实验6
1、合并两个文件到新文件中。文件名均从键盘输入
#include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <string> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; int main() { string filename1, filename2, newfilename; cout << "输入要合并的两个文件名: " ; cin >> filename1 >> filename2; cout << "输入合并后新文件名: " ; cin >> newfilename; ofstream fout; // 输出文件流对象 ifstream fin; // 输入文件流对象 fin.open(filename1); // 将输入文件流对象fin与文件filename1建立关联 if(!fin.is_open()) { // 如果打开文件失败,则输出错误提示信息并退出 cerr << "fail to open file " << filename1 << endl; system("pause"); exit(0); } fout.open(newfilename); // 将输出文件流对象fout与文件newfilename建立关联 if(!fin.is_open()) { // 如果创建/打开文件失败,输出错误提示信息并退出 cerr << "fail to open file " << newfilename << endl; system("pause"); exit(0); } char ch; // 从文件输入流对象fin中获取字符,并将其插入到文件输出流对象fout中 while(fin.get(ch)) fout << ch; fin.close(); // 关闭文件输入流对象fin与文件filename1的关联 fout << endl; // 向文件输出流对象fout中插入换行 fin.open(filename2); // 将输入文件流对象fin与文件filename2建立关联 if(!fin.is_open()) { // 如果打开文件失败,则输出错误提示信息并退出 cerr << "fail to open file " << filename2 << endl; system("pause"); exit(0); } // 从文件输入流对象fin中获取字符,并将其插入到文件输出流对象fout中 while(fin.get(ch)) fout << ch; fin.close(); // 关闭文件输入流对象fin与文件filename2的关联 fout.close(); // 关闭文件输出流对象fout与文件newfilename的关联 system("pause"); return 0; } // 说明: // 这个简单示例中,合并两个文件的具体方法,是逐个读取文件中的字符直到文件末尾,并写入到新文件中 // 还可以一次读取一行 // 或者,直接利用标准模板库的成员函数,一次性将整个文件内容读取至缓冲区 // 等过了期末考,时间宽松一些的时候可以学习体验更多标准模板库的内容,对后续专业课的学习(如数据结构、算法、操作系统等)也会有帮助
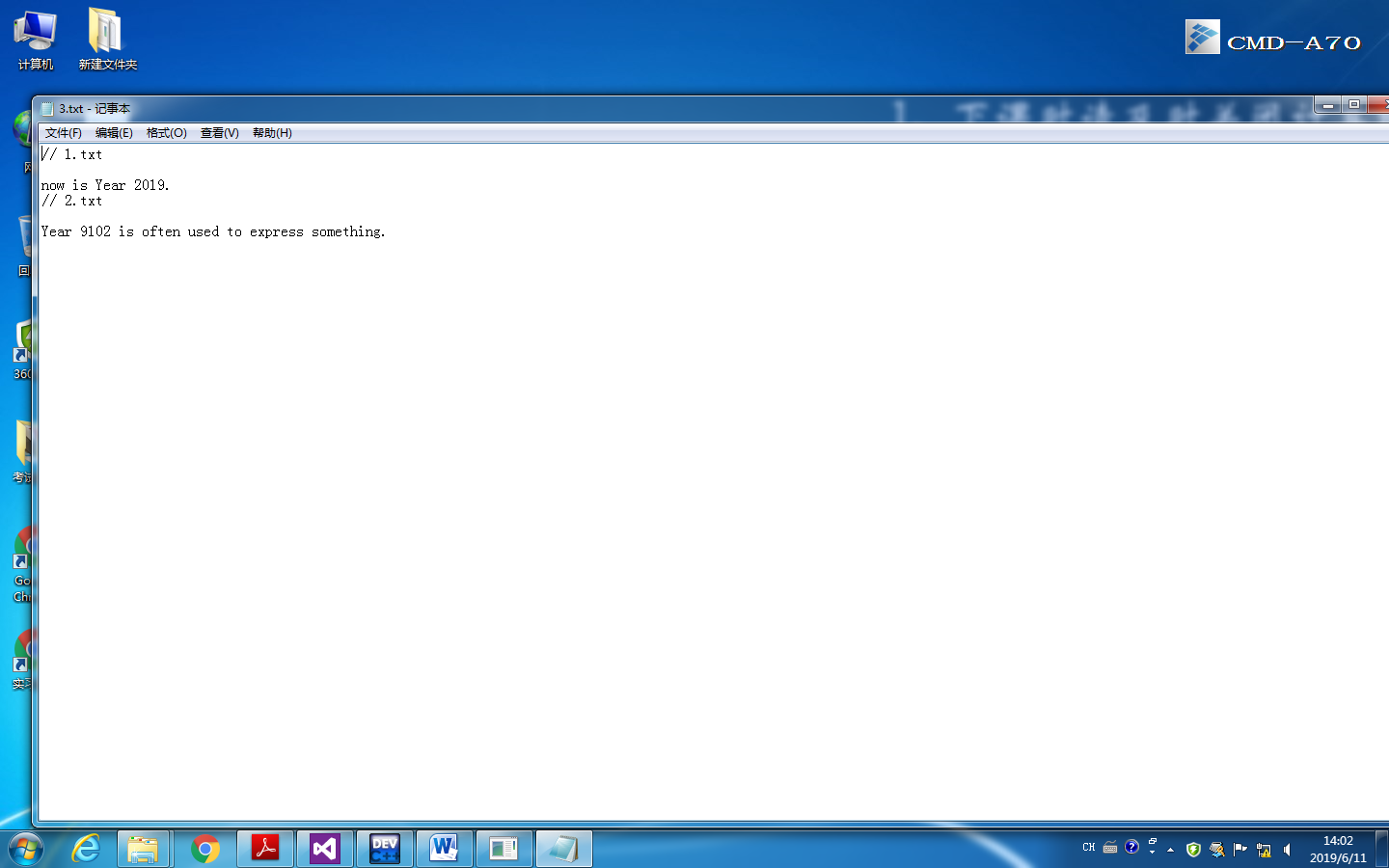
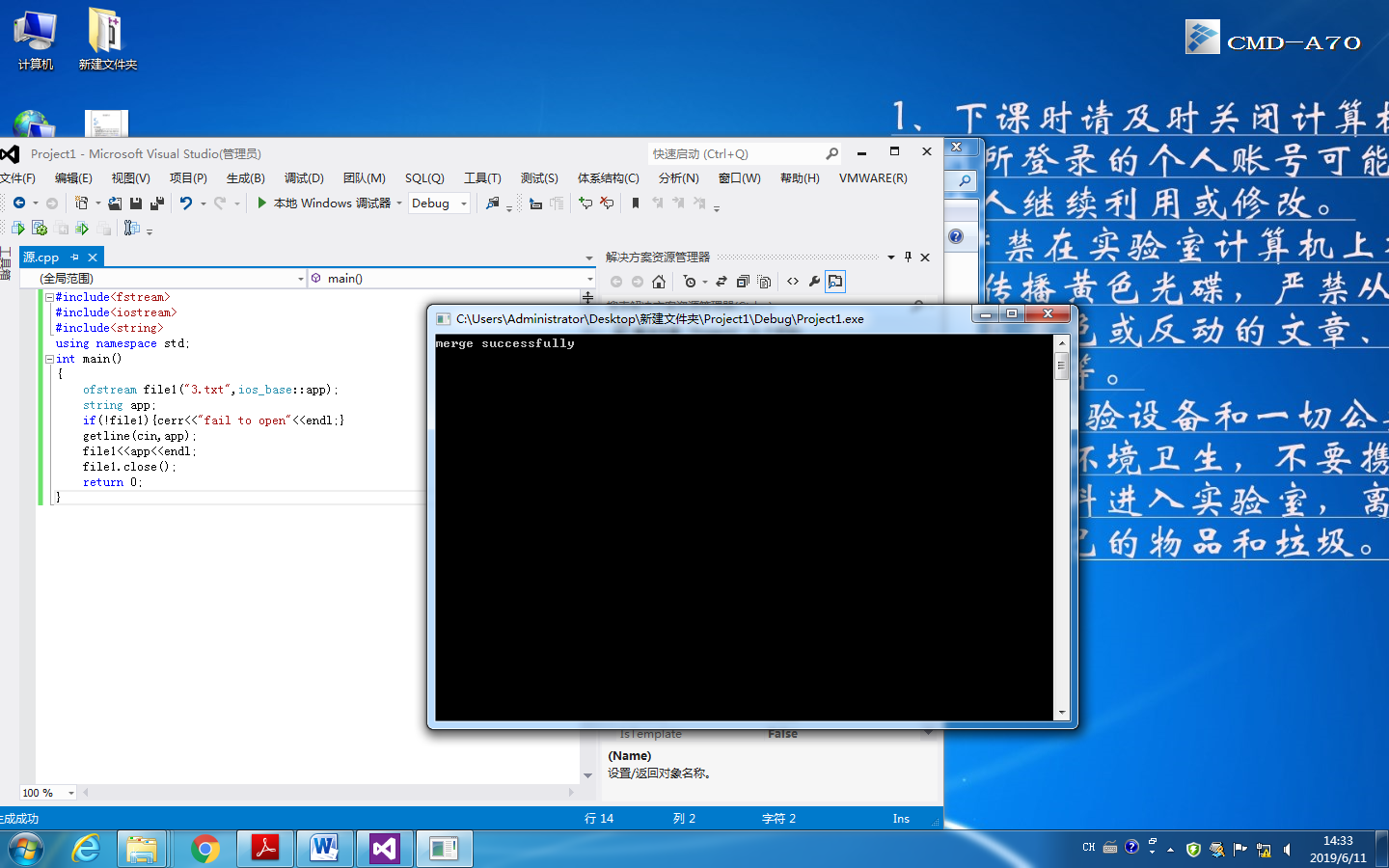
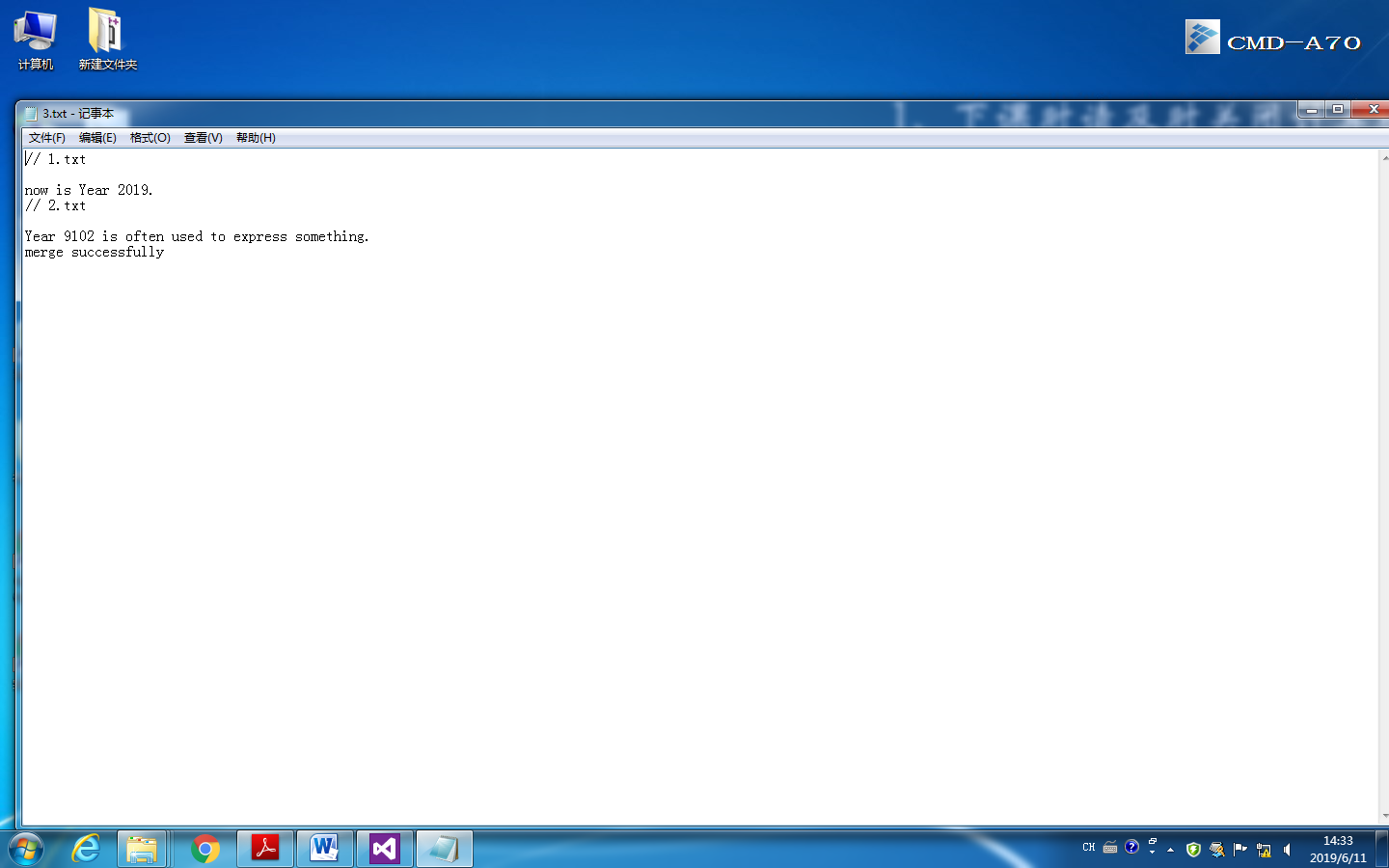
2、使用文件I/O流,以文本方式打开Part1中合并后的文件,在文件最后一行添加字符"merge successfully.
#include<fstream> #include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; int main() { ofstream file1("3.txt",ios_base::app); string app; if(!file1){cerr<<"fail to open"<<endl;} getline(cin,app); file1<<app<<endl; file1.close(); return 0; }
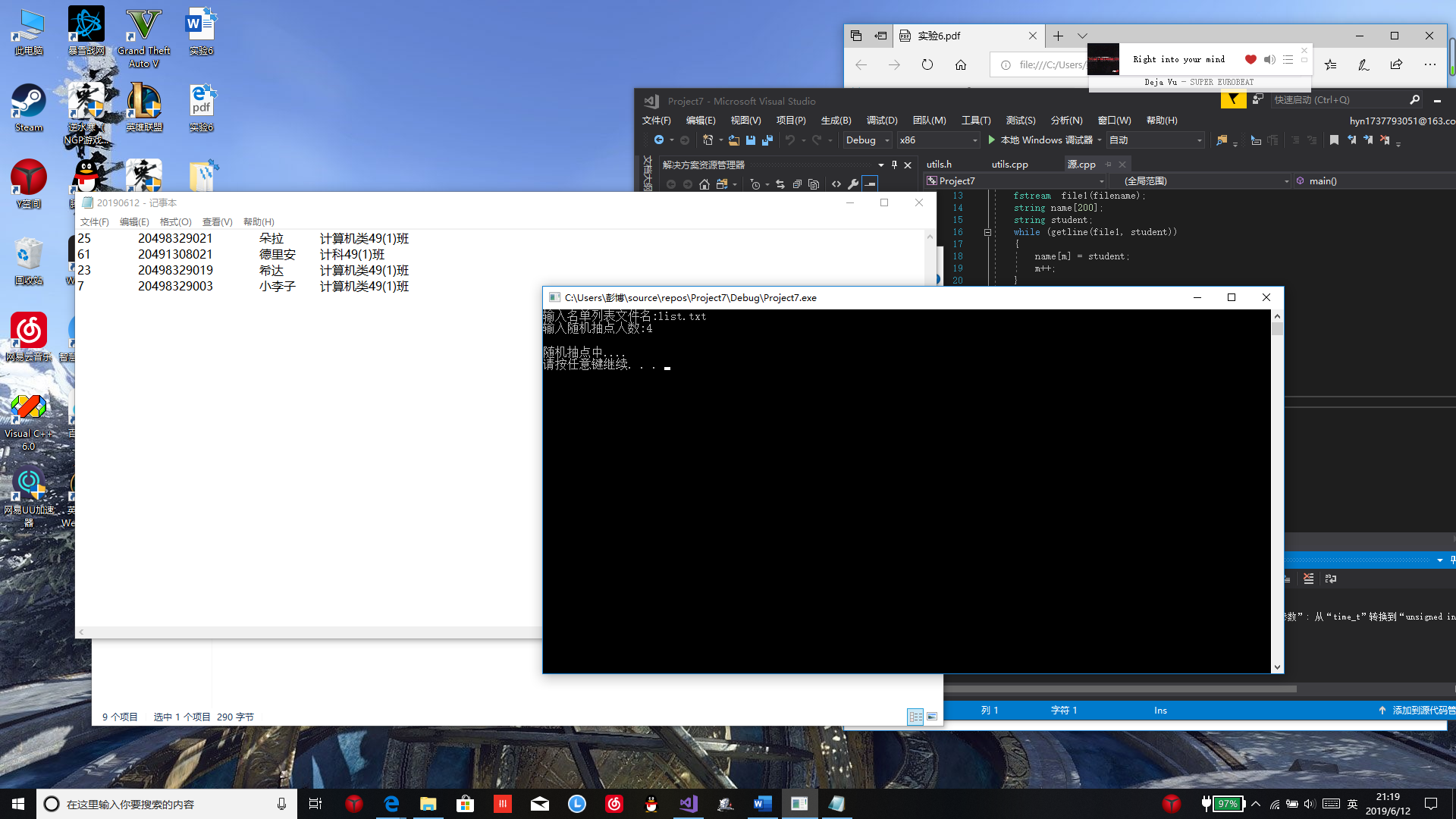
3.随机抽人
#include<iostream> #include<fstream> #include<string> #include<ctime> #include”utils.h” using namespace std; int main() { int n,m=0,t; cout<<"输入名单列表文件名:"; string filename; cin>>filename; fstream file1(filename); string name[200]; string student; while(getline(file1,student)) { name[m]=student; m++; } cout<<"输入随机抽点人数:"; cin>>n; cout<<endl; cout<<"随机抽点中...."<<endl; srand(time(NULL)); fstream file2(getCurrentDate()+”.txt”,ios::app); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { t=rand()%m; file2<<name[t]<<endl; } System(“pause”); return 0; }
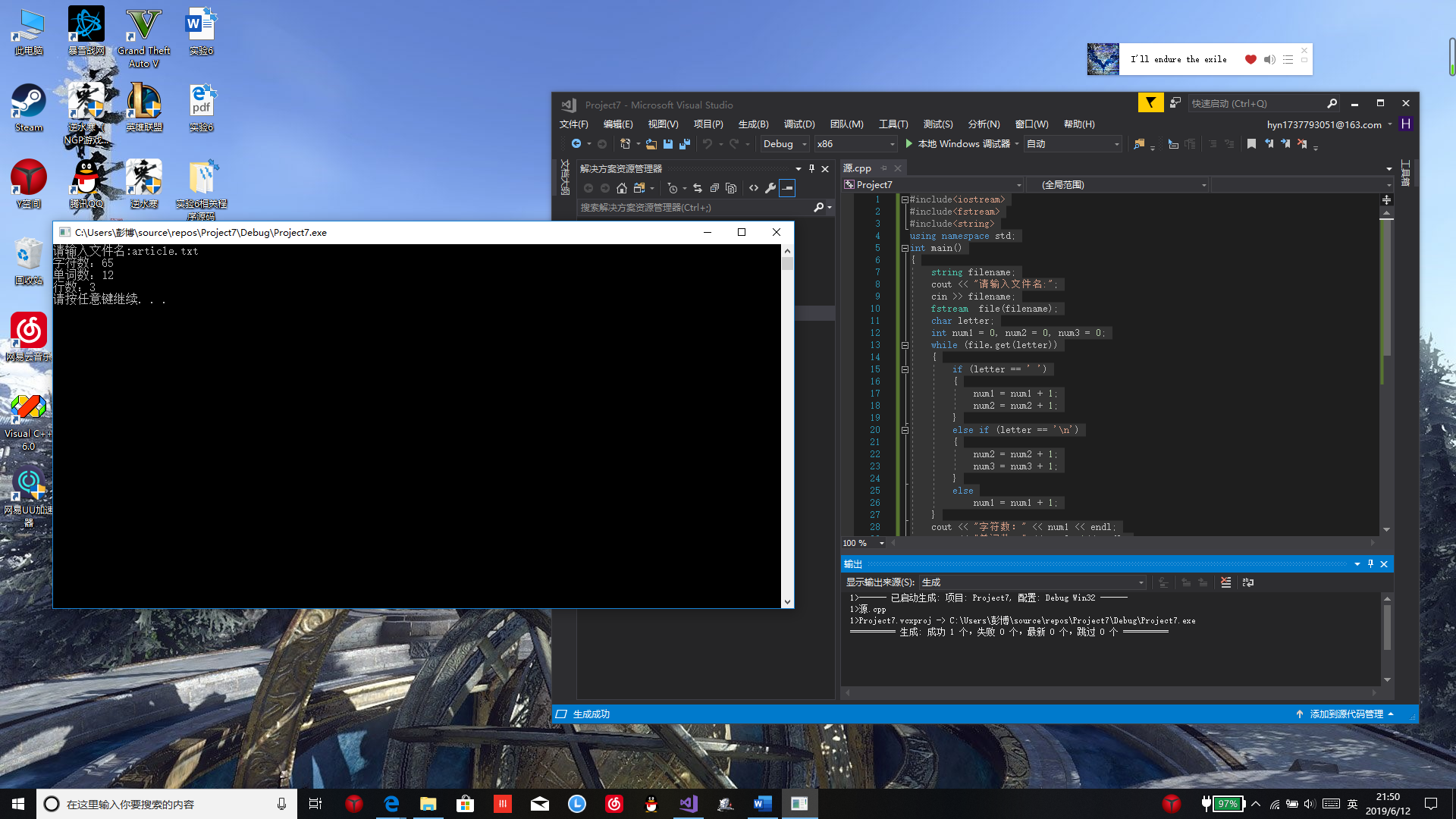
4、统计字符数
#include<iostream> #include<fstream> #include<string> using namespace std; int main() { string filename; cout << "请输入文件名:"; cin >> filename; fstream file(filename); char letter; int num1 = 0, num2 = 0, num3 = 0; while (file.get(letter)) { if (letter == ' ') { num1 = num1 + 1; num2 = num2 + 1; } else if (letter == '\n') { num2 = num2 + 1; num3 = num3 + 1; } else num1 = num1 + 1; } cout << "字符数:" << num1 << endl; cout << "单词数:" << num2 +1<< endl; string line; cout << "行数:" << num3+1 << endl; system("pause"); file.close(); }
1、这次实验使用了很多的新知识,我靠着不停翻书加上请教室友才明白文件的输入输出的方式。
2、随机抽取人数是以前讲过的知识,运用时却跟陌生的一样,还是要多加复习以前的知识。
3、进行文件类编程时还是经常忘记将要打开的文件放入与源代码同一目录下,以后要注意。
4、随机抽取中我将每一行的数据都存为一个string字符串,再保存到数组中再加以操作,后续希望可以学习其他同学更高效的方法。




