【读书笔记】组合计数中的行列式方法
看不懂啦停止更新啦
由于过长分成了若干部分。下面的四个专题链接导向我的博客园随笔
upd 2020-07-22 最后一部分加上去了,越写越烂,,,,
upd 2020-07-21 23:00 增加了Routings: the Lindstrm–Gessel–Viennot lemma章节,写到了这一节的Example3
upd 2020-07-14 17:36 增加了完美匹配的部分,已经快看不懂了😭
upd 2020-07-14 增加了欧拉路径和BEST theorem 章节
做笔记,不然学了忘
流水账警告❗
- 预备知识
- 一些结论
- 应用
- 专题1-生成树
- 专题2-欧拉回路,the BEST theorem
- 专题3-Perfect matchings: the Pfaffian method
- 专题4-Routings: the Lindstrm–Gessel–Viennot lemma
- 一些定义
- the Lindstrm–Gessel–Viennot lemma
- Lindstrm–Gessel–Viennot lemma 应用
- 计算行列式
- 附录
把计数问题转化为计算矩阵行列式
预备知识
adjacency matrix 中文是邻接矩阵
有向图 The adjacency matrix \(A = A(G)\) is the\(V×V\) matrix whose entries are
\(a_{uv}\)= number of edges from u to v.
无向图 The (undirected) adjacency matrix \(A = A(G)\) is the \(V ×V\) matrix whose entries are
\(a_{uv}\) = number of edges connecting u and v.
一些结论
不解释,邻接矩阵定义和矩阵乘法定义
算矩阵幂\(A^n\) ,如果\(A\)可对角化是容易计算的
嗯其实也有办法,我找到了《矩阵分析与应用》(第2版)7.3.3矩阵幂的计算,我放在末尾附录了
第一个等号是等比数列的求和,第二个等号是克拉姆法则
不解释
\(x\)我楞了一下,应该是\(1×1\)的
\(det(A-xI)=(x-\lambda_1)...(x-\lambda_k)\)
证明那里\(Q(x)=(1-\lambda_1x)...(1-\lambda_kx)\)我楞了一下,你把A对角形式带进去就比较容易理解了
\(u,v\)和\(i,j\)记号混用,意思是那么个意思
联系了前面的Corollary 1.4.2
应用
Example1 项链染色
\(n\)个珠子围成一圈,给你\(k\)种颜色来染色,要求相邻颜色不同,求方案数目\(f(n,k)\)。(旋转和翻转视为不同的方案)
把\(k\)种颜色想成\(k\)个节点,完全图\(K_k\) ,邻接矩阵是\(A=J-I\) ,\(J\)是全1矩阵
\(A\)的\(k\)个特征值是\(-1,--1,...,-1,k-1\)
答案就是此图中长度为\(n\)的closed walk的数目
利用前面的Corollary 1.4.3
答案是\((k-1)^n+(k-1)(-1)^n\)
Example2 Words with forbidden subwords,1
给定一长\(n\)的字符串,只由{a,b}组成,且不会有子串aa(子串是连续的)。问你方案数目\(f_n\)。
说实话这个递推方程都能直接写,\(f_n=f_{n-1}+f_{n-2},f_{1}=2,f_{2}=3\)
建图就是节点a和节点b,边a→b,b→a,b→b
\(f_n\)是\(A^{n-1}\)的元素和,是Fibonacci[n+2]
Example3 Words with forbidden subwords,2
给定一长\(n\)的cyclic word,只由{a,b}组成,且不会有子串aa,abba(子串是连续的)。问你方案数目\(g_n\)。
不会,吃了没文化的亏,看不懂cyclic word是啥
我认为是好比babbb,然后它就是你的重复单元
。。。babbb|babbb|babbb|babbb。。。里找子串
这样就解释通了
Example4 Monomer-dimer problem
给你1×1和1×2的砖都是无数个,问你无重叠填充\(m×n\)大矩形的方案数目
这里介绍简单的情形,\(m=3,n=5\)
强制加上顺序,一列一列的铺,共有6条竖线
每次从上往下数,突出计0,不突出计1
一种方案的图解如下,
111--110-->011-->101-->010-->111.
这正好对应图\(G\)从111到111的长为\(5\)路径
要求的答案就是111到111的长度为6的路径数
图\(G\)到底长什么样呢?规律不是很明显
比如:
000到000肯定是0条边,
111到111有3种铺法(2+1,1+2,1+1+1),111到111有3条边
101到111有1条
110到111有2条(1+1,2)
图G长这样
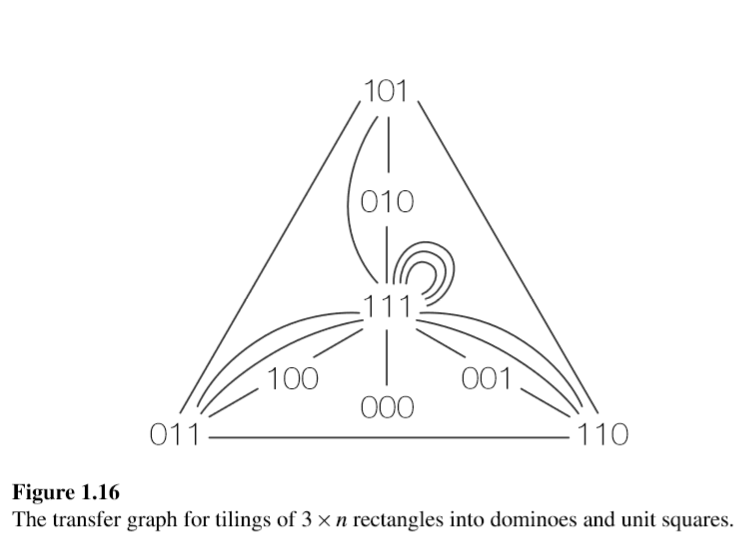
接着图的邻接矩阵写出来就可以上手算啦
专题1-生成树
这里研究的第一个问题就是图的生成树计数问题 (节点带序,1-2-3和1-3-2不同)
记号说明
A principal cofactor \(L_v(G)\) is obtained from \(L(G)\) by removing the \(v\)th row and \(v\)th column for some vertex v.
基尔霍夫矩阵树定理
证明我看不懂
矩阵树定理的应用-一些典型图的生成树数目
给一个完全图的生成树数目的证明:
塔特有向矩阵树定理
有向矩阵树定理证明
专题2-欧拉回路,the BEST theorem
一些定义
- An Eulerian path is a path in the graph that visits every edge exactly once.
- If the path starts and ends at the same vertex,then it is called an Eulerian cycle.
- We say \(G\) is an Eulerian graph if it has an Eulerian cycle.
一个有向图是欧拉的充要条件
Theorem 1.4.8 A directed graph is Eulerian if and only if it is connected and every vertex \(v\) satisfies \(indeg(v) = outdeg(v)\).
定理1.4.8 一个有向图而言,它是欧拉的当且仅当对所有节点出度等于入度。
BEST定理
BSET定理推论
在欧拉有向图中,每个节点的有向生成树数目都是相等的。
k-ary de Bruijn sequence定义
A k-ary de Bruijn sequence of order n
定义为一个cyclic word,长度是\(k^n\),用的字母表是{0,1,...,k-1},
它的每一个subword正好遍历【长度为\(n\),用字母表为{0,1,...,k-1}组成的\(k^n\)个序列】(每个出现一次)
举个例子,我从维基百科截的图:
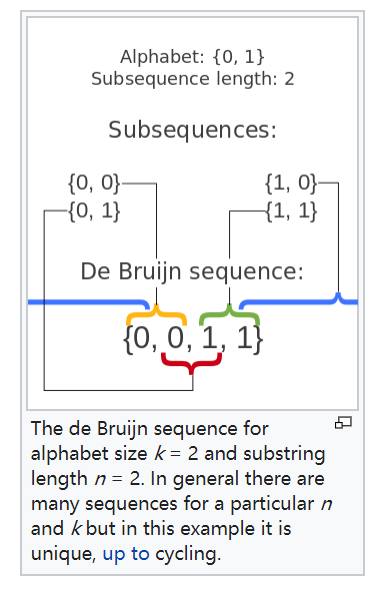
BSET theorem在k-ary de Bruijn sequences of order n计数 中的应用
建图呗。下面这也是维基截的图。
比如你想求解2-ary de Bruijn sequences of order 3的数目,每个节点的序列长度是3,
数哈密顿路径。(收集的序列就是点上的序列)
或者,你想求解2-ary de Bruijn sequences of order 4的数目,每个节点的序列长度是3,
数欧拉环。 (收集的序列就是【边和边的发出点】构成的序列)
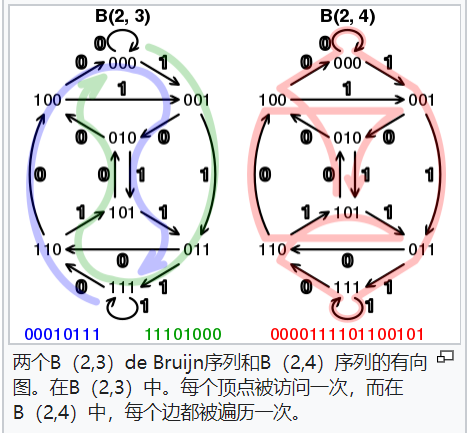
下面定理证明中用到的是把长度为n-1的序列作为点,找到欧拉环。
彩蛋-超排列
“我对普通的人类没有兴趣,你们只要能求出超排列的准确公式,就尽管来找我吧!以上”
专题3-Perfect matchings: the Pfaffian method
一些定义
-
一个图\(G\)的完美匹配\(M\)是说一系列边,使得\(G\)的每一个点都在且仅在\(M\)的一条边上。或者你从字面理解:\(2m\)个点正好分成\(m\)组,每组2个,...
-
skew-symmetric matrix \(A^T=-A\) (就是说关于主对角线对称的元素是相反数,\(a_{ij}=-a_{ji}\))
-
Pfaffian的定义。emm这里书讲得不清楚,直接截图维基。
Pfaffian是对满足\(A^T=-A\)的矩阵\(A\)定义的。
-
定理 \(det(A)=\operatorname{Pfaffian}(A)^2\) 证明看不懂
-
有向图的邻接矩阵 当然有\([S(G)]^{T}=-S(G)\) \(s_{i j}= \begin{cases}1 & \text { if } i \rightarrow j \text { is an edge of } G \\ -1 & \text { if } j \rightarrow i \text { is an edge of } G \\ 0 & \text { otherwise. }\end{cases}\)
用2×1的砖密铺a×b的大矩形的方法数
假设了\(b\)是偶数是因为:都是奇数肯定密铺不了
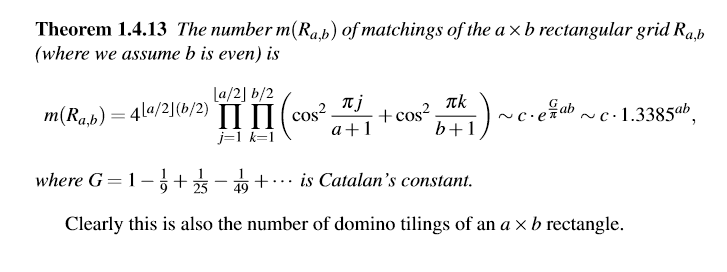
这里不写了 ┏(゜ロ゜;)┛
专题4-Routings: the Lindstrm–Gessel–Viennot lemma
一些定义
- DAG 有向无环图
- \(\mathrm{wt}(e)\) 边的权重
- \(\mathrm{wt}(P)=\prod \mathrm {wt}(e)\) 路径的权重
- \(\mathrm{wt}(R)=\prod _{i=1}^n \mathrm {wt}(P)\) routing的权重
- 源,汇 Let S ={s1,...,sn} and T ={t1,...,tn} be two (not necessarily disjoint) sets of vertices,which we call sources and sinks,respectively
- Routing定义 A routing from S to T is a set of paths P1,..., Pn from the n sources s1,...,sn to the n sinks t1,...,tn such that no two paths share a vertex.
- Let π be the permutation of [n] such that \(P_i\) starts at source \(s_i\) and ends at sink \(t_{π(i)}\), and define sign(R) = sign(π).
- path matrix Q定义 \(q_{ij}=\sum\limits_{P\ path from\ s_i to\ t_j }\mathrm{wt}(P)\) 考虑Q的元素时只是看\(s_i\)到\(t_j\)的所有路径
原文如下
the Lindstrm–Gessel–Viennot lemma
维基百科词条-Lindstrm–Gessel–Viennot lemma
式子右边的求和是对\(S\)到\(T\)的所有routings
【In particular】那里是说,
如果正好图还有这样的性质:每条边权都是1,而且\(S\)到\(T\)的所有routing都是1->1,2->2...这样的形式,那么\(\operatorname{det}\ Q=\text{number of routings from S to T}\)
Lindstrm–Gessel–Viennot lemma 应用
Example1 Binomial determinants
\(\begin{gathered}
\begin{pmatrix} a_1,...,a_n \\ b_1,...,b_n \end{pmatrix}
\end{gathered}\)记号表示的是那个行列式
...开始我还看不懂为什么there are \(\begin{gathered} \begin{pmatrix} a_i \\ b_j \end{pmatrix} \end{gathered}\) SE paths from \(A_i\) to \(B_j\)
SE path 是说south 和 east ,我以为是往东往北了
since every SE routing from A to B takes Ai to Bi for all i, 这是因为0≤a1 <···<an and 0≤b1 <···<bn ; points A ={A1,...,An} and B ={B1,...,Bn} where Ai = (0,ai) and Bi = (bi,bi) for1≤i≤n 然后你还要要走SE path
Example2 Counting permutations by descent set
先定义一个n排列的decent set是说一个集合\(S\),集合\(S\)的元素是index i使得\(\pi_i>\pi_{i+1}\)
然后问你 number of permutations of [n] with descent set\(\{c_1,...,c_k\}\)
可以构造一个A到B的SE routings构成bijeciton,答案是\(\begin{gathered} \begin{pmatrix} c_1,...c_k,n \\ 0,c_1,...,c_k \end{pmatrix} \end{gathered}\)(前面的行列式记号)
Example3 Rhombus tilings and plane partitions
让你用【1,1,1,1 60° 120°】的菱形密铺边长为\(n\)的正六边形(需要按照网格线摆放)。问你方案数\(R_n\)
有几种观点:
-
看成正视图,如此,容易看到3种【\(60^°120^°\)的菱形】每种都是\(n^2\)个
-
思路是把每个菱形都看成是两个正三角形拼接,每个正三角形的中心作为一个节点,一般而言(内部的)每个节点和最近的3个节点相连。构成hexagonal grid。
相邻两个节点相连如果两个等边三角形上面正好是覆盖所用的菱形。问题转变为求完美匹配。 -
plane partition理解。从观点1的角度往前一步,给出【表明每个格子上垒有多少个cube】的俯视图。 an array of nonnegative integers(finitely many of which are non-zero)that is weakly decreasing in each row and column. We conclude that \(R_n\) is also the number of plane partitions whose non-zero entries are at most n, and fit inside an n×n square.
-
从观点1的角度出发,看高度\(n-0.5\),...,高度2.5,高度1.5,高度0.5,截cube stack的曲线。这对应于 n sources S1,...,Sn on the left to the sinks T1,...,Tn ,(S1到T1,S2到T2....)的routing。利用前面的Lindstrm–Gessel–Viennot lemma,矩阵元素\(\begin{gathered} \begin{pmatrix} 2n \\ n+i-j \end{pmatrix} \end{gathered}\)
\[R_n=det\bigg[\begin{gathered} \begin{pmatrix} 2n \\ n+i-j \end{pmatrix}\bigg] \end{gathered}_{1\leq i,j\leq n}=\prod\limits_{i,j,k=1}^{n}\frac{i+j+k-1}{i+j+k-2} \]
Example4 Catalan determinants, multitriangulations, and Pfaffian rings
定义一个序列\(A=(a_0,a_1,a_2,...)\)的Hankel矩阵\(H_n(A)\)和\(H_n'(A)\)
和
如果我们知道 the Hankel determinants \(det \ H_n(A)\) and \(det\ H_n'(A)\) ,而且对所有的n它们都是非零的,我们可以利用递推关系从 \(a_0,…, a_{k-1}\)来恢复每一个 \(a_k\) 。
如果序列是卡特兰序列\(C=(C_0,C_1,C_2,...)\)的话,恰好有一种很好的解释。
式(1.9)是许多事物的组合计数。
the number of k-fans of Dyck paths of length \(2(n−2k)\)
式(1.9)也是the number of k-fans of Dyck paths of length \(2(n-2k)\)
the number of k triangulations of an n-gon
k-crossing 定义 a k-crossing in an n-gon to be a set of k diagonals that cross pairwise(两两相交)
k-triangulation定义 A k-triangulation is a maximal set of diagonals with no(k+1)-crossings.
式(1.9)也是 the number of k triangulations of an n-gon 。
Example5 Schr¨oder determinants and Aztec diamonds
计算行列式
这里方法太多了哈,方法不要太多
Of course, when we wish to evaluate a new determinant, one first step is to check whether it is a special case of some known determinantal evaluation
确实确实,能找到现成的或者是现成的特例情形绝不自己动手
附录
利用Cayley-Hamilton定理变形一下,
先求特征值,再解\(n\)个线性方程构成的方程组
算法和例子如下,如果矩阵阶数\(n\)也很大的话就。。。。

书用的是Handbook of enumerative combinatorics
资料来自网络



