python安全编程学习
python正则表达式
python使用re模块提供对正则表达式的支持
import re
- 先将正则表达式的字符串形式编译成pattern实例
p = re.compile('hello') - 使用pattern实例处理文本并获得匹配结果
m = p.match('hello world') - 使用实例获得信息,进行其他操作
m.group() => 'hello'
或直接:
word = re.findall('hello','hello world') => ['hello']
字符
常用正则表达式
贪婪模式 (.+?)
匹配任意内容:非贪婪模式 (.?)
屏蔽中间多余代码 :[\s\S]?
匹配网址url:[a-zA-Z]+://[^\s]
匹配IP地址: \d+.\d+.\d+.\d+
匹配链接地址:href *= [’"](\S+)["’]
python web编程
相关模块 :urllib,urllib2,requests
urllib
url = ‘https://baidu.com’
r = urllib.urlopen(url)
print r.read() => 返回源代码
urllib2
与urllib相比没有urlretrieve(),多了个requests()
requests
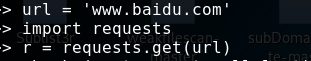




未完待续…
ps: pycharm中对headers快速加引号
1. 先ctrl+f
2. 填入
(.*?):(.*)
'$1':'$2'
3. 勾选三个选项
4. 替换

文件按行去重
#coding=utf-8
#!/usr/bin/python
import shutil
a = 0
readfile = "C:/windows/1.txt" #要去重的文件路径
writefile = "C:/windows/2.txt" #新生成的路径
lineset = set() #去重,set()函数创建一个无序不重复元素集
outfile = open(writefile,'w') #生成文件的对象并写入
f = open(readfile,'r') #生成文件的对象并读出
for line in f:
if line not in lineset:
a +=1
outfile.write(line)
lineset.add(line)
print(a)
print('\n')
outfile.close()
print('success')
读取文件每一行
f = open("c:\\1.txt","r")
lines = f.readlines()#读取全部内容
for line in lines
print line
python的动态语言特性
1. 运行的过程中给类绑定(添加)方法
class person(object):
def __init__(self,name = None,age = None):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def run(self,speed):
print("the man's speed is %d km/h" %speed)
p = person("xiaohai",18)
# 添加方法
import type
person.run = types.MethodType(run,None,person)
p.run(20) # 运行
2. 运行的过程中删除属性、方法
删除的方法:
del 对象.属性名
delattr(对象, “属性名”)
3. 定义一个特殊的__slots__变量,来限制该class实例能添加的属性
class Person(object):
__slots__ = ("name", "age") #该类只能使用name,age属性
注:__slots__定义的属性仅对当前类实例起作用,对继承的子类是不起作用的
生成器
- 类似列表,但不必创建完整的list,从而节省大量的空间,这种一边循环一边计算的机制,称为生成器:generator
- 要创建一个生成器,有很多种方法。第一种方法很简单,只要把一个列表生成式的 [ ] 改成 ( )
In [15]: L = [ x*2 for x in range(5)]
In [16]: L
Out[16]: [0, 2, 4, 6, 8]
In [17]: G = ( x*2 for x in range(5))
In [18]: G
Out[18]: <generator object <genexpr> at 0x7f626c132db0>
In [19]: next(G) #使用next()函数可一个一个打印出来,但很少用,一般直接用for直接打印出来
Out[19]: 0
In [20]: next(G)
Out[20]: 2
In [26]: G = ( x*2 for x in range(5))
In [27]: for x in G:
....: print(x)
0
2
4
6
8

