数据结构与算法(22)——树
- 树
树是一种基本的“非线性”数据结构。基本术语
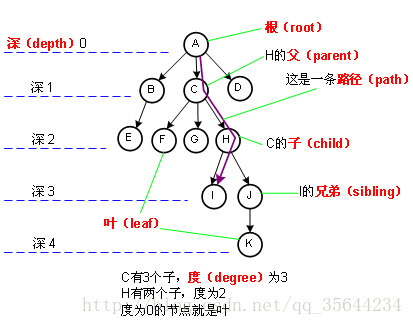
节点Node
边Edge
度:结点拥有的子树数目,如上图结点A的度为3,结点E的度为0
树的度:各个结点中度的最大值
根Root:树中唯一一个没有入边的节点
路径Path:由边依次连接在一起的节点有序表
子节点Children:入边均来自同一个节点的若干节点
父节点Paren:一个节点是其所有边所连接节点的父节点。
兄弟节点Sibling:具有同一个父节点的节点之间的节点称为兄弟节点。
子树Subtree:一个节点和其所有子孙节点,以及相关边的集合。
叶节点Leaf:没有子节点的节点称为叶节点(度为0的结点(没有子树的结点))
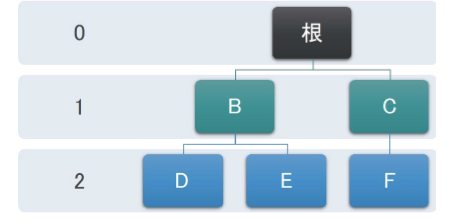
层级Level:从根节点开始到达一个节点的路径, 所包含的边的数量,称为这个节点的层级。 如下图D的层级为2,根节点的层级为0
高度(深度):树中所有节点的最大层级称为树的高度 ,如下图所示树的高度为2
二叉树:其中一个节点被设定为根; 每个节点n(除根节点),都恰连接一 条来自节点p的边,p是n的父节点; 每个节点从根开始的路径是唯一的,如果每个节点最多有两个子节点, 这样的树称为“二叉树”
- 二叉树的性质
二叉树的性质
- 在二叉树的第i层,至多有2^(i-1)个结点
- 深度为k的二叉树至多有:(2^k)-1个结点,其实这个结果就是一个等比数列的求和得到的。
- 对任意一颗二叉树,如果其叶子结点数量为:n0,度为2的结点数为:n2,则:n0=n2+1
证明:这里对第三个性质做一个解释,首先我们都知道一个二叉树每个结点都是由度为0,1,2,三种情况,这里假设,二叉树有n个结点,其中度为1的结点数为:n1,于是由已知条件可知:n=n1+n0+n2;
另外一个角度想,二叉树有B条边,假设这些边都是从父亲结点指向它的孩子,那么会发现除了根结点外,其他结点都是有一条边的,
所以:n=B+1,其中这些边都是由度为1和2的结点射出来的,
所以:B=n1+2*n2,因此:n=n1+2*n2+1.
所以,联立等式:n1+2*n2+1=n1+n0+n2,
我们可以得到一个等式:n0=n2+1;
- 具有n个结点的完全二叉树的深度为:[log2n]+1,其中[log2n]+1是向下取整。
证明:首先先定义满二叉树:一颗深度为k且结点数为:(2^k)-1的二叉树,称为满二叉树,然后,对满二叉树进行编号,从根结点开始,从左往右,从上到下。
然后可以定义一个完全二叉树:深度为k,结点数为n的二叉树,而且,每一个结点的位置都和深度为k的完全二叉树中编号为1到n的结点一一对应,我们称为完全二叉树。
如下图所示:
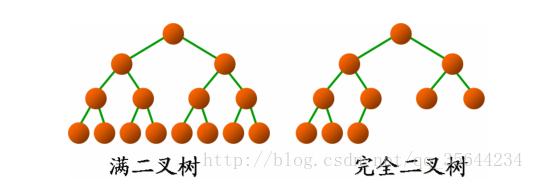
可以解释第四个性质,假设深度为k,由完全二叉树的定义,可以知
道:2^(k-1)-1< n <=(2^k)-1 即:2^(k-1)<=n<(2^k),所以:k-1 < = [log2n] < k,因为k是整数,所以k=[log2n]+1,其中[log2n]+1是向下取整。
有N个结点的完全二叉树各结点如果用顺序方式存储,则结点之间有如下关系:
若i为结点编号则 如果i>1,则其父结点的编号为[i/2],[i/2]是往下取整的;
如果2i<=N,则其左儿子(即左子树的根结点)的编号为2i;若2i>N,则无左儿子;
如果2i+1<=N,则其右儿子的结点编号为2i+1;若2i+1>N,则无右儿子。
- 树的应用
文件系统、HTML文档(嵌套标记)、域名体系。
- 实现树:嵌套列表法
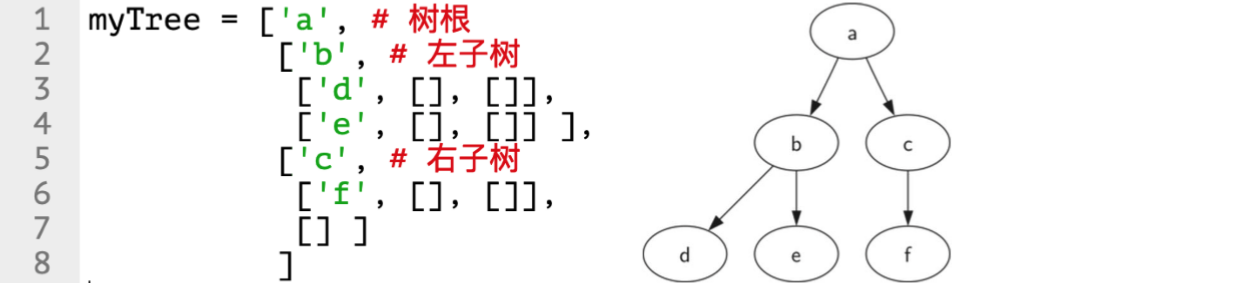
以右图的示例,一个6节点的二叉树 根是myTree[0],左子树myTree[1],右子树 myTree[2] 。
嵌套列表法的优点 子树的结构与树相同,是一种递归数据结构 很容易扩展到多叉树,仅需要增加列表元素即可
函数定义:
BinaryTree创建仅有根节点的二叉树
insertLeft/insertRight将新节点插入树中作为其直接的左/右子节点
get/setRootVal则取得或返回根节点
getLeft/RightChild返回左/右子树
#树的嵌套实现 def BinaryTree(r): return [r, [], []] def insertLeft(root, newBranch): t = root.pop(1) if len(t) > 1: root.insert(1, [newBranch,t,[]]) else: root.insert(1,[newBranch,[],[]]) return root def insertRight(root, newBranch): t = root.pop(2) if len(t) > 1: root.insert(2, [newBranch,[], t]) else: root.insert(2,[newBranch,[],[]]) return root def grtRootVal(root): return root[0] def setRootVal(root, newVal): root[0] = newVal def getLeftChild(root): return root[1] def getRightChild(root): return root[2] r = BinaryTree(3) insertLeft(r, 4) insertLeft(r, 5) insertRight(r,6) insertRight(r,7) l = getLeftChild(r) rl = getRightChild(r) print("line1:", l) print("right line:", rl) print("root line:", r) setRootVal(l, 9) print("line2:", r) print("left sub tree:", getLeftChild(l)) insertLeft(l, 11) print("line3:",r) print(getRightChild(getRightChild(r)))
输出
line1: [5, [4, [], []], []] right line: [7, [], [6, [], []]] root line: [3, [5, [4, [], []], []], [7, [], [6, [], []]]] line2: [3, [9, [4, [], []], []], [7, [], [6, [], []]]] left sub tree: [4, [], []] line3: [3, [9, [11, [4, [], []], []], []], [7, [], [6, [], []]]] [6, [], []] Process finished with exit code 0
- 实现树:节点链接法
成员key保存根节点数据项
成员left/rightChild则保存指向左/右子树的 引用(同样是BinaryTree对象)
二叉树的前序、中序、后序遍历:
- 前序遍历(DRL)
(1)先访问根结点
(2)先序遍历左子树
(3)先序遍历右子树 - 中序遍历(LDR)
(1)先中序遍历左子树
(2)访问根结点
(3)中序遍历右子树 - 后序遍历(LRD)
(1)后序遍历左子树
(2)后序遍历右子树
(3)访问根结点

class BinaryTree: def __init__(self, rootObj): self.key = rootObj self.leftChild = None self.rightChild = None def insertLeft(self, newNode): if self.leftChild == None: self.leftChild = BinaryTree(newNode) else: #这里不是很理解,类似链表的操作,添加左子节点需要将待添加的左子节点指向原来的左子节点 t = BinaryTree(newNode) t.leftChild = self.leftChild self.leftChild = t def insertRight(self, newNode): if self.rightChild == None: self.rightChild = BinaryTree(newNode) else: t = BinaryTree(newNode) t.rightChild = self.rightChild self.rightChild = t def getRightChild(self): return self.rightChild def getLeftChild(self): return self.leftChild def setRootVal(self, obj): self.key = obj def getRootVal(self): return self.key def preorder(self): #前序遍历 print(self.key) if self.leftChild: self.leftChild.preorder() if self.rightChild: self.rightChild.preorder() def postorder(self): #后序遍历 if self.leftChild: self.leftChild.postorder() if self.rightChild: self.rightChild.postorder() print(self.key) def inorder(self): #中序遍历 if self.leftChild: self.leftChild.inorder()
print(self.key) if self.rightChild: self.rightChild.inorder()
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35644234/article/details/53013738



