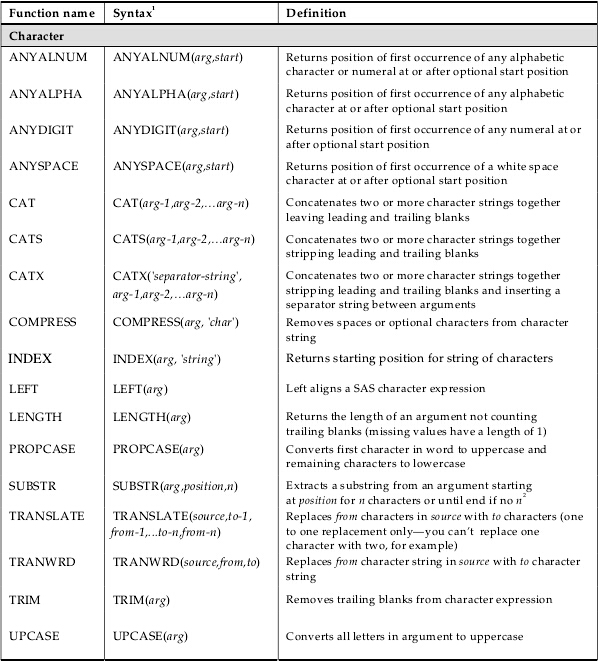
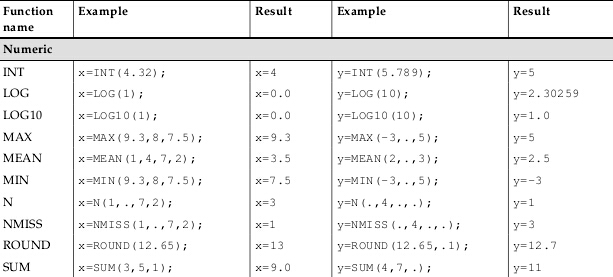
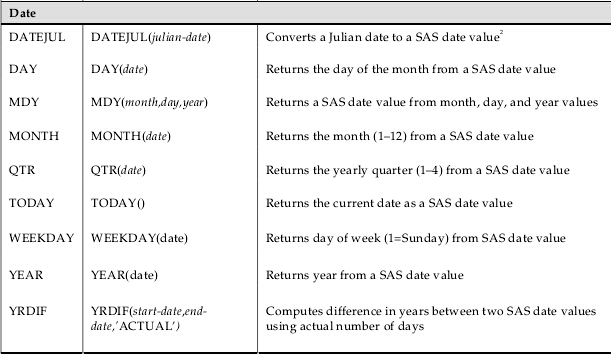
sas函数
index : 字符函数 数值函数 日期含糊 SCL函数 特殊函数
/**********************字符函数******************************/
Compress(<source><,chars><,modifiers>);
功能:消除或保留指定的字符
I or i: ignores the case of the characters to be kept or removed
k or K:keeps the characters in the list instead of removing them*消除指定的空格或字符串;
data compress1; x1 = " 1 2 3 a"; x2 = "Abacabbad";
y1 = compress(x1," ");
y = compress(x1); *作用y1的一样,消除空格,tab,暂时已知的两个; y2 = compress(x2,"Ab");*消除所有A或b的字符;
put y1 y2; run;
i 和 k的用法
data me; x = "123-102-212"; y3 = compress(x,"0123456789", 'k'); y4 = compress(x,'-'); run;
SUBSTR( matrix, position <, length> )
功能:截取子字符串
matrix is a character matrix or quoted literal
position is a numeric matrix or scalar that contains the starting position
length is a numeric matrix or scalar that contains the length of the substring
当其位于等号左边或右边时,含义有区别
右边是的情况,为给变量赋值 date='06MAY98'; month=substr(date,3,3); year=substr(date,6,2); put @1 month @5 year; 结果为MAY 98 左边时的情况,为改变字符串中子字符串的值 a='KIDNAP'; substr(a,1,3)='CAT'; put a; 结果为CATNAP
默认情况下,如果不写长度,则会从起始位置一直截取到字符串的末尾
a='KIDNAP';
y = substr(a,2);
结果为IDNAP
source:identifies the constant, variable, or expression whose value you want to reformat. The source argument can be character or numeric
format:contains the SAS format that you want applied to the value that is specified in the source
将数值型或字符型转化为字符型
data a; x = "01jan2007"d; *x是数字型,表示为17167,如果不对其输出格式做规定,则输出为数值; format x date11.; *将其转化为日期格式01-JAN-2007; y = put(x,date11.);*将x通过put函数转化为字符型; z = compress(y,'-');*通过compress函数去除'-',compress中的变量要为字符型,如果直接compress(x)达不到想要的效果; run;
name=transtrn(name, "Mrs.", "Ms."); name=transtrn(name, "Miss", "Ms."); put name; 结果为Mrs. Joan Smith Ms. Joan Smith 结果为Miss Alice Cooper Ms. Alice Cooper
除去连续的两个字符,而不是将两个字符中的任意一个都在字符串中全部清除,可以考虑同transtrn代替compress data a; x = 'abasdsab'; y = transtrn(x,'ab',''); run;
LENGTH( matrix ) ;
功能:计算字符串的长度
说明:The length of a string is equal to the position of the rightmost nonblank character in the string. If a string is entirely blank, its length value is set to 1.
中文:所计算的长度是从第一个子都到字符串最右端的一个非空字符为止,如果字符串为空,则长度设为1
c = {"Hello" "My name is Jenny "}; b = length(c); print b; b = 5 16
比较全的字符函数的实例

/********************************数值函数*******************************/
a = '20071011'; y = input(a,yymmdd10.); format y yymmdd10.;
日期也为数值型
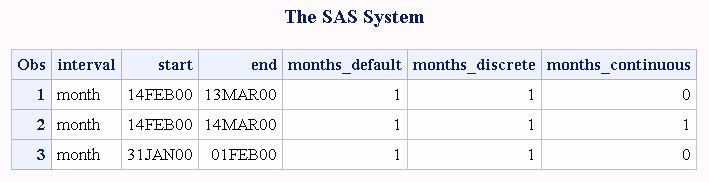
功能:向下取整取间隔时间,不到一个月按一个月计算,按此换算
interval:specifies a character constant, a variable, or an expression that contains an interval name(interval name有很多种,具体见sas帮助文档)
start-date:specifies a SAS expression that represents the starting SAS date, time, or datetime value.
end-date:specifies a SAS expression that represents the ending SAS date, time, or datetime value.
method:specifies that intervals are counted using either a discrete or a continuous method.(DISCRETE为默认,CONTINUOUS备选)
data a; interval='month'; start='14FEB2000'd; end='13MAR2000'd; months_default=intck(interval, start, end); months_discrete=intck(interval, start, end,'d'); months_continuous=intck(interval, start, end,'c');*相隔时间大于一个月小于两个月,按一个月计算; output; end='14MAR2000'd; months_default=intck(interval, start, end); months_discrete=intck(interval, start, end,'d'); months_continuous=intck(interval, start, end,'c'); output; start='31JAN2000'd; end='01FEB2000'd; months_default=intck(interval, start, end); months_discrete=intck(interval, start, end,'d'); months_continuous=intck(interval, start, end,'c'); output; format start end date.; run; proc print data=a; run;
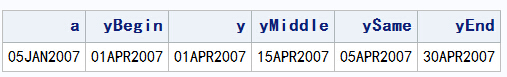
2.3:INTNX(custom-interval, start-from, increment <, 'alignment'> )
功能:返回指定时间间隔的日期
前两个参数同上
increment:specifies a negative, positive, or zero integer that represents the number of date, time, or datetime intervals. Increment is the number of intervals to shift the value of start-from.
alignment:controls the position of SAS dates within the interval(Default:BEGINNING,MIDDLE,END,SAME),是字符型在函数中要打引号。
alignment应用的区别
data a; a = '05jan2007'd; yBegin = intnx('month',a,3,'beginning'); y = intnx('month',a,3); yMiddle = intnx('month',a,3,'middle'); ySame = intnx('month',a,3,'same'); yEnd = intnx('month',a,3,'end'); format a yBegin y yMiddle ySame yEnd date10.; run; proc print data=a noobs;run;
2.4:INT( matrix ) ;
The INT function truncates the decimal portion of the value of the argument
proc iml; y = 2.8; b = int(y); x={12.95 10.9999999999999, -30.5 1e-6}; c = int(x); print b, c; quit;
b=2 x={12,10,-30,0}
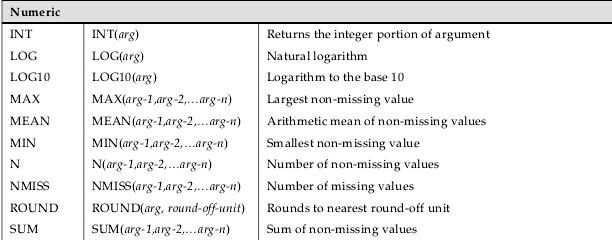
/*********************************日期函数********************************/
yactact=yrdif(sdate, edate, 'actual'); *用的较多,暂时记这个,得到的是小数;
int(yactact); *取整,4.x 全部变为4;
round(yactact,.x); *保留到小数点后x位,如果省略第二项则四舍五入;
option yearcutoff=1920; 所以计算的日期都在1920年后的一百年内,所以01/01/01是表示2001年而不是1901年

/*********************************SCL函数********************************/
OPEN(<table-name<>,mode>); 对应CLOSE(data-set-id)返回值和OPEN相反
功能:打开一个数据集,并返回一直独一无二的ID,成功是ID>0,失败时ID=0;
table-name:the SAS table or SAS/ACCESS view descriptor to open, specified as <libref.>member-name<(data-set-options)>. The default value for table-name is _LAST_, which is the last table created in the current SAS session.
mode:不同的访问模式,见sas帮助文档
FETCHOBS(table-id,row-number<,options>);
功能:获取打开数据集的一条观测,成功返回0,否则为非0
VARNUM(table-id,var-name);
功能:contains the position number of the column in the SAS table, or 0 if the column is not in the SAS table
/********************************特殊函数*********************************/
argument:specifies a numeric or character constant, variable, or expression.
n:specifies the number of lagged values.
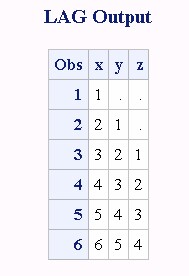
作用:Storing values at the bottom of the queue and returning values from the top of the queue occurs only when the function is executed(将上一个lag函数作用的数值保存在队列底部,每一次运行都读取队列顶部的)。
data one; input x @@; y=lag1(x); z=lag2(x); datalines; 1 2 3 4 5 6 ;
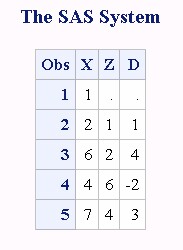
功能:DIFn is defined as DIFn(x)=x-LAGn(x). 计算当前值与上一个值的差!
data two; input X @@; Z=lag(x); D=dif(x); datalines; 1 2 6 4 7 ; proc print data=two; run;

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号