编译原理实验之SLR1文法分析
这是一份编译原理实验报告,分析表是手动造的,可以作为借鉴。
基于 SLR(1) 分析法的语法制导翻译及中间代码生成程序设计原理与实现
1 、理论传授
语法制导的基本概念,目标代码结构分析的基本方法,赋值语句语法制导生成四元式的基本原理和方法,该过程包括语法分析和语义分析过程。
2、目标任务
[ 实验项目 ] 完成以下描述赋值语句 SLR(1)文法语法制导生成中间代码四元式的过程。
G[A]:A→V=E
E→E+T∣E-T∣T
T→T*F∣T/F∣F
F→(E)∣i
V→i
[ 设计说明 ] 终结符号 i 为用户定义的简单变量,即标识符的定义。
[ 设计要求 ]
- 构造文法的 SLR(1)分析表,设计语法制导翻译过程,给出每一产生式对应的语义动作;
- 设计中间代码四元式的结构;
- 输入串应是词法分析的输出二元式序列,即某赋值语句“专题 1”的输出结果,输出为赋值语句的四元式序列中间文件;
- 设计两个测试用例(尽可能完备),并给出程序执行结果四元式序列。
3、 程序功能描述
在第一次实验词法分析输出结果的基础上设计SLR1文法分析过程,并了解四元式的形成:
- 输入串为实验一的二元式序列
- 输出为对输入串的SLR(1)文法的判断结果
- 输出有针对输入串的SLR(1)文法的具体分析过程
- 有对输入串的四元式输出序列
4、 主要数据结构描述
二元组结构体,用来存储词法分析程序输出的二元组对 <类别,单词>:
int count;
struct eryuanzu
{
int a;
char temp[COUNT];
}m[COUNT];
void out(int a,char* temp){// 打印二元组
printf("< %d %s >\n",a,temp);
m[count].a=a;
strcpy(m[count].temp,temp); //
count++;
}
SLR1分析过程中所要用到的状态栈、符号栈等:
stack<int> state; //状态栈
stack<char> sign; //符号栈
char st; //规约弹出时,状态栈顶元素
int flag=0; //标志是否是SLR
stack<string> place; //变量地址栈
ACTION表,二维数组表示:
/* i ( ) + - * / = #
以1开头的百位数为s移进项,0为error,-1为accept,其余的一位两位数是r规约项*/
int ACTION[20][9]={{103,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},//0
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,-1},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,104,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,10,0},
{109,108,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,110,111,0,0,0,1},//5 mnl;;huhyhjhjio
{0,0,4,4,4,112,113,0,4},
{0,0,7,7,7,7,7,0,7},
{109,108,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,9,9,9,9,9,0,9},
{109,108,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},//10
{109,108,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{109,108,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{109,108,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,119,110,111,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,2,2,2,112,113,0,2},//
{0,0,3,3,3,112,113,0,3},
{0,0,5,5,5,5,5,0,5},
{0,0,6,6,6,6,6,0,6},
{0,0,8,8,8,8,8,0,8}};//19
·GOTO表,二维数组表示:
//A V E T F
int GOTO[20][5]={{1,2,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0},//1
{0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,5,6,7},
{0,0,0,0,0},//5
{0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,14,6,7},
{0,0,0,15,7},
{0,0,0,16,7},//10
{0,0,0,0,17},
{0,0,0,0,18},
{0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0},//15
{0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0}};//19
规约时所用到的函数,分别对应每一条规则:
void R1(); //A→V=E
void R2(); //E→E+T
void R3(); //E→E-T
void R4(); //E→T
void R5(); //T→T*F
void R6(); //T→T/F
void R7(); //T→F
void R8(); //F→(E)
void R9(); //F→i
void R10(); //V→i
void R1() {
sign.pop(); sign.pop(); sign.pop(); //弹出符号栈
state.pop(); state.pop(); state.pop(); //弹出状态栈
sign.push('A'); //符号'A'入栈
st=state.top();
printf("r1\t");
}
void R2() {
sign.pop(); sign.pop(); sign.pop(); //弹出符号栈
state.pop(); state.pop(); state.pop(); //弹出状态栈
sign.push('E'); st=state.top(); //符号'E'入栈
printf("r2\t\t");
}
void R3() {
sign.pop(); sign.pop(); sign.pop();
state.pop(); state.pop(); state.pop();
sign.push('E');st=state.top();
printf("r3\t\t");
}
void R4() {
sign.pop();
state.pop();
sign.push('E');st=state.top();
printf("r4\t\t");
}
void R5() {
sign.pop(); sign.pop(); sign.pop();
state.pop(); state.pop(); state.pop();
sign.push('T');st=state.top();
printf("r5\t\t");
}
void R6() {
sign.pop(); sign.pop(); sign.pop();
state.pop(); state.pop(); state.pop();
sign.push('T');st=state.top();
printf("r6\t\t");
}
void R7() {
sign.pop();
state.pop();
sign.push('T');st=state.top();
printf("r7\t\t");
}
void R8() {
sign.pop(); sign.pop(); sign.pop();
state.pop(); state.pop(); state.pop();
sign.push('F');st=state.top();
printf("r8\t\t");
}
void R9() {
sign.pop();
state.pop();
sign.push('F');st=state.top();
printf("r9\t\t");
}
void R10() {
sign.pop();
state.pop();
sign.push('V');st=state.top();
printf("r10\t\t");
}
SLR1分析处理函数:
void SLR()
{
printf("输入串\t\t状态栈\t\t符号栈\t\tACTION\t\tGOTO ");
int i,j,k=1;
state.push(0); //初始化
sign.push('#');
int which; //对应表项内容
char c; //输入符号串首
int a; //坐标
int b;
do{
printf("\n");
c=m[k-1].temp[0]; //输入符号串首
cout<<c<<' ';
for(int j=k;j<=count;j++)
printf("%s",m[j].temp);
printf("\t\t");
displayStack(state);
displayStack1(sign);
a=state.top(); //坐标
b=isVt(c);
/*if(isOp(c)!=-1)
temp1=c;
place.push(temp1);*/
if(b!=-1) //输入串首c是终结符
{
which=ACTION[a][b];
if(which==-1)
{
printf(" acc,分析成功!\n");
flag=1;
break;
}
else if(which==0)
{ printf("error项1\n ");break; }
else if(which>=100) //移进
{
which=s_r(which);
printf("s%d\t\t",which);
sign.push(c);
state.push(which);
k++;
}
else
{
switch(which) //which整型,case不要加''
{
case 1:R1();break;
case 2:R2();break;
case 3:R3();break;
case 4:R4();break;
case 5:R5();break;
case 6:R6();break;
case 7:R7();break;
case 8:R8();break;
case 9:R9();break;
case 10:R10();break;
default:printf("which=%derror项2\n ");break;
}
//状态转移 Vn
int e=isVn(sign.top());
if(e!=-1)
{
int convert=GOTO[st][e];
state.push(convert);
printf("GOTO[%d,%c]=%d",st,sign.top(),convert);
}
}
}
else
{ printf("error_b ");break; }
}while(which!=-1);//while
}
5、实验测试
1.测试用例:i=(i-i*i)#,输入file.txt直接从文件读取输入串,得到结果如下:
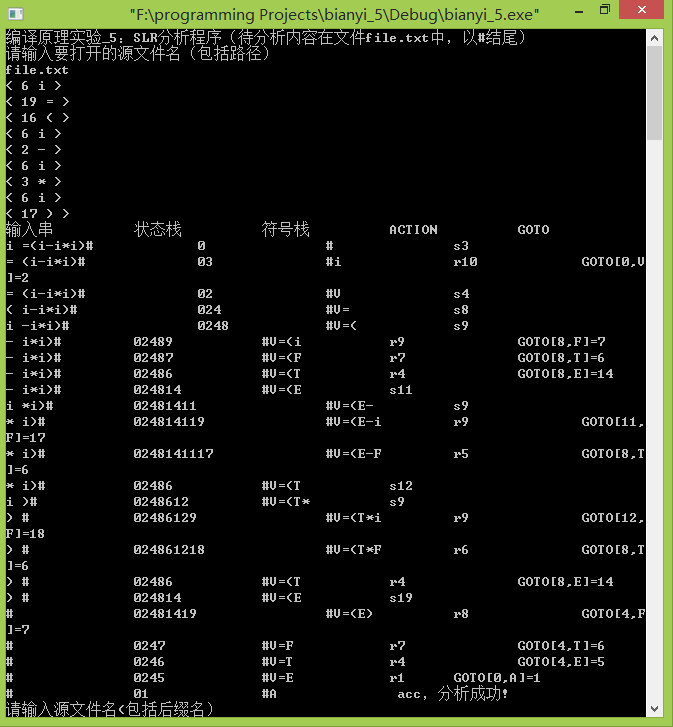
四元式结果输出:
由于图片无法上传便罢
6、 实验总结
本次实验是对理论课上所学知识的应用,重点是理解分析栈和符号栈,这里我采用自行造ACTION和GOTO表,这样SLR分析表就出来了,自动造表还是比较复杂。而且在造表的过程中经常出错,最后在大家的讨论中解决了。造完表后的分析过程并不复杂,按部就班分情况来处理。
本次实验加深了我对SLR1的分析过程的理解,也加深了对四元式的认识。
7、源代码
分为两个CPP
Siyuanshi.cpp
#include "stdafx.h" #include<stdlib.h> #include<fstream> #include<iostream> #include<stdio.h> using namespace std; #define MAX 100 int mm=0,sum=0;//sum用于计算运算符的个数 //mm用于标输入表达式中字符的个数 char JG='A'; char str[MAX];//用于存输入表达式 int token=0;//左括号的标志 /***********用于更改计算后数组中的值**************/ void change(int e) { int f=e+2; char ch=str[f]; if(ch>='A'&&ch<='Z') { for(int l=0;l<mm+10;l++) { if(str[l]==ch) str[l]=JG; } } if(str[e]>='A'&&str[e]<='Z') { for(int i=0;i<mm;i++) { if(str[i]==str[e]) str[i]=JG; } } } void chengchuchuli(int i,int mm) { i++; for( ;i<=mm-1;i++)//处理乘除运算 { if(str[i]=='*'||str[i]=='/') { cout<<"("<<str[i]<<" "<<str[i-1]<<" "<<str[i+1]<<" "<<JG<<")"<<endl; change(i-1); str[i-1]=str[i]=str[i+1]=JG; sum--; JG=(char)(int)JG++; } } } void jiajianchuli(int j,int mm) { j++; for( ;j<=mm-1;j++)//处理加减运算 { if(str[j]=='+'||str[j]=='-') { cout<<"("<<str[j]<<" "<<str[j-1]<<" "<<str[j+1]<<" "<<JG<<")"<<endl; change(j-1); str[j-1]=str[j]=str[j+1]=JG; sum--; JG=(char)(int)JG++; } } } /*扫描遍从文件中读入表达式*/ void scan(FILE *fin) { int p[MAX]; char ch='a'; int c=-1,q=0; while(ch!=EOF) { ch=getc(fin); while(ch==' '||ch=='\n'||ch=='\t') ch=getc(fin);//消除空格和换行符 str[mm++]=ch; if(ch=='='||ch=='+'||ch=='-'||ch=='*'||ch=='/') sum++; else if(ch=='(') { p[++c]=mm-1; } else if(ch==')') { q=mm-1; chengchuchuli(p[c],q);//从左括号处理到又括号 jiajianchuli(p[c],q); JG=(char)(int)JG--; str[p[c]]=str[mm-1]=JG; c--; JG=(char)(int)JG++; } } } void siyuanshi() { for(int i=0;i<=mm-1;i++)//处理乘除运算 { if(str[i]=='*'||str[i]=='/') { cout<<"("<<str[i]<<" "<<str[i-1]<<" "<<str[i+1]<<" "<<JG<<")"<<endl; change(i-1); str[i-1]=str[i]=str[i+1]=JG; sum--; JG=(char)(int)JG++; } } for(int j=0;j<=mm-1;j++)//处理加减运算 { if(str[j]=='+'||str[j]=='-') { cout<<"("<<str[j]<<" "<<str[j-1]<<" "<<str[j+1]<<" "<<JG<<")"<<endl; change(j-1); str[j-1]=str[j]=str[j+1]=JG; sum--; JG=(char)(int)JG++; } } for(int k=0;k<=mm-1;k++)//处理赋值运算 { if(str[k]=='=') { JG=(char)(int)--JG; cout<<"("<<str[k]<<" "<<str[k+1]<<" "<<" "<<" "<<str[k-1]<<")"<<endl; sum--; change(k+1); str[k-1]=JG; } } } extern void MAIN(){ char in[MAX]; //用于接收输入输出文件名 FILE *fin; cout<<"请输入源文件名(包括后缀名)"<<endl; cin>>in;; if ((fin=fopen(in,"r"))==NULL) { cout<<"error"<<endl; } cout<<"*********四元式如下*********"<<endl; scan(fin);//调用函数从文件中读入表达式 siyuanshi(); if(sum==0) printf("成功?"); else printf("有错误"); //关闭文件 fclose(fin); system("pause"); }
Bianyi_5.cpp
// bianyi_5.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application. // #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <stack> #include <map> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <iomanip> using namespace std; extern void MAIN(); #define ADD 1 #define SUB 2 #define MUL 3 #define FH 4 #define SG 5 #define ID 6 #define INT 7 #define LT 8 #define LE 9 #define EQ 10 #define NE 11 #define GT 12 #define GE 13 #define MHEQ 14 #define XGMUL 15 #define ZKH 16 #define YKH 17 #define DIV 18 #define EQ 19//= #define blz 00 #define COUNT 40 char* keyword[]={"begin","end","if","then","else","for","do","and","or","not"};//保留字 int count; struct eryuanzu { int a; char temp[COUNT]; }m[COUNT]; void out(int a,char* temp){// 打印二元组 printf("< %d %s >\n",a,temp); m[count].a=a; strcpy(m[count].temp,temp); // count++; } stack<int> state; //状态栈 stack<char> sign; //符号栈 char st; //规约弹出时,状态栈顶元素 int flag=0; //标志是否是SLR stack<string> place; //变量地址栈 /* i ( ) + - * / = # 以1开头的百位数为s移进项,0为error,-1为accept,其余的一位或两位数是r规约项*/ int ACTION[20][9]={{103,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},//0 {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,-1}, {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,104,0}, {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,10,0}, {109,108,0,0,0,0,0,0}, {0,0,0,110,111,0,0,0,1},//5 {0,0,4,4,4,112,113,0,4}, {0,0,7,7,7,7,7,0,7}, {109,108,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}, {0,0,9,9,9,9,9,0,9}, {109,108,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},//10 {109,108,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}, {109,108,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}, {109,108,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}, {0,0,119,110,111,0,0,0,0}, {0,0,2,2,2,112,113,0,2},// {0,0,3,3,3,112,113,0,3}, {0,0,5,5,5,5,5,0,5}, {0,0,6,6,6,6,6,0,6}, {0,0,8,8,8,8,8,0,8}};//19 //A V E T F int GOTO[20][5]={{1,2,0,0,0}, {0,0,0,0,0},//1 {0,0,0,0,0}, {0,0,0,0,0}, {0,0,5,6,7}, {0,0,0,0,0},//5 {0,0,0,0,0}, {0,0,0,0,0}, {0,0,14,6,7}, {0,0,0,15,7}, {0,0,0,16,7},//10 {0,0,0,0,17}, {0,0,0,0,18}, {0,0,0,0,0}, {0,0,0,0,0}, {0,0,0,0,0},//15 {0,0,0,0,0}, {0,0,0,0,0}, {0,0,0,0,0}, {0,0,0,0,0}};//19 void R1(); //A→V=E void R2(); //E→E+T void R3(); //E→E-T void R4(); //E→T void R5(); //T→T*F void R6(); //T→T/F void R7(); //T→F void R8(); //F→(E) void R9(); //F→i void R10(); //V→i int isOp(char a) //判断二元运算符及二元运算符的优先级 { int i; switch(a) { case '=':i=0;break; case '+':i=1;break; case '-':i=1;break; case '*':i=2;break; case '/':i=2;break; default:i=-1;break; } return i; } int isVt(char a) { int i; switch(a) { case 'i':i=0;break; case '(':i=1;break; case ')':i=2;break; case '+':i=3;break; case '-':i=4;break; case '*':i=5;break; case '/':i=6;break; case '=':i=7;break; case '#':i=8;break; default:i=-1;break; } return i; } int isVn(char a) { int i; switch(a) { case 'A':i=0;break; case 'V':i=1;break; case 'E':i=2;break; case 'T':i=3;break; case 'F':i=4;break; default:i=-1;break; } return i; } int s_r(int i) //移进或者其他 { int result; if(i/100==1) //移进 result=i-100; else result=i; return result; } bool invertStack(stack<int> &one_stack) { if (one_stack.empty())//if the stack is null,then don't invert it { return false; } else { //init a stack to save the inverted stack stack<int> invert; while (!one_stack.empty()) { invert.push(one_stack.top()); one_stack.pop(); } //this moment the stack's inverted state is the stack invert ,so get it back one_stack = invert; return true; } } void displayStack(stack<int> one_stack) //打印输出 { invertStack(one_stack); while (!one_stack.empty()) { cout << one_stack.top(); one_stack.pop(); } cout << '\t' << '\t' ; } bool invertStack1(stack<char> &one_stack) { if (one_stack.empty())//if the stack is null,then don't invert it { return false; } else { //init a stack to save the inverted stack stack<char> invert; while (!one_stack.empty()) { invert.push(one_stack.top()); one_stack.pop(); } //this moment the stack's inverted state is the stack invert ,so get it back one_stack = invert; return true; } } void displayStack1(stack<char> one_stack) { invertStack1(one_stack); while (!one_stack.empty()) { cout << one_stack.top(); one_stack.pop(); } cout << '\t' << '\t'; } void SLR() { printf("输入串\t\t状态栈\t\t符号栈\t\tACTION\t\tGOTO "); int i,j,k=1; state.push(0); //初始化 sign.push('#'); int which; //对应表项内容 char c; //输入符号串首 int a; //坐标 int b; do{ printf("\n"); c=m[k-1].temp[0]; //输入符号串首 cout<<c<<' '; for(int j=k;j<=count;j++) printf("%s",m[j].temp); printf("\t\t"); displayStack(state); displayStack1(sign); a=state.top(); //坐标 b=isVt(c); /*if(isOp(c)!=-1) temp1=c; place.push(temp1);*/ if(b!=-1) //输入串首c是终结符 { which=ACTION[a][b]; if(which==-1) { printf(" acc,分析成功!\n"); flag=1; break; } else if(which==0) { printf("error项1\n ");break; } else if(which>=100) //移进 { which=s_r(which); printf("s%d\t\t",which); sign.push(c); state.push(which); k++; } else { switch(which) //which整型,case不要加'' { case 1:R1();break; case 2:R2();break; case 3:R3();break; case 4:R4();break; case 5:R5();break; case 6:R6();break; case 7:R7();break; case 8:R8();break; case 9:R9();break; case 10:R10();break; default:printf("which=%derror项2\n ");break; } //状态转移 Vn int e=isVn(sign.top()); if(e!=-1) { int convert=GOTO[st][e]; state.push(convert); printf("GOTO[%d,%c]=%d",st,sign.top(),convert); } } } else { printf("error_b ");break; } }while(which!=-1);//while } void R1() { sign.pop(); sign.pop(); sign.pop(); //弹出符号栈 state.pop(); state.pop(); state.pop(); //弹出状态栈 sign.push('A'); //符号'A'入栈 st=state.top(); printf("r1\t"); } void R2() { sign.pop(); sign.pop(); sign.pop(); //弹出符号栈 state.pop(); state.pop(); state.pop(); //弹出状态栈 sign.push('E'); st=state.top(); //符号'E'入栈 printf("r2\t\t"); } void R3() { sign.pop(); sign.pop(); sign.pop(); state.pop(); state.pop(); state.pop(); sign.push('E');st=state.top(); printf("r3\t\t"); } void R4() { sign.pop(); state.pop(); sign.push('E');st=state.top(); printf("r4\t\t"); } void R5() { sign.pop(); sign.pop(); sign.pop(); state.pop(); state.pop(); state.pop(); sign.push('T');st=state.top(); printf("r5\t\t"); } void R6() { sign.pop(); sign.pop(); sign.pop(); state.pop(); state.pop(); state.pop(); sign.push('T');st=state.top(); printf("r6\t\t"); } void R7() { sign.pop(); state.pop(); sign.push('T');st=state.top(); printf("r7\t\t"); } void R8() { sign.pop(); sign.pop(); sign.pop(); state.pop(); state.pop(); state.pop(); sign.push('F');st=state.top(); printf("r8\t\t"); } void R9() { sign.pop(); state.pop(); sign.push('F');st=state.top(); printf("r9\t\t"); } void R10() { sign.pop(); state.pop(); sign.push('V');st=state.top(); printf("r10\t\t"); } /////////////////////////////////////////////// void scanner(FILE *p) { char filein[40],fileout[40]; //文件名 printf("请输入要打开的源文件名(包括路径)\n"); scanf("%s",filein); //printf("请输入要输出的目标文件名(包括路径)\n"); //scanf("%s",fileout); if((p=fopen(filein,"r"))==NULL) {printf("输入文件打开有错!\n");return;} // if((q=fopen("fileout","rw"))==NULL) {printf("输出文件打开有错!\n");return;} char token[COUNT]; //输出数组 int r=0,i=0; char ch; ch=fgetc(p); while(!feof(p)) //没有读到文件末尾 { if(isdigit(ch)) { i=0; token[i]=ch; while(isdigit(ch=fgetc(p))) { i++; token[i]=ch; } token[i+1]='\0'; //整数结束。不要忘结束标志! fseek(p,-1,1); //重定向到当前位置的前一个! out(INT,token); //fprintf(q,"%d %s\n",INT,token); } else if(isalpha(ch)) { i=0; int flag=0; //标志是否是保留字,默认不是 token[i]=tolower(ch); while(isalpha(ch=fgetc(p))) { i++; token[i]=tolower(ch); } token[i+1]='\0'; fseek(p,-1,1); for(r=0;r<8;r++) { if(!strcmp(token,keyword[r])) { printf("<blz %s>\n",token); // fprintf(q,"%d %s\n","保留字",token); flag=1; break; } } if(!flag) { out(ID,token); // fprintf(q,"%d %s\n",ID,token); } } else { i=0; switch(ch) { case '+':{ token[i]=ch; token[i+1]='\0'; out(ADD,token); }break; case '-':{ token[i]=ch; token[i+1]='\0'; out(SUB,token);}break; case '*':{ token[i]=ch; token[i+1]='\0'; out(MUL,token);}break; case ';':{ token[i]=ch; token[i+1]='\0'; out(FH,token);}break; case '|':{ token[i]=ch; token[i+1]='\0'; out(SG,token);}break; case '(':{ token[i]=ch; token[i+1]='\0'; out(ZKH,token);}break; case ')':{ token[i]=ch; token[i+1]='\0'; out(YKH,token);}break; case '=':{ token[i]=ch; token[i+1]='\0'; out(EQ,token);}break; case ' ':{ break;} //空格直接跳 case '#':{ break;} //井号用作结尾 case '<':{token[i]=ch; ch=fgetc(p); if(ch=='='){ token[i+1]='='; token[i+2]='\0'; out(LE,token); } else if(ch=='>'){ token[i+1]='>'; token[i+2]='\0'; out(NE,token); } else { printf(" error \n"); fseek(p,-1,1); //多读的要回退一个字符 } }break; case '>':{token[i]=ch; ch=fgetc(p); if(ch=='=') { token[i+1]='='; token[i+2]='\0'; out(GE,token); } else { printf(" error \n"); fseek(p,-1,1); //多读的要回退一个字符 } }break; case ':':{token[i]=ch; ch=fgetc(p); if(ch=='='){ token[i+1]='='; token[i+2]='\0'; out(MHEQ,token); } else { printf(" error \n"); fseek(p,-1,1); //多读的要回退一个字符 } }break; case '/':{token[i]=ch; ch=fgetc(p); if(ch=='*') { token[i+1]='*'; token[i+2]='\0'; out(XGMUL,token); while(1) //注释部分的处理! { ch=fgetc(p); if(ch=='*') { if((ch=fgetc(p))=='/') break; } } } else // 除号,修改第一次程序部分 { /*printf(" error \n"); fseek(p,-1,1); */ out(DIV,token); fseek(p,-1,1);//多读的要回退一个字符 } }break; default:{ printf(" error\n "); }break; } } ch=fgetc(p); } fclose(p); } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { printf("编译原理实验_5:SLR分析程序(待分析内容在文件file.txt中,以#结尾)\n"); FILE *fin,*q; scanner(fin); strcpy(m[count].temp,"#");//! count=count+1; //scanner(p,q); SLR(); MAIN(); return 0; }


