HashMap 学习笔记
先摆上JDK1.8中HashMap的类注释;我翻译了一下
/** * Hash table based implementation of the <tt>Map</tt> interface. This * implementation provides all of the optional map operations, and permits * <tt>null</tt> values and the <tt>null</tt> key. (The <tt>HashMap</tt> * class is roughly equivalent to <tt>Hashtable</tt>, except that it is * unsynchronized and permits nulls.) This class makes no guarantees as to * the order of the map; in particular, it does not guarantee that the order * will remain constant over time. * 哈希表实现了Map接口.哈希表允许空的键和值.HashMap相当于Hashtable,只是它是线程不同步的且允许空值. * 这个实现类不保证映射的顺序,尤其是随着时间变化不保证映射的顺序不发生变化. * * <p>This implementation provides constant-time performance for the basic * operations (<tt>get</tt> and <tt>put</tt>), assuming the hash function * disperses the elements properly among the buckets. Iteration over * collection views requires time proportional to the "capacity" of the * <tt>HashMap</tt> instance (the number of buckets) plus its size (the number * of key-value mappings). Thus, it's very important not to set the initial * capacity too high (or the load factor too low) if iteration performance is * important. * 当哈希表中的元素都是正常分布的,get,put操作时间复杂度都是O(1).迭代一个哈希表所需要的时间与哈希表的容量成正比, * 因此如果迭代性能不是很重要,不要将初始容量设置太高(或负载因子太低). * * <p>An instance of <tt>HashMap</tt> has two parameters that affect its * performance: <i>initial capacity</i> and <i>load factor</i>. The * <i>capacity</i> is the number of buckets in the hash table, and the initial * capacity is simply the capacity at the time the hash table is created. The * <i>load factor</i> is a measure of how full the hash table is allowed to * get before its capacity is automatically increased. When the number of * entries in the hash table exceeds the product of the load factor and the * current capacity, the hash table is <i>rehashed</i> (that is, internal data * structures are rebuilt) so that the hash table has approximately twice the * number of buckets. * 一个HashMap两个参数会影响它的性能,初始容量和负载因子.容量是哈希表中的数据量,初始容量只是创建哈希表时的指定的哈希表容量. * 负载因子loadFactor= HashMap中的数据量/HashMap中的总容量(initial capacity),map中的数据量达到 总容量*负载因子时, * HashMap的总容量就会自动扩张一倍. * 注:HashMap的三个构造函数能帮助理解,见本人博客 "HashMap构造函数" * * * <p>As a general rule, the default load factor (.75) offers a good * tradeoff between time and space costs. Higher values decrease the * space overhead but increase the lookup cost (reflected in most of * the operations of the <tt>HashMap</tt> class, including * <tt>get</tt> and <tt>put</tt>). The expected number of entries in * the map and its load factor should be taken into account when * setting its initial capacity, so as to minimize the number of * rehash operations. If the initial capacity is greater than the * maximum number of entries divided by the load factor, no rehash * operations will ever occur. * 作为一般规则,默认负载因子是0.75,这在时间成本和空间成本之间提供了一个比较好的平衡. * 较高的值会降低空间开销,但增加查找成本(大部分体现在对HashMap的操作上,比如get,put). * 在设置初始容量时,应当考虑map中的数据量和负载因子,以便最小化重新对map结构进行扩容的操作. * 注:这和ArrayList的ensureCapaciry(int size)有点类似. * * * <p>If many mappings are to be stored in a <tt>HashMap</tt> * instance, creating it with a sufficiently large capacity will allow * the mappings to be stored more efficiently than letting it perform * automatic rehashing as needed to grow the table. Note that using * many keys with the same {@code hashCode()} is a sure way to slow * down performance of any hash table. To ameliorate impact, when keys * are {@link Comparable}, this class may use comparison order among * keys to help break ties. * 如果许多映射要存储在HashMap实例中,那么将实例的初始容量设置比较大要比按需要自动扩容效率要高. * 请注意,使用相同的键(hashCode)是降低任何哈希表的一个可靠方法,为了改善这种性能问题,使用 * 连续的键. * 注:hashMap允许相同的key,只是值会被覆盖. * * <p><strong>Note that this implementation is not synchronized.</strong> * If multiple threads access a hash map concurrently, and at least one of * the threads modifies the map structurally, it <i>must</i> be * synchronized externally. (A structural modification is any operation * that adds or deletes one or more mappings; merely changing the value * associated with a key that an instance already contains is not a * structural modification.) This is typically accomplished by * synchronizing on some object that naturally encapsulates the map. * 注意,此实现线程不同步.如果多个线程同时访问hashMap,其中有一个线程修改了hashMap的结构.那么必须在 * 外部进行线程同步处理.这通常是对hashMap的操作上进行同步处理封装 * * If no such object exists, the map should be "wrapped" using the * {@link Collections#synchronizedMap Collections.synchronizedMap} * method. This is best done at creation time, to prevent accidental * unsynchronized access to the map:<pre> * Map m = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap(...));</pre> * 因为线程同步问题,可以调用Collections.synchronizedMap来(Map<K,V> m)来返回一个线程安全的hashMap. * * <p>The iterators returned by all of this class's "collection view methods" * are <i>fail-fast</i>: if the map is structurally modified at any time after * the iterator is created, in any way except through the iterator's own * <tt>remove</tt> method, the iterator will throw a * {@link ConcurrentModificationException}. Thus, in the face of concurrent * modification, the iterator fails quickly and cleanly, rather than risking * arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at an undetermined time in the * future. * hashMap同样是快速失败机制.参考我的博客 "Iterator fail-fast" * * <p>Note that the fail-fast behavior of an iterator cannot be guaranteed * as it is, generally speaking, impossible to make any hard guarantees in the * presence of unsynchronized concurrent modification. Fail-fast iterators * throw <tt>ConcurrentModificationException</tt> on a best-effort basis. * Therefore, it would be wrong to write a program that depended on this * exception for its correctness: <i>the fail-fast behavior of iterators * should be used only to detect bugs.</i> * 快速失败机制,是一种错误检测机制.它只能被用来检测错误,JDK并不保证fail-fast一定会发生. * * <p>This class is a member of the * <a href="{@docRoot}/../technotes/guides/collections/index.html"> * Java Collections Framework</a>. * * @param <K> the type of keys maintained by this map * @param <V> the type of mapped values * * @author Doug Lea * @author Josh Bloch * @author Arthur van Hoff * @author Neal Gafter * @see Object#hashCode() * @see Collection * @see Map * @see TreeMap * @see Hashtable * @since 1.2 */ public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
总结
1.数据结构
初始化一个HashMap<String,String>,存储了一些测试数据,
1 Map map = new HashMap(); 2 map.put("What", "chenyz"); 3 map.put("You", "chenyz"); 4 map.put("Don't", "chenyz"); 5 map.put("Know", "chenyz"); 6 map.put("About", "chenyz"); 7 map.put("Geo", "chenyz"); 8 map.put("APIs", "chenyz"); 9 map.put("Can't", "chenyz"); 10 map.put("Hurt", "chenyz"); 11 map.put("you", "chenyz"); 12 map.put("google", "chenyz"); 13 map.put("map", "chenyz"); 14 map.put("hello", "chenyz"); 15 // 每个<k,v>的hash(key)如下: 16 // What-->hash值:8 17 // You-->hash值:3 18 // Don't-->hash值:7 19 // Know-->hash值:13 20 // About-->hash值:11 21 // Geo-->hash值:12 22 // APIs-->hash值:1 23 // Can't-->hash值:7 24 // Hurt-->hash值:1 25 // you-->hash值:10 26 // google-->hash值:3 27 // map-->hash值:8 28 // hello-->hash值:0
此时HashMap的内部如 图1:
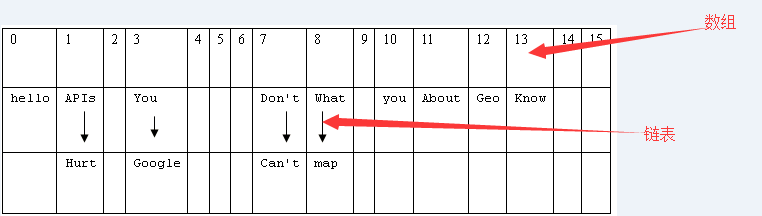
在Java中,最基础的数据类型是数组和链表,HashMap是两者结合体。所以在数据结构中被称作“链表散列”。每创建一个HashMap,就初始化一个数组。
关于这个数组源码是这样定义的:
1 /** 2 * The table, initialized on first use, and resized as 3 * necessary. When allocated, length is always a power of two. 4 * (We also tolerate length zero in some operations to allow 5 * bootstrapping mechanics that are currently not needed.) 6 * 该表首先使用初始化,并根据需要调整大小.分配时长度总是2的幂. 7 * (这个数组的长度有些时候也允许为0) 8 */ 9 transient Node<K,V>[] table; 10 11 static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { 12 final int hash; 13 final K key; 14 V value; 15 Node<K,V> next; 16 17 Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { 18 this.hash = hash; 19 this.key = key; 20 this.value = value; 21 this.next = next; 22 } 23 }
所以,数组中存储的是一个Map.Entry<K,V>,它由hash,key,value,next组成。next是指向下一个元素的引用,这就形成了链表。
2.存储元素
源码如下 :
1 /** 2 * Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map. 3 * If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old 4 * value is replaced. 5 * 6 * @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated 7 * @param value value to be associated with the specified key 8 * @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or 9 * <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>. 10 * (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map 11 * previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.) 12 */ 13 public V put(K key, V value) { 14 return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); 15 } 16 17 /** 18 * Implements Map.put and related methods 19 * 20 * @param hash hash for key 21 * @param key the key 22 * @param value the value to put 23 * @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value 24 * @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode. 25 * @return previous value, or null if none 26 */ 27 final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, 28 boolean evict) { 29 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; 30 if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) 31 n = (tab = resize()).length; 32 if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) 33 tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); 34 else { 35 Node<K,V> e; K k; 36 if (p.hash == hash && 37 ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 38 e = p; 39 else if (p instanceof TreeNode) 40 e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); 41 else { 42 for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { 43 if ((e = p.next) == null) { 44 p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); 45 if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st 46 treeifyBin(tab, hash); 47 break; 48 } 49 if (e.hash == hash && 50 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 51 break; 52 p = e; 53 } 54 } 55 if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key 56 V oldValue = e.value; 57 if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) 58 e.value = value; 59 afterNodeAccess(e); 60 return oldValue; 61 } 62 } 63 ++modCount; 64 if (++size > threshold) 65 resize(); 66 afterNodeInsertion(evict); 67 return null; 68 }
不难理解,首先hash(key)得到key的哈希值,这些值就是“数据结构”中数组的元素。根据hash值确定当前元素的存储格子,如果当前格子已经存储了元素,那么就以链表形式
存到这个格子中,新加入的放在链表的头部,所以最早加入的就被排在了链尾部。如图1中hash值为1的位置,就以链表的形式存储了两个值。
每一次添加元素都会修改modCount全局变量,这是是用来检测HashMap在迭代的过程中是否发生了结构变化
同时这里还会设计到扩容resize().详见“HashMap负载因子”
3.索引元素
源码如下:
1 public V get(Object key) { 2 Node<K,V> e; 3 return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value; 4 } 5 6 /** 7 * Implements Map.get and related methods 8 * 9 * @param hash hash for key 10 * @param key the key 11 * @return the node, or null if none 12 */ 13 final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) { 14 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k; 15 if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && 16 (first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) { 17 if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node 18 ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 19 return first; 20 if ((e = first.next) != null) { 21 if (first instanceof TreeNode) 22 return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key); 23 do { 24 if (e.hash == hash && 25 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 26 return e; 27 } while ((e = e.next) != null); 28 } 29 } 30 return null; 31 }
首先计算出key的hash值,找到数组中对应的下标,然后通过key的equals方法匹配出对应位置的链表中的元素,这就完成了元素get的操作。这也是为什么要成对复写hashCode
和equals方法的原因。由此可知HashMap的get操作,效率会有瓶颈,如果一个位置存放了大量的元素,由于是链表存储的,就需要挨个比对,才能找到匹配的值。
所以让HashMap中的元素均匀的分布,每个位置上的链表只存储一个元素那么HashMap的效率就会很高。
4.性能因素
创建一个HashMap时,有initialCapacity和loadFactor这两个初始化参数,初始容量和负载因子。
这两个参数的设置会决定一个HashMap结构是否合理。详见“HashMap 负载因子”
5.hash算法
这是整个HashMap最核心的方法了,因为get(),put()操作都会用到这个方法,用于定位。确定新元素的存放位置。这关系着元素分布是否合理。
1 /** 2 * Computes key.hashCode() and spreads (XORs) higher bits of hash 3 * to lower. Because the table uses power-of-two masking, sets of 4 * hashes that vary only in bits above the current mask will 5 * always collide. (Among known examples are sets of Float keys 6 * holding consecutive whole numbers in small tables.) So we 7 * apply a transform that spreads the impact of higher bits 8 * downward. There is a tradeoff between speed, utility, and 9 * quality of bit-spreading. Because many common sets of hashes 10 * are already reasonably distributed (so don't benefit from 11 * spreading), and because we use trees to handle large sets of 12 * collisions in bins, we just XOR some shifted bits in the 13 * cheapest possible way to reduce systematic lossage, as well as 14 * to incorporate impact of the highest bits that would otherwise 15 * never be used in index calculations because of table bounds. 16 */ 17 static final int hash(Object key) { 18 int h; 19 return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); 20 }
这与以往jdk中有些区别,至于为什么这样计算,目前还在学习中。
6.安全问题
HashMap线程不同步,采用fail-fast机制。多线程下,在迭代器中,如果有线程修改了HashMap结构,会抛出 Java.util.ConcurrentModificationException异常
学海无涯,学习是苦涩的.坚持,看了两天了,还有很多不明白的地方,不放弃,持续更新。
谢谢一下同仁的分享
参考资料:



