reactive({
// message:"helloworld"
// }),
// setMessage(value){
// this.state.message = value;
// }
// }
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
HelloWorld
},
provide:{
store
}
}
</script>
Helloworld.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>{{ store.state.message }}</h1>
<button @click="store.setMessage('老陈真帅!')">count is: {{ count }}</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
props: {
msg: String
},
data() {
return {
count: 0
}
},
inject:['store']
}
</script>
store/index.js
import {reactive} from 'vue'
const store={
state:reactive({
message:"helloworld"
}),
setMessage(value){
this.state.message = value;
}
}
//导出默认值
export default store;
17.vue3中如何使用axios实现前后端交互
使用axios实现前后端交互时需要先安装axios:
npm install axios --save
App.vue
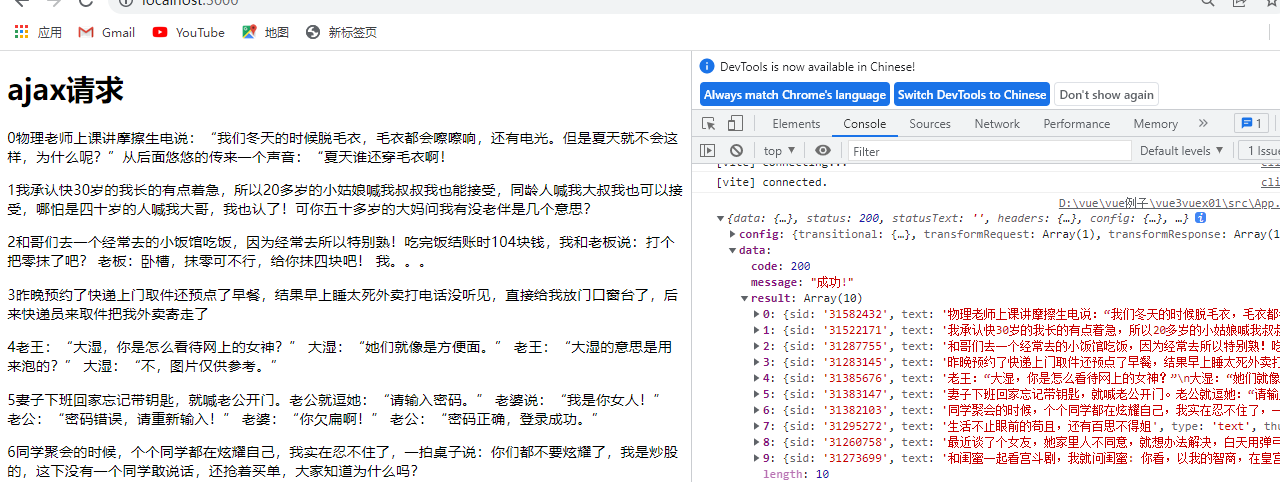
<template>
<div>
<h1>ajax请求</h1>
<div v-for="(item,i) in store.state.duanziList" :key="i">
<p>{{i}}{{item.text}}</p>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
import store from './store/index.js'
import axios from 'axios'
export default {
name: 'App',
provide:{
store
},
setup(){
//方法一
var api = "https://api.apiopen.top/getJoke?page=1&count=10&type=text"
// fetch(api).then(res=>res.json()).then(result=>{
// store.setDzList(result.result)
// console.log(result)
// })
//方法二:
axios.get(api).then((result)=>{
console.log(result)
store.setDzList(result.data.result)
})
return{ store }
}
}
</script>
components/HelloWorld.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>{{ store.state.message }}</h1>
<button @click="store.setMessage('老陈真帅!')">count is: {{ count }}</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
props: {
msg: String
},
data() {
return {
count: 0
}
},
inject:['store']
}
</script>
store/index.js
import {reactive} from 'vue'
const store={
state:reactive({
message:"helloworld",
duanziList:[]
}),
setMessage(value){
this.state.message = value;
},
setDzList(list){
this.state.duanziList = list
}
}
//导出默认值
export default store;
展示结果
18.vite配置跨域请求
在项目的根目录下创建一个vite.config.js配置文件
vite.config.js
module.exports = {
proxy:{
'/api':{
target:'https://pvp.qq.com/',
changeOrigin:true,//是否允许跨域
rewrite:path => path.replace(/^\/api/, '')
}
}
}
App.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>ajax请求</h1>
<div v-for="(item,i) in store.state.duanziList" :key="i">
<p>{{item.cname}}===>{{item.title}}</p>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
import store from './store/index.js'
import axios from 'axios'
export default {
name: 'App',
provide:{
store
},
setup(){
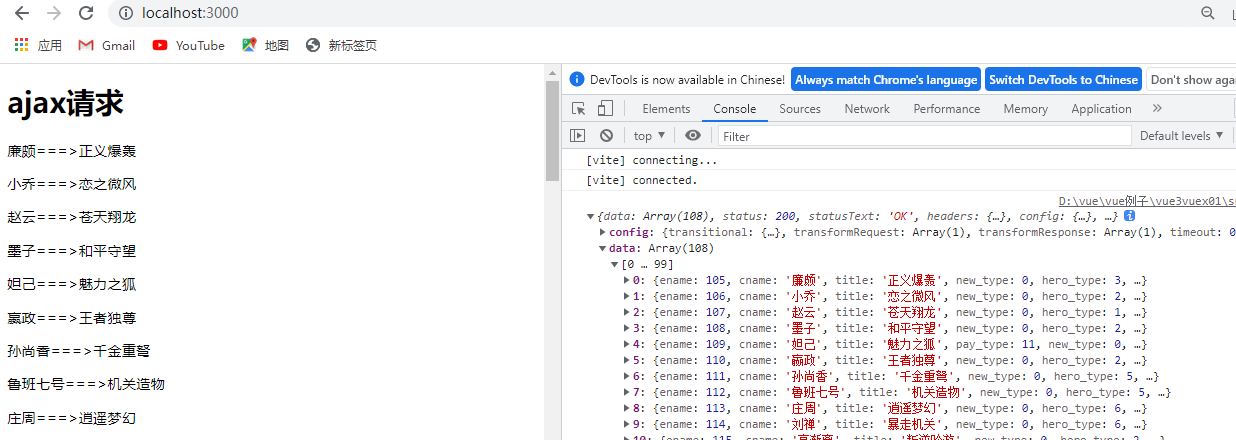
var api = "/api/web201605/js/herolist.json"
axios.get(api).then((result)=>{
console.log(result)
store.setDzList(result.data)
})
return{ store }
}
}
</script>
store/index.js
import {reactive} from 'vue'
const store={
state:reactive({
message:"helloworld",
duanziList:[]
}),
setMessage(value){
this.state.message = value;
},
setDzList(list){
this.state.duanziList = list
}
}
//导出默认值
export default store;
展示结果
19.mockjs模拟获取数据
mockjs 官网:http://mockjs.com/
# 安装
npm install mockjs --save
// 使用 Mock
var Mock = require('mockjs')
var data = Mock.mock({
// 属性 list 的值是一个数组,其中含有 1 到 10 个元素
'list|1-10': [{
// 属性 id 是一个自增数,起始值为 1,每次增 1
'id|+1': 1
}]
})
// 输出结果
console.log(JSON.stringify(data, null, 4))
例子
App.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>ajax请求</h1>
<div v-for="(item,i) in store.state.duanziList" :key="i">
<p>{{item.cname}}===>{{item.title}}</p>
</div>
<h1>{{store.state.message}}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
import store from './store/index.js'
import axios from 'axios'
export default {
name: 'App',
provide:{
store
},
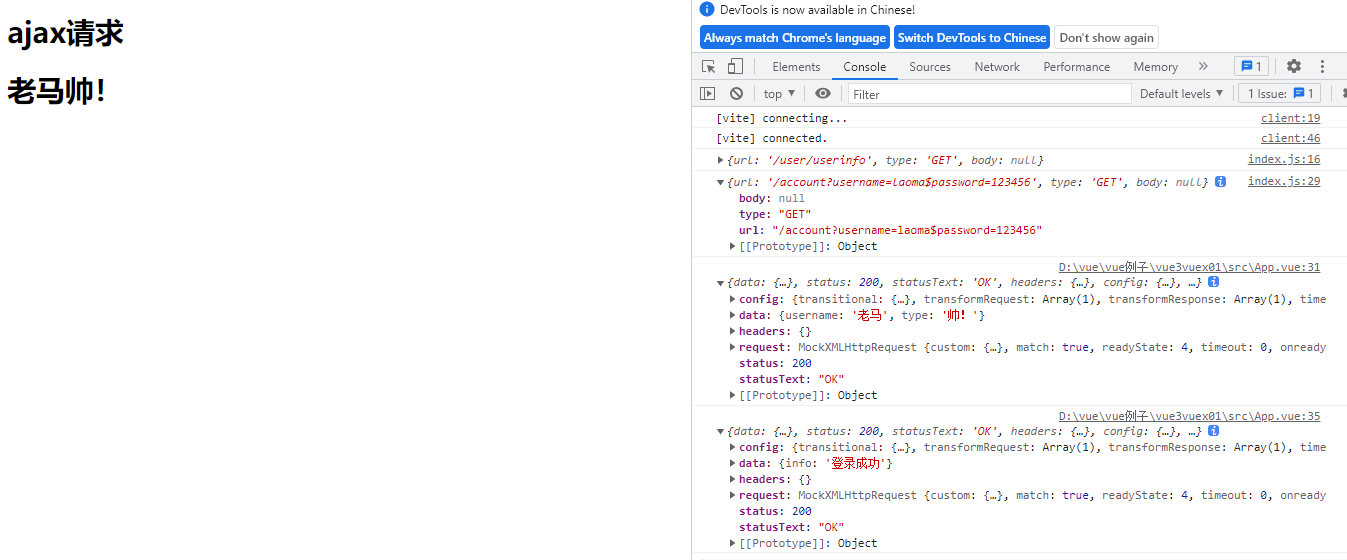
setup(){
let api = '/user/userinfo'
//let api = '/user/userinfo?username=laoma$password=123456'
axios.get(api).then((result)=>{
console.log(result)
store.setMessage(result.data.username+result.data.type)
})
axios.get('/account?username=laoma$password=123456').then((result)=>{
console.log(result)
})
return{ store }
}
}
</script>
/mock/index.js
//导入mock
import Mock from 'mockjs'
//设置一下模拟返回数据的时间
Mock.setup({
timeout:'200-600'
})
Mock.mock(
//请求的路径
"/user/userinfo",
'get',
(req)=>{
console.log(req)
return{
username:"老马",
type:'帅!'
}
}
)
Mock.mock(
//请求的路径
/\/account.*/, //正则匹配 .* :匹配 account后面所有的
'get',
(req)=>{
console.log(req)
return{
info:"登录成功"
}
}
)
main.js
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import './index.css'
import './mock/index.js' //要是与后端发送请求只需把这句话注释掉
createApp(App).mount('#app')
目录结果
输出结果:
20.vue脚手架cli的使用
安装 脚手架cli
npm install -g @vue/cli
//查看版本
vue --version
安装时出现的问题:
VSCode的终端输入vue --version报错:vue : 无法加载文件 D:\nodejs\node_global\vue.ps1,因为在此系统上禁止运行脚本。

解决办法
(1)以管理员身份运行VSCode
(2)执行命令:get-ExecutionPolicy(取得shell的当前执行策略)
显示Restricted(表示状态是禁止的)
(3)执行命令:set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
(4)执行命令:get-ExecutionPolicy,显示RemoteSigned

Vue CLI 创建项目
创建项目命令:
vue create vueproject01
#安装 element Ui
npm i element-ui -S #vue2.0版本
npm install element-plus --save
vue add element
vue add element-plus #vue3.0使用这个安装 element Ui 插件
npm install echarts@4.9.0 --save #安装echarts插件
npm i echarts -S
在main.js中引入
import echarts from 'echarts'
Vue.prototype.$echarts = echarts
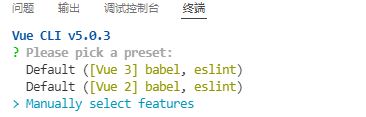
第一步,创建项目结构,第一个是vue3,第二个是vue2,第三个是自定义,我们选择第三个自定义结构,回车。
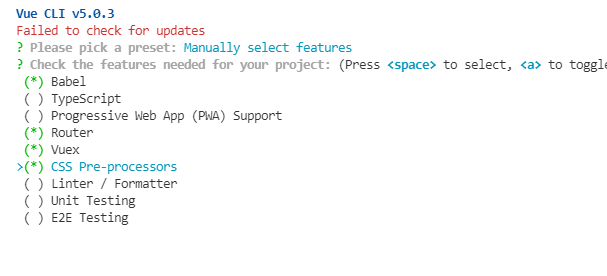
第二步,选择模块,上下选择,选中按空格,选好后按回车 。选择四个就可以了(linter 以后再选,效验用的)
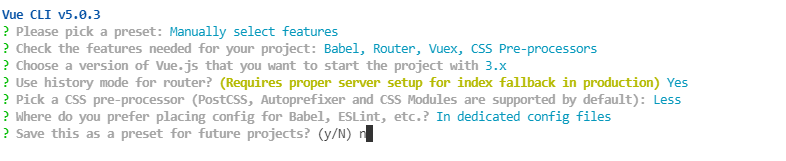
第三步:需要进行的一些配置
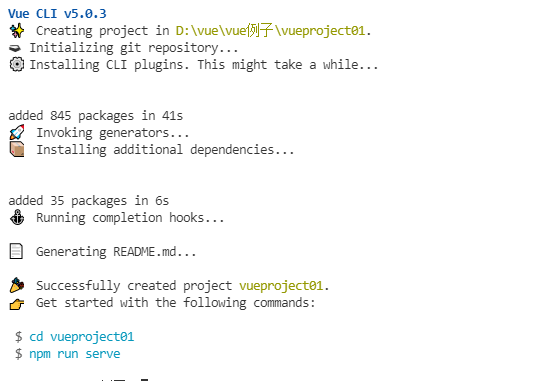
第四步:等待创建好(此时必须网好才行)
第五步:运行项目

21.vuex状态管理的应用
HomeView.vue
<template>
<div class="home">
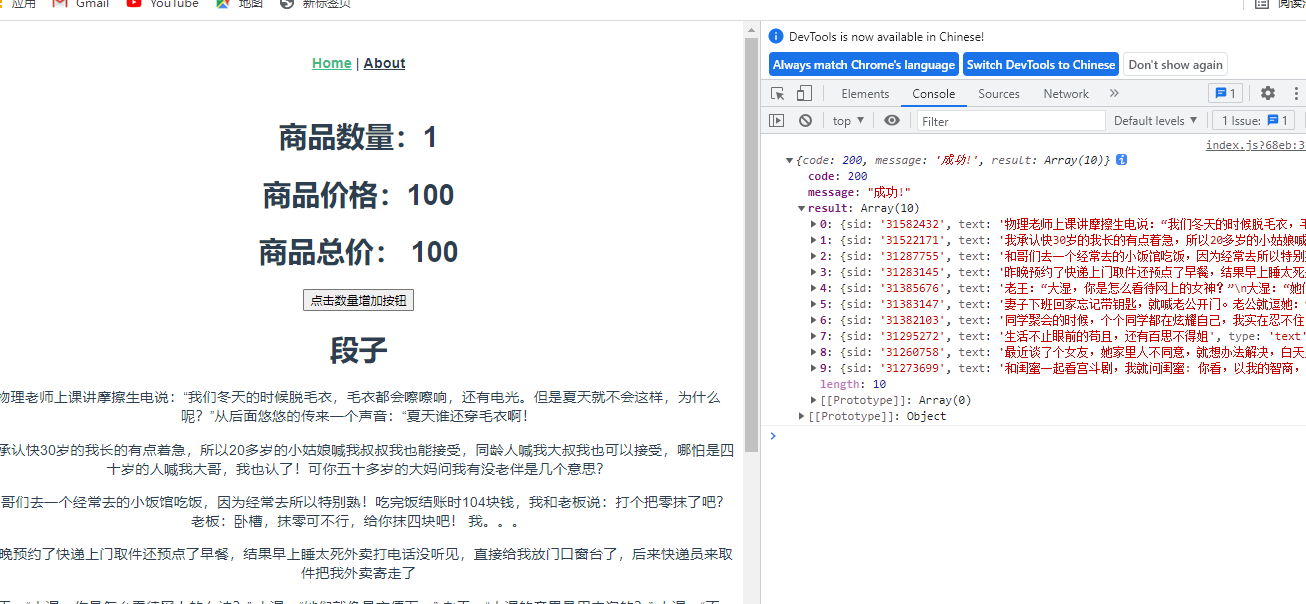
<h1>商品数量:{{$store.state.count}}</h1>
<h1>商品价格:100</h1>
<h1>商品总价: {{$store.getters.totalPrice}}</h1>
<button @click="changeEvent">点击数量增加按钮</button>
<h1>段子</h1>
<p v-for="(item,i) in $store.state.dzList" :key="i">{{item.text}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// @ is an alias to /src
import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld.vue'
export default {
name: 'HomeView',
components: {
HelloWorld
},
methods:{
changeEvent:function(){
//this.$store.commit('setCount');
this.$store.commit('setCountNum',10); //想要触发 setCountNum这个函数,必须用commit方式来执行
}
},
mounted:function(){
this.$store.dispatch('getDz') //让其触发actions这个函数, 使getDz生效
}
}
</script>
/store/index.js
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
export default createStore({
//设置全局数据的地方
state: {
count:1,
dzList:[]
},
getters: {
totalPrice:function(state){
return state.count*100
}
},
//修改状态的方法 (同步的操作)
mutations: {
setCount:function(state){
state.count++;
},
setCountNum:function(state,num){
state.count+=num;
},
setDzList:function(state,arr){
state.dzList =arr;
}
},
//异步的操作 (比如 ajax)
actions: {
getDz:function(context){
var api = "https://api.apiopen.top/getJoke?page=1&count=10&type=text"
fetch(api).then(res=>res.json()).then(result=>{
console.log(result);
context.commit('setDzList',result.result);
})
}
},
modules: {
}
})
展示效果:
22.映射状态数据和方法(map)
此映射方法让其 不用写($store.state.count)这么长的名字了
HomeView.vue
<template>
<div class="home">
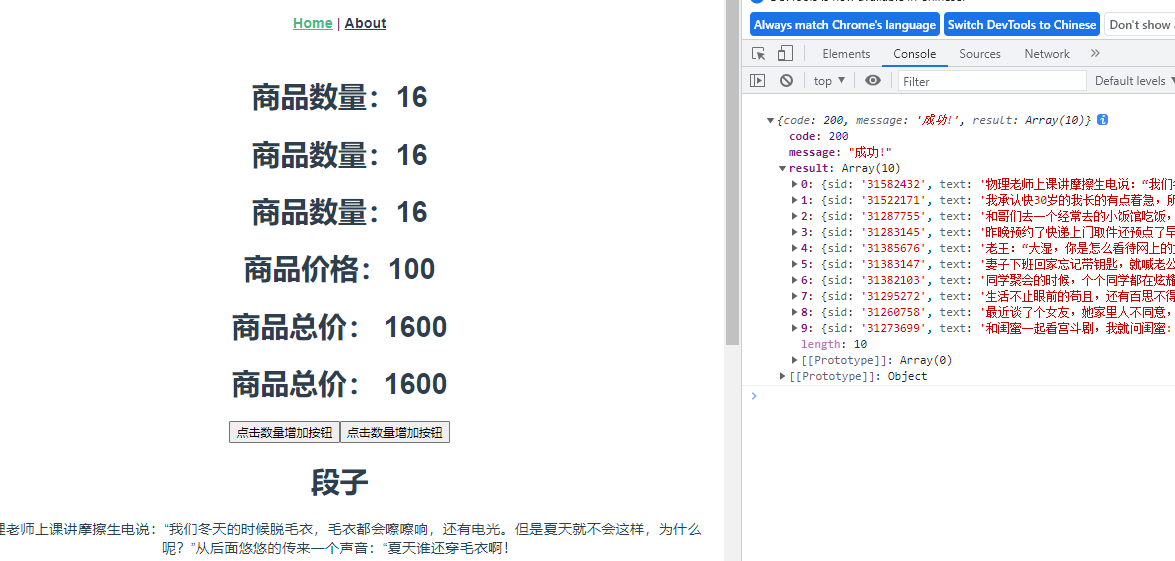
<h1>商品数量:{{$store.state.count}}</h1>
<h1>商品数量:{{count}}</h1>
<h1>商品数量:{{productCount}}</h1>
<h1>商品价格:100</h1>
<h1>商品总价: {{$store.getters.totalPrice}}</h1>
<h1>商品总价: {{totalPrice}}</h1>
<button @click="changeEvent">点击数量增加按钮</button>
<button @click="setCountNum(5)">点击数量增加按钮</button>
<h1>段子</h1>
<p v-for="(item,i) in $store.state.dzList" :key="i">{{item.text}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// @ is an alias to /src
import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld.vue'
import {mapState,mapGetters,mapMutations,mapActions} from 'vuex';
export default {
name: 'HomeView',
components: {
HelloWorld
},
computed:{
...mapState(['count']),
...mapState({
productCount:(state)=>state.count //将state.count映射进来
}),
...mapGetters(['totalPrice'])
},
methods:{
changeEvent:function(){
//this.$store.commit('setCount');
this.$store.commit('setCountNum',10); //想要触发 setCountNum这个函数,必须用commit方式来执行
}, // 前面加... 是解构一下
...mapMutations(['setCountNum']),
...mapActions(['getDz'])
},
mounted:function(){
// this.$store.dispatch('getDz') //让其触发actions这个函数, 使getDz生效
this.getDz()
}
}
</script>
/store/index.js
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
export default createStore({
//设置全局数据的地方
state: {
count:1,
dzList:[]
},
getters: {
totalPrice:function(state){
return state.count*100
}
},
//修改状态的方法 (同步的操作)
mutations: {
setCount:function(state){
state.count++;
},
setCountNum:function(state,num){
state.count+=num;
},
setDzList:function(state,arr){
state.dzList =arr;
}
},
//异步的操作 (比如 ajax)
actions: {
getDz:function(context){
var api = "https://api.apiopen.top/getJoke?page=1&count=10&type=text"
fetch(api).then(res=>res.json()).then(result=>{
console.log(result);
context.commit('setDzList',result.result);
})
}
},
modules: {
}
})
展示效果
23.模块化管理vuex(Module)
1.模块的局部状态
store/user.js
const user = {
state:() =>({
username:'老马',
age:27
}),
mutations:{
setUsername:function(state){
state.username = '小陈'
},
setAge:function(state,value){
state.age = value
}
},
actions:{
asyncSetAge:function(context){
console.log(context)
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('setAge',50);
},3000);
}
},
getters:{
description:function(state,getters,rootState){
return state.username +'的年龄是'+ state.age + '岁'
}
}
}
export default user
/views/User.vue
<template>
<div>
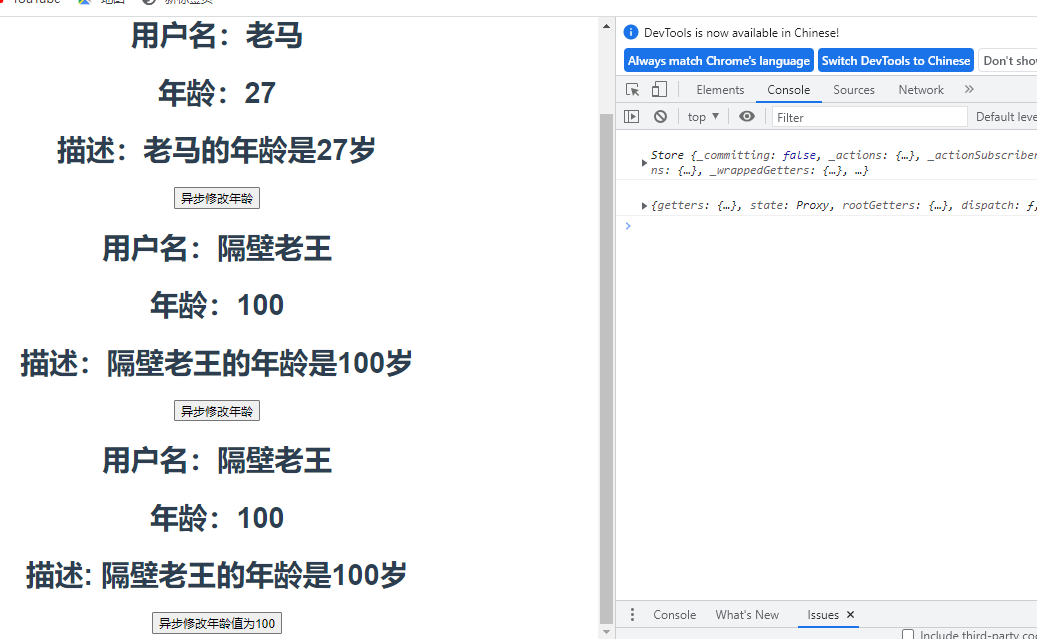
<h1>用户名:{{$store.state.user.username}}</h1>
<h1>年龄:{{$store.state.user.age}}</h1>
<h1>描述:{{$store.getters.description}}</h1>
<button @click="changeAge">异步修改年龄</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
mounted(){
console.log(this.$store)
},
methods:{
changeAge:function(){
this.$store.dispatch('asyncSetAge')
}
}
}
</script>
store/index.js
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
import user from './user'
export default createStore({
//设置全局数据的地方
state: {
count:1,
dzList:[]
},
getters: {
totalPrice:function(state){
return state.count*100
}
},
//修改状态的方法 (同步的操作)
mutations: {
setCount:function(state){
state.count++;
},
setCountNum:function(state,num){
state.count+=num;
},
setDzList:function(state,arr){
state.dzList =arr;
}
},
//异步的操作 (比如 ajax)
actions: {
getDz:function(context){
var api = "https://api.apiopen.top/getJoke?page=1&count=10&type=text"
fetch(api).then(res=>res.json()).then(result=>{
console.log(result);
context.commit('setDzList',result.result);
})
}
},
modules: {
user
}
})
router/index.js
import { createRouter, createWebHistory } from 'vue-router'
import HomeView from '../views/HomeView.vue'
import User from '../views/User.vue'
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'home',
component: HomeView
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'about',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/AboutView.vue')
},
{
path: '/user',
name: 'User',
component: User
}
]
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHistory(process.env.BASE_URL),
routes
})
export default router
2.命名空间
默认情况下,模块内部的 action 和 mutation 仍然是注册在全局命名空间的——这样使得多个模块能够对同一个 action 或 mutation 作出响应。Getter 同样也默认注册在全局命名空间,但是目前这并非出于功能上的目的(仅仅是维持现状来避免非兼容性变更)。必须注意,不要在不同的、无命名空间的模块中定义两个相同的 getter 从而导致错误。
如果希望你的模块具有更高的封装度和复用性,你可以通过添加 namespaced: true 的方式使其成为带命名空间的模块。当模块被注册后,它的所有 getter、action 及 mutation 都会自动根据模块注册的路径调整命名。
User.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>用户名:{{$store.state.user.username}}</h1>
<h1>年龄:{{$store.state.user.age}}</h1>
<h1>描述:{{$store.getters.description}}</h1>
<button @click="changeAge">异步修改年龄</button>
<!-- 命名空间的写法 -->
<h1>用户名:{{$store.state.user1.username}}</h1>
<h1>年龄:{{$store.state.user1.age}}</h1>
<h1>描述:{{$store.getters['user1/description']}}</h1>
<button @click="changeAge1">异步修改年龄</button>
<!-- 辅助函数的写法 -->
<h1>用户名:{{user1.username}}</h1>
<h1>年龄:{{user1.age}}</h1>
<h1>描述: {{description}} </h1>
<button @click="asyncSetAge(100)">异步修改年龄值为100</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState,mapGetters,mapMutations,mapActions} from 'vuex';
export default {
computed:{
...mapState(['user1']), //用user1把其解构出来
...mapGetters('user1',['description'])
},
mounted(){
console.log(this.$store)
},
methods:{
changeAge:function(){
this.$store.dispatch('asyncSetAge')
},
changeAge1:function(){
this.$store.dispatch('user1/asyncSetAge')
},
...mapActions('user1',['asyncSetAge'])
}
}
</script>
store/user1.js
const user = {
namespaced:true,
state:() =>({
username:'隔壁老王',
age:46
}),
mutations:{
setUsername:function(state){
state.username = '小王'
},
setAge:function(state,value){
state.age = value
}
},
actions:{
asyncSetAge:function(context,value){
console.log(context)
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('setAge',value);
},1000);
}
},
getters:{
description:function(state,getters,rootState){
return state.username +'的年龄是'+ state.age + '岁'
}
}
}
export default user
展示效果:
24.element-ui axios Echarts插件安装
#安装 element Ui
npm i element-ui -S #vue2.0版本
npm install element-plus --save
vue add element
vue add element-plus #vue3.0使用这个安装 element Ui 插件
#安装echarts
npm install echarts@4.9.0 --save #安装echarts插件
npm i echarts -S
在main.js中引入
import echarts from 'echarts' #v4版本这样引用echarts
Vue.prototype.$echarts = echarts
import * as echarts from 'echarts' #v5版本这样引用echarts
#安装axios
npm install axios --save
import axios from 'axios'




【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· DeepSeek “源神”启动!「GitHub 热点速览」
· 微软正式发布.NET 10 Preview 1:开启下一代开发框架新篇章
· C# 集成 DeepSeek 模型实现 AI 私有化(本地部署与 API 调用教程)
· DeepSeek R1 简明指南:架构、训练、本地部署及硬件要求
· 2 本地部署DeepSeek模型构建本地知识库+联网搜索详细步骤