「学习笔记」块状链表(STL)
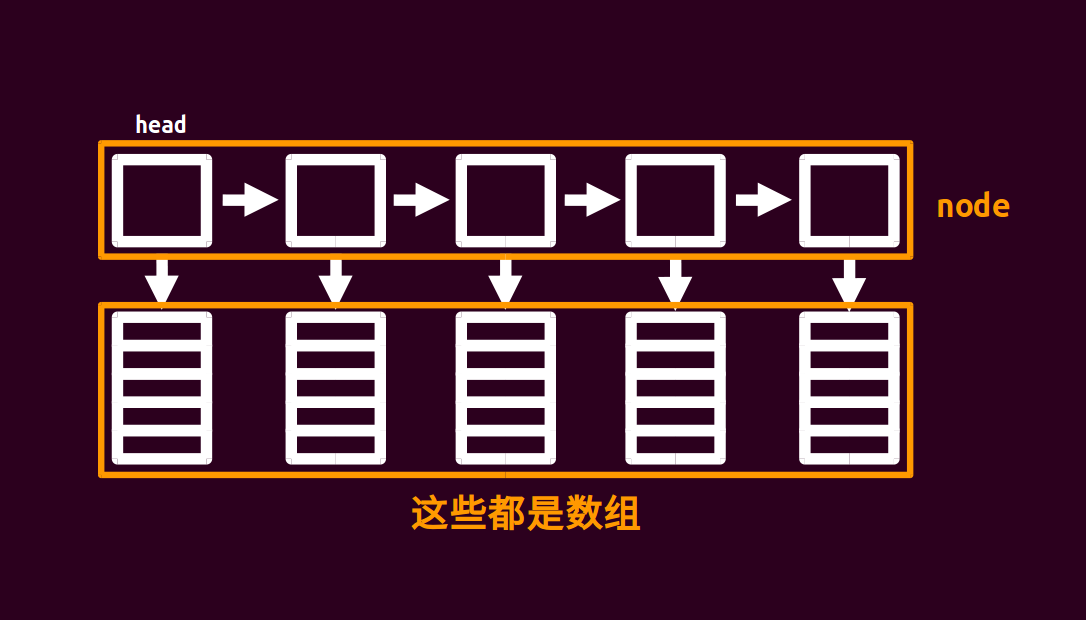
块状链表是一个集合了分块和链表的优秀数据结构。链表的每一个指针指向一个数组,每个数组的大小都接近 ,因此块状链表的复杂度都为 。
大概长这样。(图片来自 )
可以用它水过普通平衡树例题,所以又称为“五分钟平衡树”。
块状链表支持插入、分裂、查找等操作。
list<vector<ll>> List;
using lit = list<vector<ll>>::iterator;
using vit = vector<ll>::iterator;
基本操作#
查找#
遍历链表,来找到被查找元素的位置。
lit find(const int &p) {
int cnt = 0;
for (lit it = List.begin(); it != List.end(); ++ it) {
if ((*it).back() >= p) {
return it;
}
}
}
(插入)分裂#
当一个数组的大小超过 时,执行分裂操作以保证复杂度,否则就会退化成普通数组。
具体应该怎么做呢?在链表上新建一个节点和数组,将被分裂节点的后 个值复制到新节点上,被分裂节点在删除后 个值。
void insert(int x) {
lit it = find(x);
(*it).emplace(lower_bound((*it).begin(), (*it).end(), x), x);
if ((*it).size() > lim) {
List.emplace(next(it), (*it).begin() + (lim / 2), (*it).end());
(*it).erase((*it).begin() + (lim / 2), (*it).end());
}
}
删除#
void erase(int x) {
lit it = find(x);
(*it).erase(lower_bound((*it).begin(), (*it).end(), x));
if ((*it).empty()) {
List.erase(it);
}
}
例题#
// The code was written by yifan, and yifan is neutral!!!
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define bug puts("NOIP rp ++!");
#define rep(i, a, b, c) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i += (c))
#define per(i, a, b, c) for (int i = (a); i >= (b); i -= (c))
template<typename T>
inline T read() {
T x = 0;
bool fg = 0;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
fg |= (ch == '-');
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return fg ? ~x + 1 : x;
}
template<typename T>
void write(T x) {
if (x < 0) {
putchar('-');
x = -x;
}
if (x > 9) {
write(x / 10);
}
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
template<typename T>
void print(T x, char c) {
write(x);
putchar(c);
}
list<vector<ll>> List;
using lit = list<vector<ll>>::iterator;
using vit = vector<ll>::iterator;
int lim;
lit find(const int &p) {
int cnt = 0;
for (lit it = List.begin(); it != List.end(); ++ it) {
if ((*it).back() >= p) {
return it;
}
}
}
void insert(int x) {
lit it = find(x);
(*it).emplace(lower_bound((*it).begin(), (*it).end(), x), x);
if ((*it).size() > lim) {
List.emplace(next(it), (*it).begin() + (lim / 2), (*it).end());
(*it).erase((*it).begin() + (lim / 2), (*it).end());
}
}
void erase(int x) {
lit it = find(x);
(*it).erase(lower_bound((*it).begin(), (*it).end(), x));
if ((*it).empty()) {
List.erase(it);
}
}
int kth(int k) {
for (vector<ll> it : List) {
if (it.size() >= k) {
return it[k - 1];
} else {
k -= it.size();
}
}
return 0;
}
int num(int x) {
int cnt = 0;
for (vector<ll> it : List) {
if (it.back() >= x) {
cnt += lower_bound(it.begin(), it.end(), x) - it.begin() + 1;
return cnt;
} else {
cnt += it.size();
}
}
}
int qpre(int x) {
lit it = find(x);
vit it1 = lower_bound((*it).begin(), (*it).end(), x);
if (it1 == (*it).begin()) {
-- it;
return (*it).back();
} else {
-- it1;
return (*it1);
}
}
int qnxt(int x) {
lit it = find(x);
vit it1 = upper_bound((*it).begin(), (*it).end(), x);
if (it1 == (*it).end()) {
++ it;
return (*it).front();
} else {
return *it1;
}
}
int n;
int main() {
vector<ll> tmp;
tmp.emplace_back(LLONG_MAX);
List.emplace_back(tmp);
n = read<int>();
lim = sqrt(n);
for (int i = 1, op, x; i <= n; ++ i) {
op = read<int>(), x = read<int>();
if (op == 1) {
insert(x);
}
if (op == 2) {
erase(x);
}
if (op == 3) {
print(num(x), '\n');
}
if (op == 4) {
print(kth(x), '\n');
}
if (op == 5) {
print(qpre(x), '\n');
}
if (op == 6) {
print(qnxt(x), '\n');
}
}
return 0;
}
作者:yifan0305
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/yifan0305/p/17809685.html
版权:本作品采用「署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际」许可协议进行许可。
转载时还请标明出处哟!
朝气蓬勃 后生可畏
分类:
高级数据结构知识
Buy me a cup of coffee ☕.



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享4款.NET开源、免费、实用的商城系统
· 全程不用写代码,我用AI程序员写了一个飞机大战
· MongoDB 8.0这个新功能碉堡了,比商业数据库还牛
· 白话解读 Dapr 1.15:你的「微服务管家」又秀新绝活了
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示