std::out_of_range异常
使用C++容器类访问成员时由于使用问题可能会遇到"terminate called after throwing an instance of 'std::out_of_range'"或者"Abort message: 'terminating with uncaught exception of type std::out_of_range"。问题的大概意思是:访问越界了。没有捕获std::out_of_range类型的异常终止。
通常在使用vector、map这样的C++容器类型时会遇到,这里我们以map类型为例,加以说明。
- std::out_of_range异常的描述
- 导致std::out_of_range的原因
- 如何避免std::out_of_range异常(即std::xx::at的使用)
std::out_of_range异常的描述
假设我们定义了一个map类型的变量g_mapIsDestroyedRefCount,要访问容器中的数据项有多种方式。例如,获取g_mapIsDestroyedRefCount中key值为cameraId的值,可以这样:
- g_mapIsDestroyedRefCount[cameraId]
- g_mapIsDestroyedRefCount.at(cameraId)
两种写法都可以获取key为cameraId的value,一般效果看不出来差别,但是当g_mapIsDestroyedRefCount中不存在key为cameraId的<key, value>时就会出现“std::out_of_range”访问越界问题。
那么疑问来了:为什么at方式访问存在访问越界问题,[]方式访问不存在越界问题?因为C++容器类实现有关。
当[]方式访问不存在的<key, value>时为什么不会std::out_of_range
[]方式访问map容器元素时,遍历容器元素没找到指定的键值对时会将相应的键值对插入,键为检索的key,value为零值。例如,下面例子中cameraId:2不在map中,这时通过[]式访问,会自动将<2, 0>插入到
g_mapIsDestroyedRefCount,然后返回[2]。
导致std::out_of_range的原因
容器类型访问方法使用有问题
对于std::map::at官方声明:
mapped_type& at (const key_type& k); const mapped_type& at (const key_type& k) const;
Returns a reference to the mapped value of the element identified with key k. 返回元素键为k的映射值的引用,即Key为k的元素的对应value值。
If k does not match the key of any element in the container, the function throws an out_of_range exception. 如果容器中没有匹配的k键,该函数将抛出一个out_of_range异常
如何避免std::out_of_range异常
- 正确使用
- 错误使用
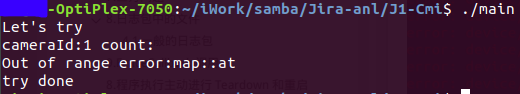
1.std::map::at的正确使用
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <map> std::map<int, int> g_mapIsDestroyedRefCount; int main() { int cameraId = 1; cout << "Let's try"<< endl; //向map中添加测试数据 g_mapIsDestroyedRefCount.insert(std::pair<int, int>(0, 2))' cout << "cameraId:"<< cameraId<< "count:"; try { cout<< g_mapIsDestroyedRefCount.at(cameraId) <<endl; } catch (const std::out_of_range& oor) { std::cerr << "\nOut of range error:" << oor.what()<< endl; } cout << "try done"<< endl; return 0; }
运行结果:
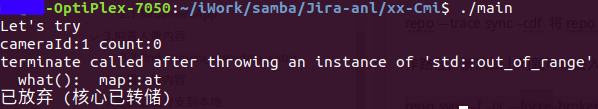
2.std::map::at错误使用
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <map> using namespace std; std::map<int, int> g_mapIsDestroyedRefCount; int main() { int cameraId = 2; cout<< "Let's try"<< endl; g_mapIsDestroyedRefCount.insert(std::pair<int, int>(0, 2)); cout<< "cameraId:"<< cameraId<< "count:"; //介绍中说的方法一,可以访问 cout<< g_mapIsDestroyedRefCount[cameraId]<< endl;
//方法二,异常
cameraId = 2; count<< g_mapIsDestroyedRefCount.at(cameraId)<< endl;
cout<< "try done"<< endl;
}
运行结果:(程序异常退出)