原型模式(Prototype Pattern)
- 原型模式概述
定义:使用原型实例指定待创建对象的类型,并且通过复制这个原型来创建新的对象。简单的来说就是克隆(Clone),通过已经存在的,将其复制而产生新的。原型模式属于创建型模式,将一个原型对象传给要发动创建的对象(客户端对象),该对象通过请求原型对象复制自己来实现创建过程。
既然是通过Clone创建的,那么就会存该拷贝是浅拷贝还是深拷贝的问题了。
浅拷贝(Shallow Clone):当原型对象被复制时,只复制它本身和其中包含的值类型的成员变量,而引用类型的成员变量并没没复制。如我想将A复制一份出来,命名为为B,那么我在浅拷贝后,确实可以得到A和B。而且A和B的值也相等,但是,我将B的值稍作修改,A的值也会变动,这往往不是我们想要的。因为我们想拷贝一个副本出来,二者也能独立,这样才算拷贝。但是,浅拷贝后A和B却是指向同一片地址空间,也就是二者共用一个值,改一个,两个都变。
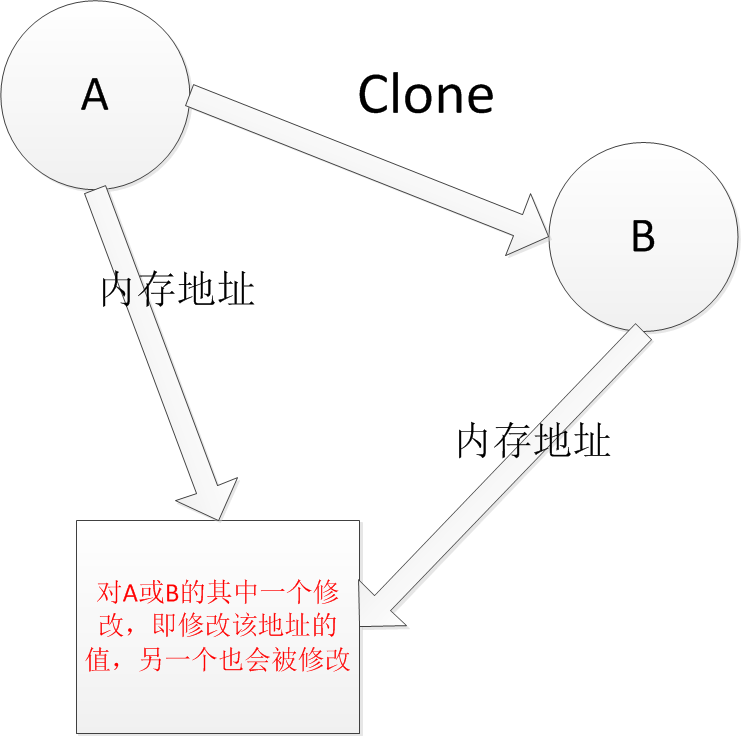
深拷贝(Deep Clone):除了对象本身被复制外,对象所包含的所有成员变量也被复制,就是我们想要的那种拷贝,即有一个副本,与原者老死不想往来,互不影响

原型模式的实现 :
结构:
- Prototype(抽象原型类):声明克隆方法的接口,所有具体原型类的公共父类,抽象类、接口皆可,也可是具体类
- ConcretePrototpye(具体原型类):实现在抽象原型类中声明的克隆方法,返回自己的克隆对象
- Client(客户类):让一个原型对象克隆自身而创建一个新的对象,直接实例化或通过工厂方法创建一个原型对象,在调用克隆方法即可

- 原型模式应用实例
问题描述:为某销售管理系统设计并实现一个客户类Customer,在客户类中包含一个名为客户地址的成员变量,客户地址的类型为Address,用浅克隆和深克隆分别实现Customer对象的复制,并比较这两种克隆方式的异同(异同前面简单说了,就不重复了)
结构 :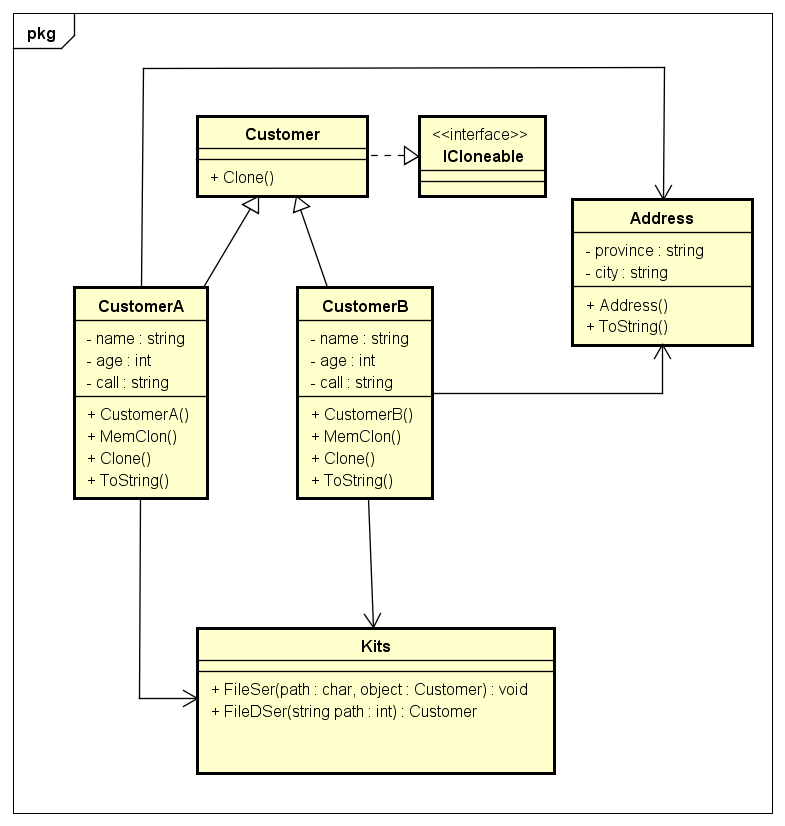

1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 using System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary; //序列化 6 using System.IO;//文件 7 using System.Runtime.Serialization;//序列化异常处理 8 9 namespace Customer 10 { 11 [Serializable]//将Customer类设置为可序列化 12 public abstract class Customer : ICloneable 13 { 14 public abstract object Clone(); 15 } 16 17 [Serializable]//将Address类设置为可序列化 18 public class Address//地址类 19 { 20 private string province; 21 private string city; 22 23 public string City 24 { 25 get { return city; } 26 set { city = value; } 27 } 28 29 public string Province 30 { 31 get { return province; } 32 set { province = value; } 33 } 34 35 public Address(string province,string city) 36 { 37 this.province = province; 38 this.city = city; 39 } 40 41 public override string ToString()//打印地区 42 { 43 return "地址为:" + province + " 省," + city + " 市。"; 44 } 45 } 46 47 [Serializable]//将CustomerA设置为可序列化 48 public class CustomerA : Customer//顾客A类 49 { 50 private string name; 51 private int age; 52 private string call; 53 private Address address; 54 55 public Address Address 56 { 57 get { return address; } 58 set { address = value; } 59 } 60 61 public string Name 62 { 63 get { return name; } 64 set { name = value; } 65 } 66 67 public int Age 68 { 69 get { return age; } 70 set { age = value; } 71 } 72 73 public string Call 74 { 75 get { return call; } 76 set { call = value; } 77 } 78 79 public CustomerA(string name, int age, string call,Address address) 80 { 81 this.name = name; 82 this.age = age; 83 this.call = call; 84 this.address = address; 85 } 86 87 public override string ToString() 88 { 89 return "客户A--姓名:" + this.name + " 年龄:" + this.age + " 联系方式:" + this.call + " "+ this.address.ToString(); 90 } 91 92 #region 浅克隆+this.MemberwiseClone() 93 public object MemClone() 94 { 95 return this.MemberwiseClone(); 96 } 97 #endregion 98 99 #region 深克隆+object Clone() 100 public override object Clone() 101 { 102 Kits.FileSer(@"d:\1.txt", this);// 103 object obj = Kits.FileDSer(@"d:\1.txt"); 104 return obj; 105 } 106 #endregion 107 } 108 109 [Serializable]//将CustomerB设置为可序列化 110 public class CustomerB : Customer//顾客B类 111 { 112 private string name; 113 private int age; 114 private string call; 115 private Address address; 116 117 public Address Address 118 { 119 get { return address; } 120 set { address = value; } 121 } 122 123 public string Name 124 { 125 get { return name; } 126 set { name = value; } 127 } 128 129 public int Age 130 { 131 get { return age; } 132 set { age = value; } 133 } 134 135 public string Call 136 { 137 get { return call; } 138 set { call = value; } 139 } 140 141 public CustomerB(string name, int age, string call, Address address) 142 { 143 this.name = name; 144 this.age = age; 145 this.call = call; 146 this.address = address; 147 } 148 149 public override string ToString() 150 { 151 return "客户B--姓名:" + this.name + " 年龄:" + this.age + " 联系方式:" + this.call + " " + this.address.ToString(); 152 } 153 154 #region 浅克隆+this.MemberwiseClone() 155 public object MemClone() 156 { 157 return this.MemberwiseClone(); 158 } 159 #endregion 160 161 #region 深克隆+object Clone() 162 public override object Clone() 163 { 164 Kits.FileSer(@"d:\1.txt", this);//读 165 object obj = Kits.FileDSer(@"d:\1.txt");//写 166 return obj; 167 } 168 #endregion 169 } 170 171 public class Kits//工具类 172 { 173 public static void FileSer(string path,object obj)//读出信息 174 { 175 FileStream fs = new FileStream(path, FileMode.OpenOrCreate);//通道 序列化 176 BinaryFormatter bf = new BinaryFormatter();//搬运工 177 try 178 { 179 bf.Serialize(fs, obj);//序列化 180 } 181 catch (SerializationException e) 182 { 183 Console.WriteLine("该文件进行序列化失败。原因 : " + e.Message); 184 throw; 185 186 } 187 finally { fs.Close(); } 188 } 189 190 public static object FileDSer(string path)//写入 191 { 192 FileStream fs = new FileStream(path, FileMode.Open);//通道、路径,权限 193 BinaryFormatter bf = new BinaryFormatter();//搬运工 194 object obj = null; 195 try 196 { 197 obj=bf.Deserialize(fs);//反序列化 198 } 199 catch (SerializationException e) 200 { 201 Console.WriteLine("该文件进行反序列化失败。原因 : " + e.Message); 202 throw; 203 204 } 205 finally 206 { 207 fs.Close(); 208 } 209 return obj; 210 } 211 } 212 213 class Program 214 { 215 static void Main(string[] args) 216 { 217 Console.WriteLine("\n--------------------------------Customer-------------------------------------"); 218 Address addr1 = new Address("中国江苏", "扬州"); 219 CustomerA c1 = new CustomerA("社会人c1", 20, "13288888888", addr1); 220 Console.WriteLine(c1.ToString());//c1的作为原对象 221 222 Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------------------------Copy(c2 = c1)-------------------------------------"); 223 CustomerA c2 = c1; 224 Console.WriteLine("社会人c2,更新信息.直接复制对象\n"); 225 Console.WriteLine(); 226 Console.WriteLine(c2.ToString()); 227 228 Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------------------ShallowCopy-------------------------------------"); 229 Console.WriteLine(); 230 Console.WriteLine("社会人c3,更新信息\n"); 231 CustomerA c3 = (CustomerA)c1.MemClone();//浅克隆 232 Console.WriteLine(c3.ToString()); 233 234 Console.WriteLine("此时 c2:"); 235 Console.WriteLine(c2.ToString()); 236 237 Console.WriteLine("\n--------------------------------Customer-------------------------------------\n"); 238 Console.WriteLine(); 239 Address addr2 = new Address("中国广东", "广州"); 240 CustomerB c4 = new CustomerB("小猪佩琪", 24, "16612345678", addr2); 241 Console.WriteLine("c4 "+c4.ToString()); 242 Console.WriteLine("\n--------------------------------DeepCopy(update c5.Age = 26)--------------------------\n"); 243 244 CustomerB c5 = (CustomerB)c4.Clone(); 245 c5.Age = 26; 246 Console.WriteLine("一年后,搬家\n"); 247 c5.Address = new Address("中国天津", "河西区"); 248 Console.WriteLine(c5.ToString()); 249 250 Console.WriteLine("此时 c4:"); 251 Console.WriteLine(c4.ToString()); 252 ; 253 } 254 } 255 }
运行结果:

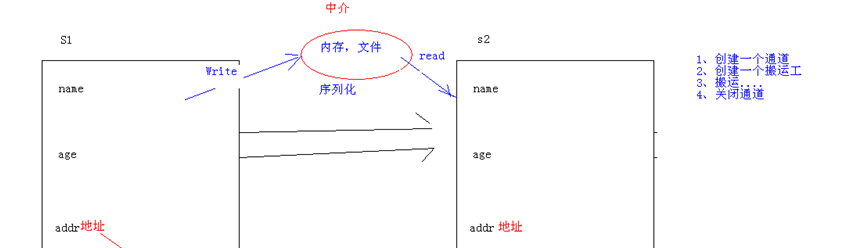
上述FileStream类和BinaryFormatter类是实现对象序列化和反序列化的操作的,就是用序列化把当前对象写入流中,流入文件,再用反序列化从文件中流出对象。文件相当于中介,当然,中介还可以是内存、网络。
- 原型管理器
简单介绍:原型管理器(Prototype Manager)就是将多个原型对象存储在一个集合中供客户端使用,它是一个专门负责克隆对象的工厂,其中定义了一个集合用于存储原型对象,如果需要某个原型对象的一个克隆,可以通过复制集合中对应的原型对象获得。


1 using System.Collections; 2 class PrototypeManager 3 { 4 Hashtable ht = new Hashtable(); //使用Hashtable存储原型对象 5 public PrototypeManager() 6 { 7 ht.Add("A", new ConcretePrototypeA()); 8 ht.Add("B", new ConcretePrototypeB()); 9 } 10 public void Add(string key, Prototype prototype) 11 { 12 ht.Add(key,prototype); 13 } 14 public Prototype Get(string key) 15 { 16 Prototype clone = null; 17 clone = ((Prototype)ht[key]).Clone(); //通过克隆方法创建新对象 18 return clone; 19 } 20 }
原型模式的优缺点和适用环境
- 原型模式的优点:
- 简化对象的创建过程,通过复制一个已有对象实例可以提高新实例的创建效率
- 扩展性好
- 提供了简化的创建结构,原型模式中的产品的复制是通过封装在原型类中的克隆方法实现的,无需专门的工厂类来创建产品
- 可以通过深克隆的方式保存对象的状态,使用原型模式将对象复制一份并其状态保存起来,以便在需要的时候使用,可辅助实现撤销操作
- 原型模式的缺点:
- 需要为每一个类准备一个克隆方法,而且该克隆方法位于一个类的内部,当对已有类进行改造时,需要修改原代码,违背了开闭原则
- 在实现深克隆时需要写较复杂的代码,而且当对象之间存在多重的嵌套引用时,为了实现深克隆,每一层对象对应的类必须支持深克隆,实现起来较烦较烦....
- 原型模式的适用环境:
- 创建新对象成本较大,新对象可以通过复制已有对象来获得,如果是相似对象,则可以对其成员变量修改
- 系统要保存对象的状态,而对象的状态变化很小
- 需要避免使用分层次的工厂类来创建分层次的对象,并且类的实例对象只有一个或很少的几个组合状态,通过复制原型对象得到新实例可能比使用构造函数创建一个新实例更方便




