Python算法题常用函数记忆清单
系统设计题&模拟题链接:https://leetcode.cn/problem-list/design/
字符串操作
(1)split 按指定分隔符转成 list
str_list= text.split() # 默认按空格分割 (函数写在后面,用 . 来调用)
str_list= text.split(",") # 按逗号分割
(2)strip()去除两边的空格
(3)join把list转成字符串输出,是把分割符写在变量前面的
# 假设我们有一个包含整数的列表
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
# 以空格分割,将整数转换为字符串,输出: '1 2 3 4 5'
my_string = ' '.join([str(i) for i in my_list])
(4)字符串比大小,unicode,大小写转换相关操作
判断是否为字符串:char.isalpha() 返回bool
ord(x)-ord('a') --判断x与字母a的Unicode差值,0~25内说明为小写字母
str.upper()转大写,str.lower() 转小写
进制转换
十转其他
bin() 可以将十进制整数转换为二进制字符串。注意,结果字符串的前缀是 '0b',因此需要切片得到01字符串oct() 可以将十进制整数转换为八进制字符串。注意,结果字符串的前缀是 '0o'hex() 可以将十进制整数转换为十六进制字符串。注意,结果字符串的前缀是 '0x'其他转十
int转就行,第二个参数传进制数,进制数为字符串类型且不需要前缀!!
decimal_number = int(binary_string, 2) #十转二 decimal_number = int(octal_string, 8) #十转八 decimal_number = int(hexadecimal_string, 16) #十转十六
list 列表
字典 Dictionary,也称散列表,hashmap
以leetcode 1396为例
重点记忆:初始化,dic[key] 索引访问value,value = dic.get(key,None)
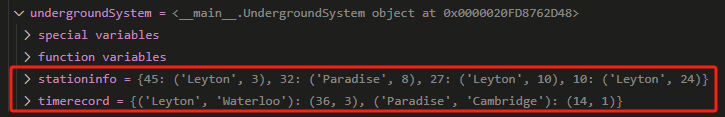
class UndergroundSystem: def __init__(self): self.stationinfo=dict() #初始化方式1 self.timerecord={} #初始化方式2 def checkIn(self, id: int, stationName: str, t: int) -> None: self.stationinfo[id] = (stationName,t) # id为key,(stationName,t)这个元组tuple为value,不允许用list为key def checkOut(self, id: int, stationName: str, t: int) -> None: # self.stationinfo[id] = [stationName,t] starttime = self.stationinfo[id][1] #查表找入站时间,第二维度01用来表示元组索引 startstation = self.stationinfo[id][0] # 查表找入站名称 # if self.timerecord[[startstation,stationName]] == None: #不能用不可hash的list做key,下面换成tuple正解 # self.timerecord[[startstation,stationName]] = {0,0} tmp = self.timerecord.get((startstation,stationName),(0,0)) #字典get的写法,第一个参为key,第二个参为访存没中的返回值,默认为None self.timerecord[(startstation,stationName)] = (tmp[0]+t-starttime,tmp[1]+1) #{‘起点站’,‘终点站’} = {原来总时间+新乘客时间,乘客数量+1} def getAverageTime(self, startStation: str, endStation: str) -> float: timeAmount,touristNum = self.timerecord[(startStation,endStation)] return timeAmount/touristNum if touristNum>0 else 0
上面变量里的值长下面这样:
字典的补充
自定义的排序键(key)来对字典进行排序。字典值是包含三个元素的数组,按照先第二个数,再第一个数,最后第三个数的顺序对字典进行排序。
# 示例字典 data = { 'a': [1, 2, 3], 'b': [4, 1, 6], 'c': [7, 5, 8], 'd': [1, 3, 2] } # 自定义排序键对字典进行排序,说白就是给list排序,根据里面tuple的value这个list的元素索引排序 sorted_data = dict(sorted(data.items(), key=lambda item: (item[1][1], item[1][0], item[1][2]))) # 输出排序后的字典 print(sorted_data)
上面例子中:
1. data.items() 以列表返回可遍历的(键, 值) 元组数组,每个项是一个 (k, v) 对。
2. sorted() 函数用于对这些项进行排序。
3. key=lambda item: (item[1][1], item[1][0], item[1][2]) 定义了一个排序键,其中 item[1] 是字典的值(即包含三个元素的列表),item[1][1] 是列表中的第二个元素,item[1][0] 是列表中的第一个元素,item[1][2] 是列表中的第三个元素。
set 集合(元素唯一但无序)
初始化:parame = {value01,value02,...} 或者 set(value),注意与字典区分
增:set.add(x) 添加元素,重复则略过
删:
s.remove(x) --元素不存在,则会发生错误
s.discard(x) --不会报错,强烈建议用这个!!
改:删了再增?
查: if a in set: True则表示a在set里
set转list直接:list(set)即可;
set转list并排序的话:sorted_list = sorted(set)
堆排序
首先明确python里只有小根堆,实现大根堆需要对元素取负值实现。
常见函数:
heapq.heappush(heap, item):将元素添加到堆中。heapq.heappop(heap):移除并返回堆中的最小元素。heapq.heapify(x):将列表转换为堆。heapq.heapreplace(heap, item):移除并返回堆中的最小元素,并添加新元素。heapq.heappushpop(heap, item):移除并返回堆中的最小元素,并添加新元素,如果新元素小于最小元素,则返回新元素,否则返回最小元素。
实例:
import heapq # 铭记import!!! # 创建一个空堆 heap = [] # 添加元素,实例名称作为变量在函数内部传递 heapq.heappush(heap, 5) heapq.heappush(heap, 3) heapq.heappush(heap, 10) heapq.heappush(heap, 2) # 查看堆 print(heap) # 输出: [2, 3, 5, 10] # 移除并返回最小元素 print(heapq.heappop(heap)) # 输出: 2 # 将列表转换为堆 data = [3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6, 5, 3, 5] heapq.heapify(data) print(data) # 输出: [1, 1, 3, 2, 5, 9, 4, 6, 5, 3, 5] # 替换堆中的最小元素 heapq.heapreplace(heap, 1) print(heap) # 输出: [1, 3, 5, 10] # 移除并返回最小元素,同时添加新元素 new_min = heapq.heappushpop(heap, 0) print(new_min) # 输出: 1 print(heap) # 输出: [0, 3, 5, 10]
双端队列 Deque
常用方法
append(x):在右侧添加一个元素。appendleft(x):在左侧添加一个元素。pop():移除并返回右侧的一个元素。popleft():移除并返回左侧的一个元素。extend(iterable):在右侧添加多个元素。extendleft(iterable):在左侧添加多个元素(注意,这个操作是 O(n) 时间复杂度,因为元素需要被逐个插入)。rotate(n):向右旋转队列 n 步。如果 n 是负数,则向左旋转。clear():移除所有的元素。copy():返回一个包含所有元素的浅拷贝。count(x):返回某个值出现的次数。index(x):返回某个值在队列中的位置。
示例:
from collections import deque # 创建一个空的 deque d = deque() # 在右侧添加元素 d.append('a') d.append('b') # 在左侧添加元素 d.appendleft('c') d.appendleft('d') # 打印 deque print(d) # 输出: deque(['d', 'c', 'a', 'b']) # 从右侧和左侧移除元素 right_popped = d.pop() left_popped = d.popleft() print(f"Popped from right: {right_popped}") # 输出: Popped from right: b print(f"Popped from left: {left_popped}") # 输出: Popped from left: d # 打印 deque print(d) # 输出: deque(['c', 'a']) # 旋转 deque d.rotate(1) print(d) # 输出: deque(['a', 'c']) # 清空 deque d.clear() print(d) # 输出: deque([])
BFS&DFS模板
(1)bfs模板
from collections import deque def bfs(graph, start): visited = set() queue = deque([start]) while queue: vertex = queue.popleft() if vertex not in visited: print(vertex, end=' ') visited.add(vertex) queue.extend(set(graph[vertex]) - visited)
(2)dfs模板
递归最easy,注意参数个数
def dfs(graph, node, visited=None): if visited is None: visited = set() visited.add(node) print(node, end=' ') # 处理节点的逻辑,例如打印节点 for neighbour in graph[node]: if neighbour not in visited: dfs(graph, neighbour, visited)
迭代版本用栈后进先出,只有这里跟bfs有区别
def dfs(graph, start): visited = set() stack = [start] while stack: vertex = stack.pop() if vertex not in visited: print(vertex, end=' ') visited.add(vertex) stack.extend(set(graph[vertex]) - visited) #所有未访问节点入栈




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」