「刷题记录」LOJ/一本通提高篇 贪心算法
[活动安排]#
题目传送门:活动安排
思路:我们按照活动的结束时间进行升序排序,因为一个活动结束的越早,就越不容易与其他活动起冲突,从前往后枚举时判断一下就行了
代码:
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e3 + 5;
int n, ans;
struct hd {
int str, las;
int operator < (const hd &b) const {
return las == b.las ? str < b.str : las < b.las;
}
} a[N];
inline ll read() {
ll x = 0;
int fg = 0;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
fg |= (ch == '-');
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return fg ? ~x + 1 : x;
}
int main() {
int last = 0;
n = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
a[i].str = read(), a[i].las = read();
}
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if(last <= a[i].str) {
ans++;
last = a[i].las;
}
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}
[种树]#
题目传送门:种树
思路:
1、贪心
依然是按照路段的结束位置进行升序排序,以便于我们从前往后按顺序枚举,枚举每一个路段时,从路段的开头枚举到结尾,由于一个位置只能种一棵树,所以只要这个位置有树,这个路段要求的树的数量就-1,具体看代码吧
贪心 代码:
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 3e4 + 5;
int n, h, ans;
int vis[N];
struct dl {
int str, las, w;
int operator < (const dl &b) const {
return las < b.las;
}
} d[N];
inline ll read() {
ll x = 0;
int fg = 0;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
fg |= (ch == '-');
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return fg ? ~x + 1 : x;
}
int main() {
n = read(), h = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= h; ++i) {
d[i].str = read();
d[i].las = read();
d[i].w = read();
}
sort(d + 1, d + h + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= h; ++i) {
int l = d[i].str, r = d[i].las, sum = d[i].w;
for (int j = l; j <= r && sum; ++j) {
if (vis[j]) {
--sum;
}
}
for (int j = r; j >= l && sum; --j) {
if (!vis[j]) {
vis[j] = 1;
--sum, ++ans;
}
}
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}
2、差分约束
路段 到 之间至少要种 棵树
每个路段最多种一棵树,对于路段 和路段 来说
将式子化简开就是 和
关系式有了,又因为是 ,建图跑最长路
差分约束 代码:
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 3e4 + 5;
const int M = 5e3 + 5;
const int inf = - 1e9 - 5;
int n, m, cnt;
int h[N], dis[N], vis[N], in[N];
struct edge {
int v, nxt;
ll w;
} e[M << 4];
inline ll read() {
ll x = 0;
int fg = 0;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
fg |= (ch == '-');
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return fg ? ~x + 1 : x;
}
void add(int u, int v, ll w) {
e[++cnt].v = v;
e[cnt].w = w;
e[cnt].nxt = h[u];
h[u] = cnt;
}
ll spfa(int x) {
deque<int> q;
q.push_back(x);
vis[x] = 1;
while(!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop_front();
vis[u] = 0;
for(int i = h[u]; i; i = e[i].nxt) {
int v = e[i].v;
ll w = e[i].w;
if(dis[v] < dis[u] + w){
dis[v] = dis[u] + w;
++in[v];
if(in[v] > n) return 0;
if(!vis[v]) {
vis[v] = 1;
if(!q.empty() && dis[v] >= dis[q.front()]) {
q.push_front(v);
}
else {
q.push_back(v);
}
}
}
}
}
return dis[n];
}
int main() {
n = read();
m = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
int a = read(), b = read();
ll w = read();
add(a - 1, b, w);
}
for(int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
if(i) add(i, i-1, -1), dis[i] = inf;
if(i != n) add(i, i + 1, 0);
}
printf("%lld\n",spfa(0));
return 0;
}
[喷水装置]#
题目传送门:喷水装置
思路:由于范围是圆,如图: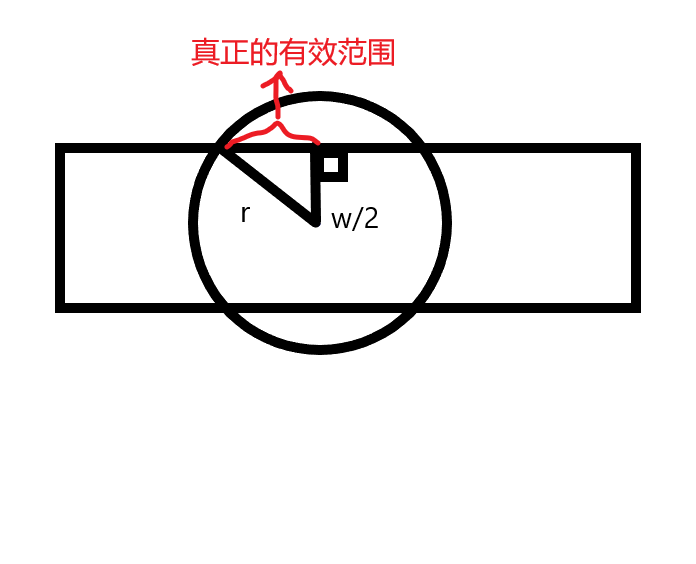
所以我们要利用勾股定理来求出这个有效范围 贪心忽然成了数学题,我们可以求出一个喷头有效范围的最左端和最右端,按照最左端进行升序排序,以便不会漏下没覆盖到的区域,从左到右一个一个检查,具体看代码吧
代码:
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 2e4;
int T, n, l, ans, cnt;
double h, t, r, x;
struct node {
double x, y;
int operator < (const node &b) const {
return x < b.x;
}
} a[N];
int main() {
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--) {
scanf("%d %d %lf", &n, &l, &h);
cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
scanf("%lf %lf", &x, &r);
if(r <= h/2) continue;
a[++cnt].x = x - (sqrt(r * r - h * h * 0.25));
a[cnt].y = x + (sqrt(r * r - h * h * 0.25));
}
sort(a + 1, a + cnt + 1);
int fg = 1;
t = 0, ans = 0;
while(t < l) {
++ans;
double s = t;
for(int i = 1; i <= cnt && a[i].x <= s; ++i) {
t = max(a[i].y, t);
}
if(s == t && s < l) {
printf("-1\n");
fg = 0;
break;
}
}
if(fg) printf("%d\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}
[加工生产调度]#
题目传送门:加工生产调度
思路:第一个产品,在 加工时,没有其他产品在 加工,所以要选 小的,最后一个物品,在 加工时,没有其他产品在 加工,所以要选 小的,对于其他产品,如果该产品的 比 小,那么把这个产品放到前面去,它越早离开A工厂,其他产品就能越早进入A工厂;如果 比 小,那就往后放,它越早离开 工厂,其他产品就能越早进入 工厂。
为什么这么排呢?因为一个物品必须先进入 工厂,在进入 工厂,我们先尽快让所有产品进入 工厂,再尽快让所有产品离开 工厂,这就是我们的贪心策略
代码:
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e3 + 5;
const int inf = ~(1 << 31);
int n, k, t;
int a[N], b[N], m[N], ans[N], s[N];
inline ll read() {
ll x = 0;
int fg = 0;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
fg |= (ch == '-');
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return fg ? ~x + 1 : x;
}
int main() {
n = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
a[i] = read();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
b[i] = read();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
m[i] = min(a[i], b[i]);
s[i] = i;
}
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
for(int j = i + 1; j <= n; ++j) {
if(m[i] > m[j]) {
swap(m[i], m[j]);
swap(s[i], s[j]);
}
}
}
k = 0, t = n + 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if(m[i] == a[s[i]]) {
ans[++k] = s[i];
}
else {
ans[--t] = s[i];
}
}
k = 0, t = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
k += a[ans[i]];
if(t < k) {
t = k;
}
t += b[ans[i]];
}
printf("%d\n", t);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
printf("%d ", ans[i]);
}
return 0;
}
[智力大冲浪]#
题目传送门:智力大冲浪
思路:
1、搜索 + 剪枝
每个小游戏有选与不选两种结果,如果选,那么总奖金不变,如果主动不选或被迫不选,那么总奖金要减少,我们记录着总奖金的变化,如果总奖金已经比我们找到的最优解小了,那它最后的结果就不可能成为最优解了,最优性剪枝 数据很水,竟然让暴搜 个小剪枝过了
搜索 + 剪枝 代码:
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 510;
int n, m, maxn;
struct node {
int tim, w;
int operator < (const node &b) const {
return tim == b.tim ? w > b.w : tim < b.tim;
}
} a[N];
inline ll read() {
ll x = 0;
int fg = 0;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
fg |= (ch == '-');
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return fg ? ~x + 1 : x;
}
void dfs(int cur, int ti, int sum) {
if(sum < maxn) return ;
if(cur == n + 1) {
maxn = max(maxn, sum);
return ;
}
if(ti > a[cur].tim) {
dfs(cur + 1, ti, sum - a[cur].w);
return ;
}
dfs(cur + 1, ti + 1, sum);
dfs(cur + 1, ti, sum - a[cur].w);
}
int main() {
m = read();
n = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
a[i].tim = read();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
a[i].w = read();
}
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1);
dfs(1, 1, m);
printf("%d\n", maxn);
return 0;
}
2、贪心(正解)
我们按照每个游戏所扣除的钱按降序排序,因为所扣除的钱越大,对答案的影响就越大,我们考虑每个游戏都在最后的限制时间做,那它前面的时间就可以分配给其他游戏了,如果它找到可以占用时间,那这个时间就标记一下,如果它找不到可以占用的时间,那就只能扣钱了
贪心 代码:
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 510;
int n, m;
int vis[N];
struct node {
int ti, w;
int operator < (const node &b) const {
return w > b.w;
}
} a[N];
inline ll read() {
ll x = 0;
int fg = 0;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
fg |= (ch == '-');
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return fg ? ~x + 1 : x;
}
int main() {
m = read();
n = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
a[i].ti = read();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
a[i].w = read();
}
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
int fg = 0;
for(int j = a[i].ti; j; --j) {
if(!vis[j]) {
vis[j] = 1;
fg = 1;
break;
}
}
if(!fg) {
m -= a[i].w;
continue;
}
}
printf("%d\n", m);
return 0;
}
[数列极差]#
题目传送门:数列极差
思路:可以发现,按照小数到大数的顺序乘起来可以得到最大值,按照大数到小数的顺序乘起来可以得到最小值,那我们直接用堆来维护顺序,一个大根堆,一个小根堆,每次弹堆顶,插入即可
代码:
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int n;
priority_queue<int> q1;
priority_queue<int, vector <int>, greater<int> > q2;
inline ll read() {
ll x = 0;
int fg = 0;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
fg |= (ch == '-');
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return fg ? ~x + 1 : x;
}
int main() {
int maxn, minn, x, y;
n = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
x = read();
q1.push(x);
q2.push(x);
}
while (q2.size() != 1) {
x = q2.top();
q2.pop();
y = q2.top();
q2.pop();
q2.push(x * y + 1);
}
maxn = q2.top();
while (q1.size() != 1) {
x = q1.top();
q1.pop();
y = q1.top();
q1.pop();
q1.push(x * y + 1);
}
minn = q1.top();
printf("%d\n", maxn - minn);
return 0;
}
[数列分段]#
题目传送门:数列分段
思路:这个应该算是最简单最基础的贪心了,甚至都不用排序,从前往后扫,一旦和大于 ,再分新的一段
代码:
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
ll n, m, ans, sum;
ll a[N];
inline ll read() {
ll x = 0;
int fg = 0;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
fg |= (ch == '-');
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return fg ? ~x + 1 : x;
}
int main() {
n = read(), m = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
a[i] = read();
}
int l = 1, r = n;
ans = 1;
for(int i = l; i <= r; ++i) {
if(sum + a[i] > m) {
sum = a[i];
++ans;
}
else sum += a[i];
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}
>[线段]#
题目传送门:线段
思路:跟第一题除了题面不同外,基本一模一样,按照每条线段的右端点升序排序,扫一遍即可
代码:
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
int n;
ll last, ans;
struct node {
ll str, lat;
int operator < (const node &b) const {
return lat < b.lat;
}
} a[N];
inline ll read() {
ll x = 0;
int fg = 0;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
fg |= (ch == '-');
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return fg ? ~x + 1 : x;
}
int main() {
n = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
a[i].str = read(), a[i].lat = read();
}
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if(last <= a[i].str) {
++ans;
last = a[i].lat;
}
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}
[家庭作业]#
题目传送门:家庭作业
思路:与种树那道题思路基本一样,但它的数据范围太大,会超时,所以要再优化一下,当往前扫描时,如果找不到可以占用的时间,那就将这个作业的截至时间记录下来,如果后面的作业截止时间小于等于我们所记录的时间,那他们也一定完不成,直接跳过就行了
代码:
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
int n, sum, l, fg;
int vis[N];
struct node {
int tim, val;
int operator < (const node &b) const {
return val > b.val;
}
} a[N];
inline ll read() {
ll x = 0;
int fg = 0;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
fg |= (ch == '-');
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return fg ? ~x + 1 : x;
}
int main() {
n = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
a[i].tim = read();
a[i].val = read();
}
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
fg = 0;
if(a[i].tim < l) continue;
for(int j = a[i].tim; j; --j) {
if(!vis[j]) {
vis[j] = 1;
sum += a[i].val;
fg = 1;
break;
}
}
if(!fg) l = a[i].tim;
}
printf("%d\n", sum);
return 0;
}
[钓鱼]#
题目传送门:钓鱼
思路:与堆的应用题 鱼塘钓鱼 很像,但这道题要枚举结束的鱼塘,其他思路基本一样
代码:
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 110;
int n, h, sum, maxn;
int tim[N], fish[N], num[N], del[N];
struct node {
int num, w;
int operator < (const node &b) const {
return w < b.w;
}
};
priority_queue<node> q;
inline ll read() {
ll x = 0;
int fg = 0;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
fg |= (ch == '-');
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return fg ? ~x + 1 : x;
}
int main() {
n = read(), h = read();
h *= 12;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
fish[i] = read();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
del[i] = read();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n - 1; ++i) {
int x = read();
tim[i] = tim[i - 1] + x;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
sum = 0;
for(int j = 1; j <= i; ++j) {
q.push(node{j, fish[j]});
}
int k = h - tim[i - 1];
for(int j = 1; j <= k; ++j) {
if(q.empty()) break;
node fis = q.top();
q.pop();
int k = fis.w - del[fis.num];
if(k > 0) q.push(node{fis.num, k});
sum += fis.w;
}
maxn = max(maxn, sum);
}
printf("%d\n", maxn);
return 0;
}
[糖果传递]#
题目传送门:糖果传递
思路:这个题应该是最难的了,我们设 为第 个小朋友向第 个小朋友传递了 个糖果, 为第 个小朋友向第 个小朋友传递了 个糖果
每个小朋友最后的糖果数为 ,又因为要获得均等糖果,所以
这样的方程有 个,但是最后一个 是没有意义的,推到这里, 已经推出来了,可以直接算出来 是多少,所以实际上有用的只有前 个公式
这样看肯定无法直接求出 ,我们要转换一下,把式子变成 ,再转换一下 ,这样就可以直接求出 了。
最后,我们的答案为 ,我们要让它最小化,取中位数即可.
代码:
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
int n;
ll sum, ans;
ll a[N], x[N];
inline ll read() {
ll x = 0;
int fg = 0;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
fg |= (ch == '-');
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return fg ? ~x + 1 : x;
}
int main() {
n = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
a[i] = read();
sum += a[i];
}
sum = sum / n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
x[i] = x[i - 1] + sum - a[i - 1];
}
sort(x + 1, x + n + 1);
ll k = x[(n + 1) / 2];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
ans += abs(x[i] - k);
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}
结束#
这里面有很基础的题目,也有很难的题目,笔者贪心部分完成了,接下来就要奋斗分治部分了!
作者:yifan0305
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/yifan0305/p/16581002.html
版权:本作品采用「署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际」许可协议进行许可。
转载时还请标明出处哟!



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY