Priority_Queue(优先队列)
我们都知道,队列是一种FIFO的数据结构,规定在队尾增加元素,在队首删除元素,和食堂排队打饭一个道理。(当然,插队的人是很鄙视的)。而在优先队列中,每个元素却有了特权,被赋予了优先级,从而在访问元素时,优先级高的最先出队(如有特权的军人则可以率先购票,就是这个道理)。
对PQ的操作有Search,Insert和Delete。在最小优先队列(min priorIty queue)中,查找用来搜索优先权最小的元素,删处即删处该元素,反之,最大优先队列(max priority queue)中,查找优先权最大的元素,删除即删处该元素。
基本操作:empty() 判空、pop()删处第一个元素、push()增加元素、size()返回元素个数,top()返回优先级最高的元素。
PQ的特征:priority_queue<int,vector<int>,cmp > que;第一个参数为数据类型,第二个为容器类型,第三个为比较类型。
接下来是构造PQ,构造好了才可以用它。
priority_queue<int> que; 这里构造int型数据类型,默认优先级(最大值优先)
如果我们要最小值优先的话,可以有4种优先级控制方法。
- C++中库函数<functional>
<functional> 首先头文件包含#inclu<functional> 而functional提供了基于模板的比较函数对象、
equal_to<Type> 等于
not_equal_to<Type 不等于
greater<Type>大于
greater_equal<Type>大于等于
less<Type> 小于
less_equal<Type>小于等于
构造:
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,less<int> >que1;//最大值优先
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater <int> >que2;//最小值优先
- 自定义1(队列元素为数值型)
struct cmp1 { bool operator ()(int &a,int &b) { return a < b;//最大值优先 } }; struct cmp2 { bool operator() (int &a,int &b) { return a > b;//最小值优先 } };
//构造 priority_queue<int,vector<int>,cmp1>que1;//最大值优先 priority_queue<int,vector<int>,cmp2>que2;//最小值优先
- 自定义2(队列元素为结构体型)
struct node1 { int x,y; bool operator < (const node1 &a) const { return x<a.x;//最大值优先 } }; struct node2 { int x,y; bool operator < (const node2 &a) const { return x>a.x;//最小值优先 } }; //构造 priority_queue<node1>que1; priority_queue<node2>que2;
- 自定义3(队列元素为结构体型)
struct node1 { int x; int y; }; bool operator < (const node1 &a,const node1 &b) { return a.x <b.x;//按成员x最大值优先 } struct node2 { int x; int y; }; bool operator < (const node2 &a,const node2 &b) { return a.y > b.y;//按成员y最小值优先 } //构造 priority_queue<node1>que1; priority_queue<node2>que2;
- Code
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct Stud
{
int no;
string name;
Stud(int no1,string name1)
{
no = no1;
name = name1;
}
bool operator < (const Stud & s)const
{
return no < s.no;
}
bool operator > (const Stud & s)const
{
return no > s.no;
}
};
struct Cmp
{
bool operator()(const Stud &s,const Stud &t)const
{
return s.name < t.name;//name越大越优先
}
};
int main()
{
Stud a[] = {Stud(2,"Mary"),Stud(1,"John"),Stud(5,"Smith")};
int n = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
//使用Stud结构体中的《 关系定义pq1
priority_queue<Stud>pq1(a,a+n);
cout<<"pq1: ";
while(! pq1.empty())//no递减输出
{
cout<<"["<<pq1.top().no<<","<<pq1.top().name<<"]"<<endl;
pq1.pop();
}
//使用Stud结构体的》 关系定义pq2
priority_queue<Stud,deque<Stud>,greater<Stud> >pq2(a,a+n);
cout<<"pq2:";
while(! pq2.empty())//no递增输出
{
cout<<"["<<pq2.top().no<<","<<pq2.top().name<<"]"<<endl;
pq2.pop();
}
//使用Stud结构体的StudCmp定义pq3
priority_queue<Stud,deque<Stud>,Cmp>pq3(a,a+n);
cout<<"pq3:";
while(! pq3.empty())//name递减输出
{
cout<<"["<<pq3.top().no<<","<<pq3.top().name<<"]"<<endl;
pq3.pop();
}
return 0;
}
- 运行结果
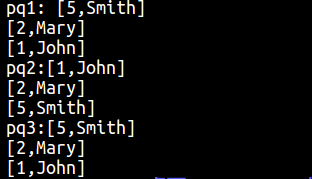
- 注意事项
有时晕的地方。在对内置数据类型的排序处理中,sort()默认是用less<T>作为对函数实现递增排序,如(sort(iterator.begin(),iteraotr.emd(),less<Data_Type>) 等同于sort(iterator.begin(),iterator,end())
而在结构体排序中,默认less<T>,但也要重载<运算符,也可改变排列顺序 。如
struct Stud { int no; string name; Stud(int no1,string name1) { no = no1; name = name1; } bool operator < (const Stud &s )const//重载 < { return no > s.no;//用于将no 递减排序,将>改为 < 为增序 } }; struct Cmp { bool operator() (const Stud &s1,const Stud &s2) const { return s1.name<s2.name;//将name递增排序 } };



