Oracle 索引
b*tree索引
位图索引
函数索引
关于索引的常见问题
全文索引
1 b*tree索引
B*tree索引树最底层的块称为叶子节点或叶子块(包括各个索引键以及一个rowid),叶子节点之上的称为分支块,比如知道叶子节点从哪里开始,然后执行值有序扫描称为index range scan
B*tree索引中存在非唯一索引的条目,在这些非唯一条目中,oracle会把rowid作为一个额外的列追加到键上,使得键唯一,比如crate index idx_x on table table_x(x,y),从概念上讲,它
就是create unique index idx_x on table_x(x,y,rowid),在一个唯一索引中,根据键的唯一性,oracle不会向索引键中追加rowid,索引只按索引键值排序
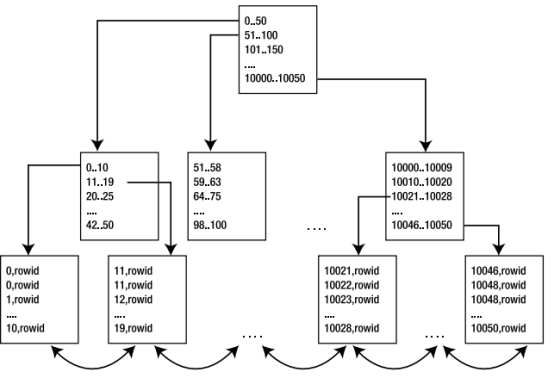
B*tree索引的特点是所有的叶子节点都在同一层上,这一层也称为高度,说明从索引的根块到叶子块的遍历都需要访问同样数目的块,换句话说索引是高度平衡的,
大多数b*tree的高度都是2或3,一般来讲,在索引中找到一个键需要执行2次到3次的io,
Note:从根块到叶子块遍历所需要的块数,用analyze index<name> validate structure,这样可以从index_stats得到hight,收集统计信息后在user_indexes中有个blevel,这是分支层数,与hight相差1,
ANALYZE INDEX IDX_T1 VALIDATE STRUCTURE
select * from index_stats where name='IDX_T1'
select index_name,blevel,num_rows from user_indexes where table_name='T1'
Statistics
---------------------------------------------------
0 recursive calls
0 db block gets
3 consistent gets---IO
0 physical reads
0 redo size
1.1 索引压缩
对于b*tree索引,可以进修压缩,指串联多列索引去除冗余,
ANALYZE INDEX IDX_T1 VALIDATE STRUCTURE
1.2 反向键索引
能够将索引键反转,反向键是一种减少竞争的方法,
1.3 什么情况下使用b*tree索引
1 仅当需要通过索引访问表中很少的一部分行时,才能用b*tree在该列上建立索引
2 如果要处理表中的多行,而且可以使用index而不用表,就可以使用b*tree索引
SQL> select count(*) from t1;
COUNT(*)
----------
49847
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 2101382132
------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 27 (4)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | SORT AGGREGATE | | 1 | | |
| 2 | INDEX FAST FULL SCAN| IDX_T1 | 49847 | 27 (4)| 00:00:01 |
------------------------------------------------------------------------
SQL> select count(*) from t1 where id=6;
COUNT(*)
----------
1
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 1970818898
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 5 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | SORT AGGREGATE | | 1 | 5 | | |
|* 2 | INDEX RANGE SCAN| IDX_T1 | 1 | 5 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
索引按索引键的顺序存储,索引会按键的有序顺序的访问,
如果行大小为80字节,在一个块大小为8k的数据库中,每个块上大约有100行数据,
2 位图索引
位图索引并不适合用于oltp,如果系统中的数据会由多个并发会话频繁的更新,也不适合用位图索引
什么情况下使用位图索引
对于(ˇˍˇ) 相异基数很低的情况下,
3 基于函数的索引
将函数运算的结果存入在列中
能够对计算得出的列建立索引
要让优化器使用基于函数的索引,必须设置一下会话或系统变量
QUERY_REWRITE_ENABLED=TRUE,QUERY_REWRITE_INTEGRITY=TRUSTED
可以在会话级用alter session来完成,也可以alter system来设置,也可也在init.ora文件中设置
Example
create index idx_emp on emp(lower(ename))
execute dbms_stats.gather_table_stats(USER,'EMP',cascade=>true);
SQL> select * from emp where lower(ename)='king';
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
--------------------------------------------------
2 - access(LOWER("ENAME")='king')
Statistics
--------------------------------------------------------
0 recursive calls
0 db block gets
3 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
使用函数索引,在dml上速度可能会慢,但在select时会很快,找个平衡点。
4 只对部分行建立索引
Create index I on t(a,b)
如果a,b两列都为null,则在b*tree中不会存在。
如果1列不为null,则会存储那列不为null的列。可以使用函数来控制
Create index I on t (decode(a,‘x’,’y‘)) 这样a列就会只有列值为x的索引值,人为的控制该列的另外一个值为空,减少不必要的。
也可以使用case a when ‘x’then‘y’end,可以使用改进的函数索引,添加一个伪列
t(object_id,0)是一个特殊的函数索引,使用object_id作为前导列,它有明显的优点,可以不管object_id的值,也不用改SQL,这比较好,因为加入的0是1个字节,也不会很大。
4 关与index的常见问题
4.1 视图能使用索引么
视图实际上就是一个查询,在视图上建立索引就是在基表建立索引
4.2 null和索引能协作么
B*tree索引中不会存储完全为null的条目,
Create index I on t (a,b)
像 select * from emp where empno is null;不能使用索引一样
create table t_null (x number,y number not null)
create unique index idx_t_null on t_null(x,y)
insert into t_null values(null,1)
execute dbms_stats.gather_table_stats(USER,'T_NULL');
SQL> select * from t_null where x is null;
X Y
---------- ----------
1
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 2028527423
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 5 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 1 | INDEX RANGE SCAN| IDX_T_NULL | 1 | 5 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
1 - access("X" IS NULL)
4.3 外键是否应该加索引
外键一般都需要加索引,除非 为删除父表中的行,不会从父表连接到字表
4.4 为什么没使用我们的索引
4.4.1 复合列
假设有个索引t(x,y),这时查询是select * from t where y=5
create index idx_xy on T_TABLE(id,name)
execute dbms_stats.gather_table_stats(USER,'T_TABLE');
SQL> select * from T_TABLE where name='yhq';
ID NAME
---------- --------------------
1 yhq
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 3151666041
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 7 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 1 | INDEX FAST FULL SCAN| IDX_XY | 1 | 7 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
1 - filter("NAME"='yhq')
SQL> select * from t_table where id=1;
ID NAME
---------- --------------------
1 yhq
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 955686434
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 7 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 1 | INDEX RANGE SCAN| IDX_XY | 1 | 7 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
1 - access("ID"=1)
4.4.2 select count(*) from table
类似select count(*) from table的查询,在表上有个b*tree索引,但是优化器并不是统计索引的条目,而是全扫描表,因为index上不存储为null的列,
4.4.3 where f(name)=value
在where谓词中的左列使用了函数,或者发生了隐式转换
select * from t where f(indexed_column) = value
4.4.4 发生了隐式转换
select * from t where indexed_column = 5
-- select * from t where to_number(indexed_column) = 5
select * from t where trunc(date_col) = trunc(sysdate);
TRUNC(DATE_COL) = TRUNC(SYSDATE) 转换成
where date_col >= trunc(sysdate)
and date_col < trunc(sysdate+1)
尽量不要对数据库列使用函数(左列保持纯净),不要函数,不要数学运算,不要表达式
4.4.5 有时候查询大量数据使用index会很慢
select count(y) from t where x < 15000;
这时候使用index就不会很明智,优化器会权衡在index跟全表扫描,或者其他
SQL> select count(id) from t1 where id<15;
COUNT(ID)
----------
13
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 1970818898
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 5 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | SORT AGGREGATE | | 1 | 5 | | |
|* 2 | INDEX RANGE SCAN| IDX_T1 | 3 | 15 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 |
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
2 - access("ID"<15)
Statistics
-----------------------------------------------------
1 recursive calls
0 db block gets
2 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
414 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
385 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
2 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
1 rows processed
SQL> select count(text) from t1 where id<50000;
COUNT(TEXT)
-----------
48099
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 2101382132
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 5 | 28 (8)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | SORT AGGREGATE | | 1 | 5 | | |
|* 2 | INDEX FAST FULL SCAN| IDX_T1 | 46882 | 228K| 28 (8)| 00:00:01 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
2 - filter("ID"<50000)
Statistics
----------------------------------------------------------
1 recursive calls
0 db block gets
117 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
416 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
385 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
2 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
1 rows processed
4.4.6 有段时间没有分析表
由于长时间没有收集表的相关统计信息,这是cbo就无法作出正确的决定
execute dbms_stats.gather_table_stats(USER,'T_TABLE');
4.4.7 谓词使用<>,!=
谓词使用<>,!=,目前的优化器认为不等于的选择性不好,会找到很多行,所以用不上索引,用了也是全部扫描索引,走不了range index scan,
1)如果不等条件之外的值不多,而且是确认的,可以改为等值或IN查询,比如status状态字段一般值类别很少
2)如果不等条件之外的值很多,可以改为> OR <的形式,当然第2种方法包含了方法1.
SQL> set autotrace traceonly
SQL> select * from emp where empno<>7369;
13 rows selected.
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 3956160932
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 13 | 507 | 3 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 1 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| EMP | 13 | 507 | 3 (0)| 00:00:01 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
1 - filter("EMPNO"<>7369)
SELECT /*+ INDEX(T IDX_EMP)*/ * FROM EMP WHERE ENAME<>'SMITH'-- TABLE ACCESS FULL
SQL> select * from emp where empno>7369 or empno<7369;
13 rows selected.
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 3956160932
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 13 | 507 | 3 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 1 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| EMP | 13 | 507 | 3 (0)| 00:00:01 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
1 - filter("EMPNO">7369 OR "EMPNO"<7369)
SQL> set long 5000
SQL> set linesize 100
SQL> set pagesize 9999
SQL> select * from emp where empno=7369
2 ;
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 2949544139
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 39 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| EMP | 1 | 39 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 2 | INDEX UNIQUE SCAN | PK_EMP | 1 | | 0 (0)| 00:00:01 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
2 - access("EMPNO"=7369)
SQL> SELECT/*+ INDEX(T IDX_EMP)*/ * FROM EMP T WHERE T.ENAME>'SMITH' OR T.ENAME<'SMITH';
13 rows selected.
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 4271840806
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 12 | 444 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| EMP | 12 | 444 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 2 | INDEX FULL SCAN | IDX_EMP | 12 | | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
4.4.7 like前通配查询,like全通配查询不走index
1 是否可以通过业务把前通配去掉
SQL> select * from emp where ename like'%SMITH%';
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 3956160932
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 37 | 3 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 1 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| EMP | 1 | 37 | 3 (0)| 00:00:01 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
1 - filter("ENAME" LIKE '%SMITH%')
去掉前面%
SQL> select * from emp where ename like'SMITH%';
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 306890541
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 37 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| EMP | 1 | 37 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 2 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | IDX_EMP | 1 | | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
2 - access("ENAME" LIKE 'SMITH%')
filter("ENAME" LIKE 'SMITH%')
2 可以使用函数instr,substr等函数来实现,否则对于全通配的最好办法就是全文索引
create index idx_emp_fun on emp(instr(ename,'SMITH'))
SQL> select * from emp where instr(ename,'SMITH')>0;
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 1056881344
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 37 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| EMP | 1 | 37 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 2 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | IDX_EMP_FUN | 1 | | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
2 - access(INSTR("ENAME",'SMITH')>0)
3 如果只是前通配符,可以通过reverse函数(不是反转索引)
select * from emp where ename like'%SMITH'
create index idx_emp_reverse on emp(reverse(ename))
SQL> select * from emp where reverse(ename) like'SMITH%';
no rows selected
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 187710050
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 37 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01
| 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| EMP | 1 | 37 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01
|* 2 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | IDX_EMP_REVERSE | 1 | | 1 (0)| 00:00:01
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
2 - access(REVERSE("ENAME") LIKE 'SMITH%')
filter(REVERSE("ENAME") LIKE 'SMITH%')
note:注意如果是中文,不能直接写REVERSE("ENAME") LIKE 'SMITH%',REVERSE内部按字节反转,
WHERE REVERSE(t.name) LIKE REVERSE('数据')||'%';否则查询出的数据不对
SQL> select * from emp where reverse(ename) like reverse('SMITH')||'%';
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 187710050
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 39 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01
| 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| EMP | 1 | 39 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01
|* 2 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | IDX_EMP_REVERSE | 1 | | 1 (0)| 00:00:01
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
2 - access(REVERSE("ENAME") LIKE 'HTIMS%')
filter(REVERSE("ENAME") LIKE 'HTIMS%')
当然,对于两个都是范围的查询,这里只能通过一个列来轮询索引,先做access,再做filter。SQL语句的逻辑改写很重要,往往通过逻辑改写就能改变SQL的执行计划,
从不好的计划到好的计划,比如semi join,anti join与or,往往走FILTER导致执行计划较差,这时候就需要通过逻辑等价改写,逻辑等价改写往往需要掌握一些集合的知识,
比如NOT (A AND B)===NOT A OR NOT B,NOT (A OR B)===NOT A AND NOT B等。
5 oracle全文索引
5.1设置词法分析器
Oracle实现全文检索,其机制其实很简单。即通过Oracle专利的词法分析器(lexer),将文章中所有的表意单元(Oracle称为term)找出来,记录在一组以dr$开头的表中,同时记下该term出现的位置、
次数、hash值等信息。检索时,Oracle从这组表中查找相应的term,并计算其出现频率,根据某个算法来计算每个文档的得分(score),即所谓的‘匹配率’。而lexer则是该机制的核心,它决定了全
文检索的效率。Oracle针对不同的语言提供了不同的lexer,而我们通常能用到其中的三个:
basic_lexer:针对英语。它能根据空格和标点来将英语单词从句子中分离,还能自动将一些出现频率过高已经失去检索意义的单词作为‘垃圾’处理,如if , is等,具有较高的处理效率。但该lexer应用
于汉语则有很多问题,由于它只认空格和标点,而汉语的一句话中通常不会有空格,因此,它会把整句话作为一个term,事实上失去检索能力。以‘中国人民站起来了’这句话为例,basic_lexer分析的结
果只有一个term ,就是‘中国人民站起来了’。此时若检索‘中国’,将检索不到内容。
chinese_vgram_lexer:专门的汉语分析器,支持所有汉字字符集(ZHS16CGB231280ZHS16GBKZHT32EUCZHT16BIG5ZHT32TRISZHT16MSWIN950ZHT16HKSCSUTF8)。该分析器按字为单
元来分析汉语句子。‘中国人民站起来了’这句话,会被它分析成如下几个term: ‘中’,‘中国’,‘国人’,‘人民’,‘民站’,‘站起’,起来’,‘来了’,‘了’。可以看出,这种分析方法,实现算法很简单,并且能实
现‘一网打尽’,但效率则是差强人意。
chinese_lexer:这是一个新的汉语分析器,只支持utf8字符集。上面已经看到,chinese vgram lexer这个分析器由于不认识常用的汉语词汇,因此分析的单元非常机械,像上面的‘民站’,‘站起’在汉语
中根本不会单独出现,因此这种term是没有意义的,反而影响效率。chinese_lexer的最大改进就是该分析器能认识大部分常用汉语词汇,因此能更有效率地分析句子,像以上两个愚蠢的单元将不会再
出现,极大提高了效率。但是它只支持utf8,如果你的数据库是zhs16gbk字符集,则只能使用笨笨的那个Chinese vgram lexer.
如果不做任何设置,Oracle缺省使用basic_lexer这个分析器。要指定使用哪一个lexer,可以这样操作:
BEGIN
ctx_ddl.create_preference ('my_lexer', 'chinese_vgram_lexer');
END;
BEGIN
ctx_ddl.create_preference ('my_lexer', 'chinese_vgram_lexer');
END;
其中my_lexer是分析器名。
5.2 建立全文索引
1,首先查看ORACLE是否已安装“全文检索工具”
通过查看是否存在 CTXSYS 用户,CTXAPP角色即可判断
select username from dba_users;
USERNAME
------------------------------
CTXSYS 默认是没有的,需要安装2个脚本catctx.sql,drdefus.sql
2,如果ORACLE没有安装“全文检索工具”,则使用以下步骤手工安装。
a)进入ORACLE安装目录
cd $ORACLE_HOME
b)使用 DBA 角色登陆数据库
sqlplus sys/sys as sysdba
c)查看表空间文件存放路径
select name from v$datafile;
d)为 CTXSYS 用户创建表空间
CREATE TABLESPACE ctxsys
LOGGING
DATAFILE '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/LEO/file1/ctxsys01.dbf'
SIZE 32m
AUTOEXTEND ON
NEXT 32m MAXSIZE 2048m
EXTENT MANAGEMENT LOCAL ;
e)创建 CTXSYS 用户,创建 CTXAPP 角色
@?/ctx/admin/catctx.sql ctxsys ctxsys temp1 nolock
--(密码、表空间、临时表空间、用户状态)
--如果当前sql脚本无执行权限,请手工添加。
f)为 CTXSYS 执行初始化工作,如果没有此操作,后续操作会失败。
connect ctxsys/ctxsys;
@?/ctx/admin/defaults/drdefus.sql
在建立intermedia索引时,指明所用的lexer:
CREATE INDEX myindex ON mytable(mycolumn) indextype is ctxsys.context parameters('lexer my_lexer');
CREATE INDEX my_index ON emp(ename) indextype is ctxsys.context parameters('lexer my_lexer');
Toad中能看见全文索引
而本人在删除全文索引时遇到过一下报错:
SQL> drop index searchkeytbl_key;
drop index searchkeytbl_key
ORA-29868: cannot issue DDL on a domain index marked as LOADING
解决方法:
ORA-29868: cannot issue DDL on a domain index marked as LOADING
说明:在创建索引的时候断开、重启等导致索引中断没有执行成功,之后再drop或者rebuild等操作的时候都会报此错误
解决:只能drop index ind_name force强行删除,然后再重建
sort_area_size和sort_area_retained_size 2个参数
5.3 全文索引的使用
select * from emp where contains (ename,'SCOTT') >0;
SQL> select * from emp where contains (ename,'SCOTT') >0;
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 1887222286
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 43 | 4 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| EMP | 1 | 43 | 4 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 2 | DOMAIN INDEX | MY_INDEX | | | 4 (0)| 00:00:01 |
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
2 - access("CTXSYS"."CONTAINS"("ENAME",'SCOTT')>0)
SQL> select * from emp where empno=7788 and contains (ename,'SCOTT') >0;
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 2949544139
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 43 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| EMP | 1 | 43 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 2 | INDEX UNIQUE SCAN | PK_EMP | 1 | | 0 (0)| 00:00:01 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
1 - filter("CTXSYS"."CONTAINS"("ENAME",'SCOTT')>0)
2 - access("EMPNO"=7788)
5.4 索引的同步维护
用以下的两个job来完成(该job要建在和表同一个用户下) :
VARIABLE jobno number;
BEGIN
DBMS_JOB.SUBMIT(:jobno,'ctx_ddl.sync_index(''index_name'');',
SYSDATE, 'SYSDATE + (1/24/4)');
commit;
END; //同步
VARIABLE jobno number;
BEGIN
DBMS_JOB.SUBMIT(:jobno,'ctx_ddl.optimize_index(''myindex'',''FULL'');',
SYSDATE, 'SYSDATE + 1');
commit; //优化
建完后手动运行下:
exec dbms_job.run(jobno);
※个人体会:运行job可能会有问题,此时可以单独运行索引,尝试一下
exec ctx_ddl.sync_index('index_name');
如果单独运行没有问题,则检查job是否写错或者当前操作的oracle数据库用户有无运行存储过程的权限
SQL> exec dbms_job.run(190);
begin dbms_job.run(190); end;
ORA-12011: execution of 1 jobs failed
ORA-06512: at "SYS.DBMS_IJOB", line 406
ORA-06512: at "SYS.DBMS_JOB", line 272
ORA-06512: at line 1
以上报错就是用户没有运行任何存储过程造成的,此时需要对用户加上这个权限:
SQL> grant execute any procedure to oracle_username;
再看一下job的情况
select * from user_jobs;
5.5 问题
加全文索引遇到的问题(不断更新)
SQL> create index gh_ghname_idx on gh(ghname) indextype is ctxsys.context parameters('lexer gh_ghname_lexer');
create index gh_ghname_idx on gh(ghname) indextype is ctxsys.context parameters('lexer gh_ghname_lexer')
ORA-24795: Illegal COMMIT attempt made
ORA-29855: error occurred in the execution of ODCIINDEXCREATE routine
ORA-20000: Oracle Text error:
DRG-50857: oracle error in drvddl.IndexCreate
ORA-20000: Oracle Text error:
DRG-50857: oracle error in drvdml.MaintainKTab
ORA-24795: Illegal COMMIT attempt made
ORA-06512: at "CTXSYS.DRUE", line 160
ORA-06512: at "CTXSYS.TEXTINDEXMETHODS", line 364
To avoid the error, please use one of the following solutions
1. Don't use a 32k-blocksized tablespace to store the internal index objects
- or -
2. Download Patch 5596325 from Metalink and apply it as described in the README file.
看一下 可能是用于创建索引的表空间不够了
reports——>DBA——>total free space pl/sql developer工具,查看表空间的剩余空间
select * from v$datafile; 查看数据文件信息
5.6 小结
从如上实验来看,当我们检索大量文字的时候使用全文索引要比全表扫描快很多了,有弊就有利,由于全文索引会占用大量空间提前预估全文索引大小保留出足够的空间,
context类型全文索引不是基于事务的,无法保证索引和数据实时同步,DML完成后,如果在全文索引中查不到键值时,可以通过手工or定时任务来刷新同步,而B-tree、位图都是实时的。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构