一、基本介绍
(1)一个对象应该对其他对象保持最少的了解
(2)类与类关系越密切,耦合度越大
(3)迪米特法则(Demeter Principle)又叫最少知道原则,即一个类对自己依赖的类知道的越少越好。也就是说,对于被依赖的类不管多么复杂,都尽量将逻辑封装在类的内部。对外除了提供的public方法,不对外泄露任何信息
(4)迪米特法则还有个更简单的定义:只与直接的朋友通信
(5)直接的朋友:每个对象都会与其他对象有耦合关系,只要两个对象之间有耦合关系,我们就说这两个对象之间是朋友关系。耦合的方式很多,依赖,关联,组合,聚合等。其中,我们称出现成员变量,方法参数,方法返回值中的类为直接的朋友,而出现在局部变量中的类不是直接的朋友。也就是说,陌生的类最好不要以局部变量的形式出现在类的内部。
二、应用实例
有一个学校,下属有各个学院和总部,现要求打印出学校总部员工ID和学院员工的id
public class Demeter1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SchoolManager schoolManager = new SchoolManager();
schoolManager.printAllEmployee(new CollegeManager());
}
}
//学校总部员工
class Employee {
private String id;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
//学院员工
class CollegeEmployee {
private String id;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
//管理学院员工
class CollegeManager {
/**
* 获取学院的所有员工
*
* @return 学院的所有员工
*/
public List<CollegeEmployee> getAllEmployee() {
List<CollegeEmployee> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
CollegeEmployee collegeEmployee = new CollegeEmployee();
collegeEmployee.setId("学院员工id=" + String.valueOf(i + 1));
arrayList.add(collegeEmployee);
}
return arrayList;
}
}
//学校管理类
class SchoolManager {
/**
* 获取学校总部的所有员工
*
* @return 学校总部的所有员工
*/
public List<Employee> getAllEmployee() {
List<Employee> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setId("学校总部员工id=" + String.valueOf(i + 1));
list.add(employee);
}
return list;
}
/**
* 输出学校总部和学院员工信息
*/
void printAllEmployee(CollegeManager collegeManager) {
//获取学院员工
List<CollegeEmployee> allEmployee = collegeManager.getAllEmployee();
System.out.println("=================学院员工=================");
for (CollegeEmployee employee : allEmployee) {
System.out.println(employee.getId());
}
//获取学校总部员工
List<Employee> employeeList = this.getAllEmployee();
System.out.println("================学校总部员工=================");
for (Employee employee : employeeList) {
System.out.println(employee.getId());
}
}
}
输出结果:
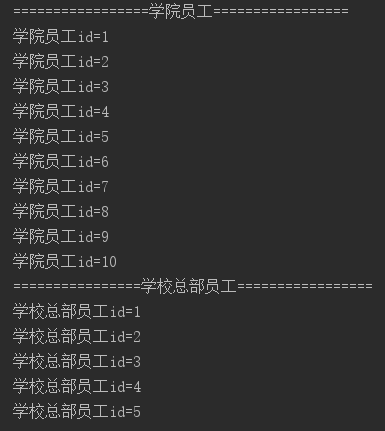
分析:
(1)前面设计的问题在于SchoolManager中,CollegeEmployee类并不是SchoolManager类的直接朋友
(2)按照迪米特法则,应该避免类中出现这样非直接朋友关系的耦合
改进:在CollegeManager类中直接新增一个printEmployee方法专门用于打印学院员工信息
public class Demeter1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SchoolManager schoolManager = new SchoolManager();
schoolManager.printAllEmployee(new CollegeManager());
}
}
//学校总部员工
class Employee {
private String id;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
//学院员工
class CollegeEmployee {
private String id;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
//管理学院员工
class CollegeManager {
/**
* 获取学院的所有员工
*
* @return 学院的所有员工
*/
public List<CollegeEmployee> getAllEmployee() {
List<CollegeEmployee> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
CollegeEmployee collegeEmployee = new CollegeEmployee();
collegeEmployee.setId("学院员工id=" + String.valueOf(i + 1));
arrayList.add(collegeEmployee);
}
return arrayList;
}
/**
* 输出学院员工信息
*
* */
public void printEmployee(){
//获取学院员工
List<CollegeEmployee> allEmployee = this.getAllEmployee();
System.out.println("=================学院员工=================");
for (CollegeEmployee employee : allEmployee) {
System.out.println(employee.getId());
}
}
}
//学校管理类
class SchoolManager {
/**
* 获取学校总部的所有员工
*
* @return 学校总部的所有员工
*/
public List<Employee> getAllEmployee() {
List<Employee> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setId("学校总部员工id=" + String.valueOf(i + 1));
list.add(employee);
}
return list;
}
/**
* 输出学校总部和学院员工信息
*/
void printAllEmployee(CollegeManager collegeManager) {
collegeManager.printEmployee();
//获取学校总部员工
List<Employee> employeeList = this.getAllEmployee();
System.out.println("================学校总部员工=================");
for (Employee employee : employeeList) {
System.out.println(employee.getId());
}
}
}
输出结果:
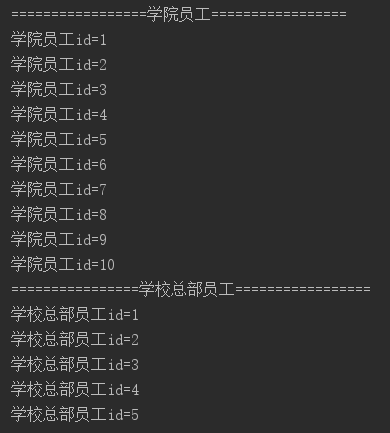
三、注意事项和细节
(1)迪米特法则的核心是降低类之间的耦合
(2)注意:由于每个类都减少了不必要的依赖,因此迪米特法则只是要求降低类间(对象间)耦合关系,并不是要求完全没有依赖关系





