mycat 分片
1 配置下面两种ER分片,并结合日志分析子表插入过程中的不同
(1).父表按照主键ID分片,子表的分片字段与主表ID关联,配置为ER分片
(2).父表的分片字段为其他字段,子表的分片字段与主表ID关联,配置为ER分片
答:(1)第一种分片:父表按照主键ID分片
表设计:父表student,子表selectcourse
student(id,stu_id);
selectcourse(id,stu_id,cou_id);
在schema.xml中增加父表、子表定义:
<table name="student" primaryKey="ID" dataNode="dn1,dn2,dn3" rule="mod-long">
<childTable name="selectcourse" primaryKey="ID" joinKey="stu_id" parentKey="id" />
</table>
在mysql客户端中执行创建表的语句:
create table student(id bigint not null primary key,stu_id bigint not null);
create table selectcourse(id bigint not null primary key,stu_id bigint not null,cou_id bigint not null);
插入父表记录
insert into student(id,stu_id) values(1,3001);//
insert into student(id,stu_id) values(2,3002);
插入子表记录
insert into selectcourse(id,stu_id,cou_id) values(1,1,1); //同时观察日志
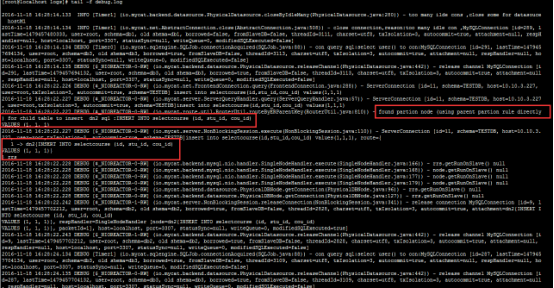
总结:直接使用父表的分片规则(id字段mod算法)来查找节点。
2)第二种分片:父表的分片字段为其他字段
表设计:父表book,子表sail
book(id,book_id);
sail(id,book_id,custo_id);
在rule.xml中增加“mod-long-book”分片方法:分片字段为book_id
<tableRule name="mod-long-book">
<rule>
<columns>book_id</columns>
<algorithm>mod-long</algorithm>
</rule>
</tableRule>
在schema.xml中增加父表、子表定义:父表用"mod-long-book"方法分片,
<table name="book" primaryKey="ID" dataNode="dn1,dn2,dn3" rule="mod-long-book">
<childTable name="sail" primaryKey="ID" joinKey="book_id" parentKey="id" />
</table>
在mysql客户端中执行创建表的语句:
create table book(id bigint not null primary key,book_id bigint not null);
create table sail(id bigint not null primary key,book_id bigint not null,customer_id bigint not null);
插入父表记录:
insert into book(id,book_id) values(1,3001);
insert into book(id,book_id) values(2,3002);
插入子表记录
insert into sail(id,book_id,customer_id) values(1,2,2001);//同时观察日志
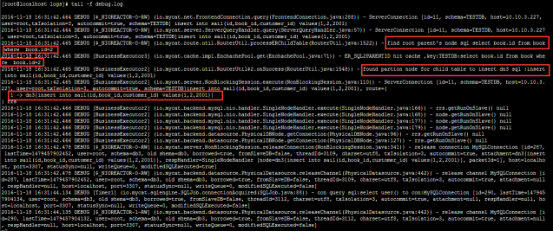
总结:先通过父表的id字段查询分片,再往相应的分片中插入数据。
比第一种方法多了一个“查找分片”的步骤。
2 选则连续分片规则中的2种,对配置和路由过程做完整的分析
(1)自定义数字范围分片:分片方法为“rang-long”
首先,在rule.xml中配置分片方法“price-rang-long”,算法为“rang-long”;

再在schema.xml中配置表信息,包括表名、主键、节点、分片方法等;

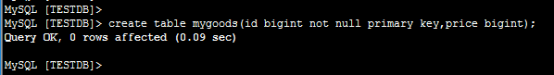
然后,在客户端执行创建表的命令(mygoods);
最后,往mygoods表中插入记录;

日志信息:
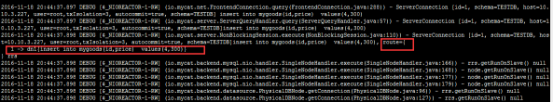
路由描述:
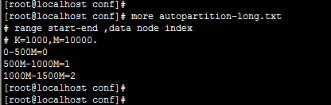
mygoods表依据rang-long算法进行分割,rang-long又依据autopartition-long.txt(如下图所示)文件中的值进行分片(制定数据节点dh),本题中的price为300,
属于0-500M的范围,所以本记录应该路由到第0个节点上(下标从0开始,第0个节点就是dn1)执行,正如上图中所示。
(2)自然月分片:分片方法为“partbymonth”
首先,在rule.xml中配置分片方法“sharding-by-month”,算法为“partbymonth”;
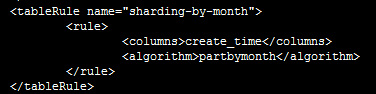
再在schema.xml中配置表信息,包括表名、主键、节点、分片方法等;

然后,在客户端执行创建表的命令(myrecords);

最后,往myrecords表中插入记录;
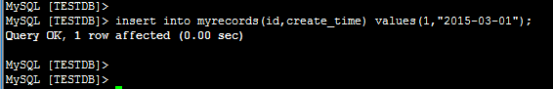
日志信息:
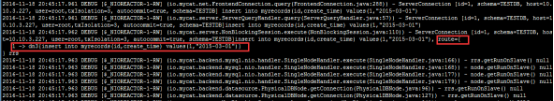
路由描述:
Myrecords表依据partbymonth算法进行分割,partbymonth的以自然月为依据,每个月一个分片,从2015-01-01开始(如下图所示:rule.xml中partbymonth分片方法),
即2015年1月份数据在第0节点,2015年2月份数据在第1节点,以此类推。本题中的create_time=”2015-03-01”对应的数据应该在第2个节点(下标从0开始,第2个节点
就是dn3)执行,所以,本记录路由到第2个节点上(dn3)执行,正如上图中所示。

3 选择离散分片规则的2种,对配置和路由过程做完整的分析
(1)十进制求模分片:分片方法为“mod-long”
首先,在rule.xml中配置分片方法;

再在schema.xml中配置表信息,包括表名、主键、节点、分片方法等;

然后,在客户端执行创建表的命令(student);
create table student(id bigint not null primary key,stu_id bigint not null);
最后,往student表中插入记录;
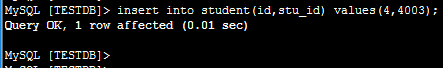
日志信息:
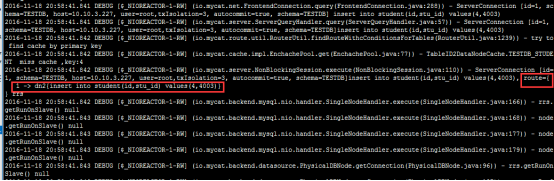
路由描述:
student表依据mod-log算法进行分割,本题中记录值为4除3的模为1,对应的数据应该在第1个节点(下标从0开始,第1个节点就是dn2)上;所以,本记录路由到第1个节点上(dn2)执行,正如上图中所示。
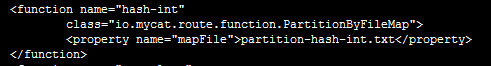
(2)哈希分片:分片方法为“hash-int”
首先,在rule.xml中配置分片方法;
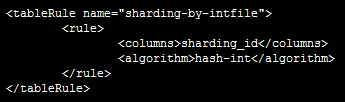
再在schema.xml中配置表信息,包括表名、主键、节点、分片方法等;

然后,在客户端执行创建表的命令(employee);
create table employee (id int not null primary key,name varchar(100),sharding_id int not null);
最后,往myrecords表中插入记录;

日志信息:
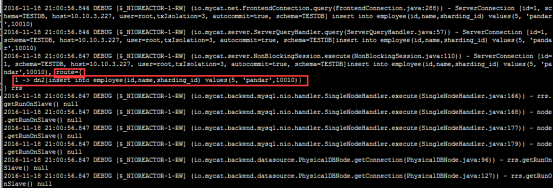
路由描述:
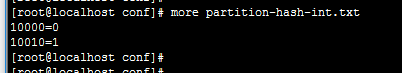
employee 表依据sharding-by-intfile算法进行分割,sharding-by-intfile算法又依据partition-hash-int.txt文件(如下图所示)中的范围进行分片,本题中记录值10010=1,
对应的数据应该在第1个节点(下标从0开始,第1个节点就是dn2)上;所以,本记录路由到第1个节点上(dn2)执行,正如上图中所示。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构