python scipy spatial.KDTree.query用法及代码示例
用法:
KDTree.query(self, x, k=1, eps=0, p=2, distance_upper_bound=inf)-
查询kd-tree附近的邻居
参数:
- x:array_like, last dimension self.m
-
要查询的点数组。
- k:int, 可选参数
-
要返回的最近邻点的数量。
- eps:nonnegative float, 可选参数
-
返回近似的最近邻居;第k个返回值保证不超过(k + 1)乘以与第k个最近邻居的距离。
- p:float, 1<=p<=infinity, 可选参数
-
使用哪个Minkowski p-norm。 1是sum-of-absolute值“Manhattan”距离2是通常的欧几里得距离无穷大是maximum-coordinate-difference距离
- distance_upper_bound:nonnegative float, 可选参数
-
仅返回该距离内的邻居。这用于修剪树搜索,因此,如果要执行一 Series nearest-neighbor查询,则可能有助于提供到最近点的最近邻居的距离。
返回值:
- d:浮点数或浮点数数组
-
到最近邻居的距离。如果x具有形状元组+(self.m,),则如果k为1,则d具有形状元组;如果k大于1,则具有元组+(k,)。丢失的邻居(例如,当k> n或给出distance_upper_bound时)以无限距离表示。如果k为None,则d为形状元组的对象数组,其中包含距离列表。不论哪种情况,命中都按距离排序(最接近的优先)。
- i:整数或整数数组
-
self.data中邻居的位置。我与d的形状相同。
例子:
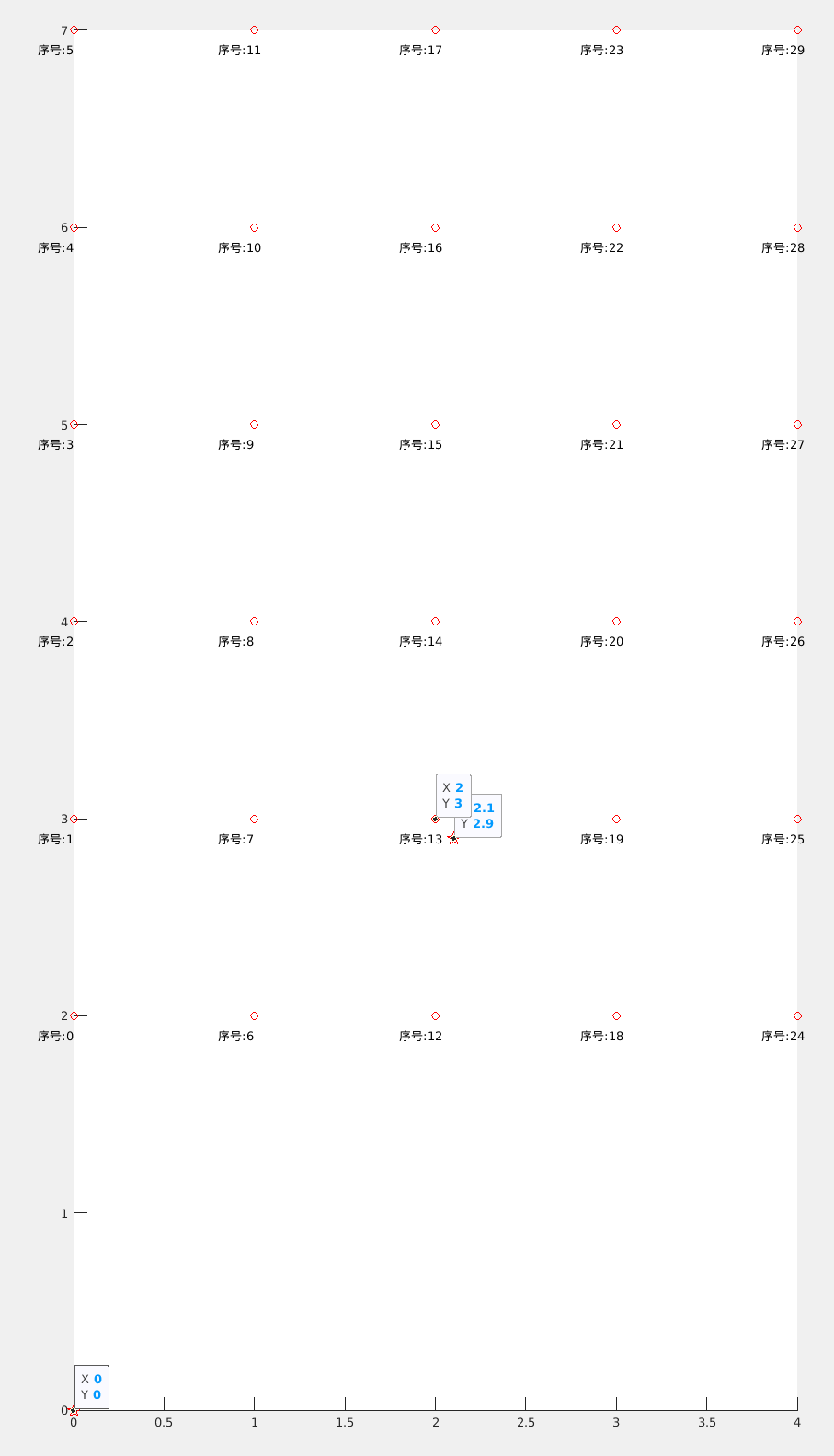
>>> from scipy import spatial >>> x, y = np.mgrid[0:5, 2:8] >>> tree = spatial.KDTree(list(zip(x.ravel(), y.ravel()))) >>> tree.data array([[0, 2], [0, 3], [0, 4], [0, 5], [0, 6], [0, 7], [1, 2], [1, 3], [1, 4], [1, 5], [1, 6], [1, 7], [2, 2], [2, 3], [2, 4], [2, 5], [2, 6], [2, 7], [3, 2], [3, 3], [3, 4], [3, 5], [3, 6], [3, 7], [4, 2], [4, 3], [4, 4], [4, 5], [4, 6], [4, 7]]) >>> pts = np.array([[0, 0], [2.1, 2.9]]) >>> tree.query(pts) (array([ 2. , 0.14142136]), array([ 0, 13])) 返回值是:离查询点最近的点的距离和索引。(array([ 2. , 0.14142136])是距离,array([ 0, 13]))是索引。 >>> tree.query(pts[0]) (2.0, 0)】 (array([ 2. , 0.14142136]) array([ 0, 13]))返回值是:离查询点最近的点的距离和索引。利用matlab代码可视化:clc;clear;close all; dian=[]; for i=0:1:4 for j=2:1:7 dian=[dian;[i,j]]; end end pts1=[0,0]; pts2=[2.1,2.9]; figure(1);hold on ;plot(dian(:,1),dian(:,2),'ro'); for k=1:size(dian,1) figure(1);hold on ;text(dian(k,1)-0.2,dian(k,2)-0.1,['序号:',num2str(k-1)],'color','k'); end figure(1);hold on ;plot(pts1(:,1),pts1(:,2),'rp','markersize',11); figure(1);hold on ;plot(pts2(:,1),pts2(:,2),'rp','markersize',11);
源码:
scipy.spatial.KDTree.query的API实现见:[源代码]





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理