1.防止订单重复提交
使用 redis 分布式锁来实现,可以使用用户ID,加购物车的商品ID,使用 MD5算法,得出一个key 作为分布式锁的key。解决问题的关键是 保持分布式锁的 key 的唯一性。
2. 缓存击穿
如果用户查的ID数据库没有值,那么缓存就击穿了,解决办法,如果数据库没有值,也给他缓存一个空值,第二次 在访问的时候,就直接给他返回null
private String Empty="-1";
public Product getProduct(String productId){
Object obj= cache.get(productId);
if(obj!=null){
if(obj instantOf(Product.class)){
return (Product)obj;
}
if(Empty.equals(obj)){
return null
}
}
Product p=dao.get(productId);
if(p!=null){
cache.put(productId,p);
}
else{
cache.put(productId,Empty);
}
return p;
}
这个方法有个问题,如果大量的 空存在会 损耗 内存,那么空缓存可以设置一个缓存过期时间,过一段时间缓存就会被清理掉。
还可以使用布隆过滤器。
- 热点数据访问。
//双重检测锁
Product getProduct(String productId){
Object obj= cache.get(productId);
if(obj!=null){
if(obj instantOf(Product.class)){
return (Product)obj;
}
if(Empty.equals(obj)){
return null
}
}
synchronized(this){
Object obj= cache.get(productId);
if(obj!=null){
if(obj instantOf(Product.class)){
return (Product)obj;
}
if(Empty.equals(obj)){
return null
}
}
Product p=dao.get(productId);
if(p!=null){
cache.put(productId,p);
}
else{
cache.put(productId,Empty,60000);
}
}
return p;
}
synchronized 性能提升
synchronized 锁定时,需要注意锁的对象。
如果在 spring 使用
// 这个代码会锁定当前控制器的实例对象,因为控制器实例是单例对象,因此效率不高。
synchronized(this){
}
性能提升
CurrentHashMap map=new CurrentHashMap();
public void save(String userId){
//产生锁对象
Object o=map.computeIfAbsent(userId,o->new Object());
//这样就每个用户ID就持有有一把锁。
synchronized(o){
}
}
分布式锁
使用redisson 做分布式锁。
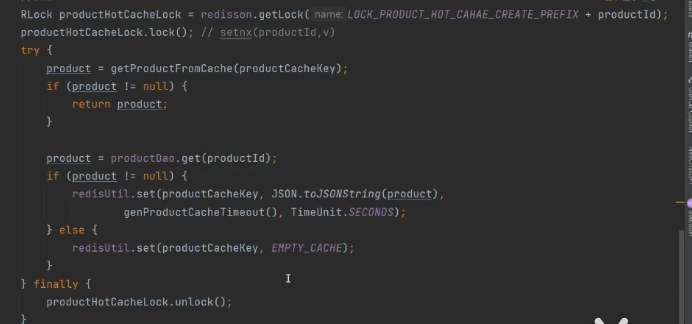
接口优化
后台代码
- 缓存机制
- 并发调用
比如有两个耗时操作,可以同时使用两个线程调用。 - 同步接口异步化
- 避免大事务
- 优化日志
数据库
- 数据库查询优化
索引,查询必要的字段,避免深分页,表数据冗余数据,使用连接池管理链接,使用数据压缩技术
网络缓慢 防止用户重复下单
使用 redis 的 setnx,关键是在于key 的选择,比如用户TOKEN和商品的KEY,可以使用MD5将KEY变短。
如何查看线程死锁
- 使用jstack 命名
- 数据库死锁
1.查询是否锁表
show open tables where in_use>0
2. 查询进程
show processlist
3.查询在锁的事务
select * from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.INNODB_LOCKS;
4.查询等待锁的事务
select * from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.INNODB_LOCK_WAITS;
要将一个第三方的类配置成为Bean有哪些方式
- 使用 @Bean 的方式
- 使用 @Import 的方式
// 这种方式无法干预实例化的过程
@Import(A.class)
public class B{
}
- 使用 ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar 方式代码如下
//定义一个普通类
public class MyService {
private String name="";
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name=name;
}
}
public class MyBeanDefinitionRegistry implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(MyService.class);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("name","xiao zhang");
registry.registerBeanDefinition("myService",beanDefinition);
}
}
@Configuration
@Import({ MyBeanDefinitionRegistry.class})
public class DemoConfig {
}
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Resource
private MyService myService;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "Hello:" +myService.getName();
}
}
- 实现 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口
@Component
public class MyBeanDefinitionRegistryProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry beanDefinitionRegistry) throws BeansException {
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(MyService.class);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("name","xiao xiaowang");
beanDefinitionRegistry.registerBeanDefinition("myService1",beanDefinition);
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory configurableListableBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
}
}
后面这两种方法的区别是,ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar 先执行 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor最后执行。
java 对象一定分配在堆中吗
对象实例:大多数情况下,对象实例是在堆上分配内存的。
局部变量:局部变量如果是基本数据类型,则存储在栈上;如果是引用类型,引用存储在栈上,对象实例存储在堆上。
逃逸分析:JVM的逃逸分析可能会将某些对象分配在栈上,以优化性能。
Java里面的双冒号“::”到底是什么意思
是方法引用的意思
public class MethodReference {
public String hello(String name)
{
System.err.println("hello " + name);
return "hello " + name;
}
public String hello()
{
System.err.println("hello ray");
return "hello ray" ;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable r = new MethodReference()::hello;
r.run();
Consumer<String> c = new MethodReference()::hello;
c.accept("老王");
}
}
上面都指向了 hello 方法,引用指向到具体的哪个方法,需要根据函数式接口推导来决定具体使用哪个方法。
上面是 实例方法的使用,下面展示一个静态方法的使用。
public class MethodReference {
public static String hello(String name)
{
System.err.println("hello " + name);
return "hello " + name;
}
public static String hello()
{
System.err.println("hello ray");
return "hello ray" ;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable r = MethodReference::hello;
r.run();
Consumer<String> c = MethodReference::hello;
c.accept("老王");
}
}




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
2014-10-19 loadrunner 打印变量