java第11次作业
一. 本周学习总结
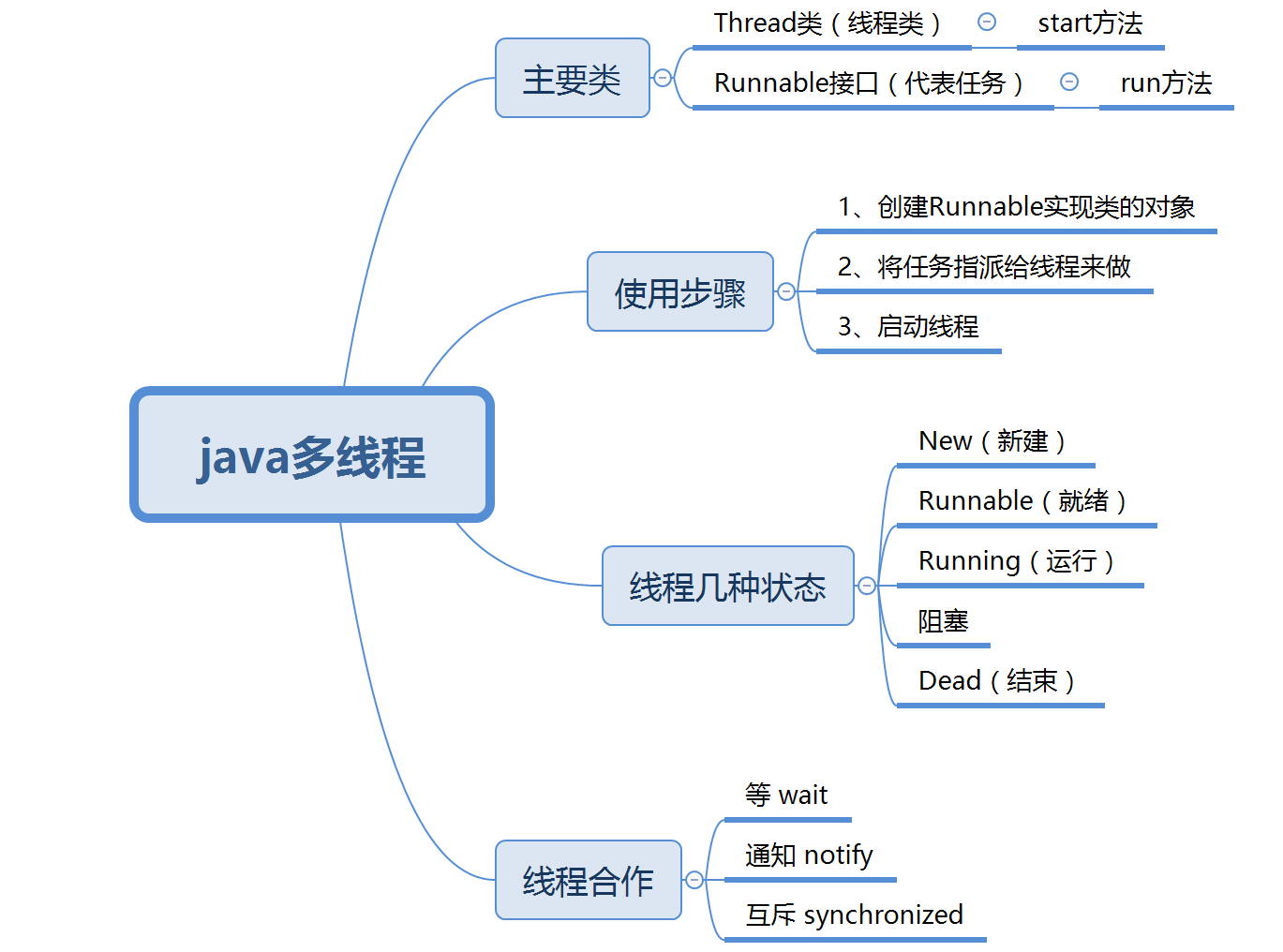
1.1 以你喜欢的方式(思维导图或其他)归纳总结多线程相关内容。
二. 书面作业
本次PTA作业题集多线程
1. 源代码阅读:多线程程序BounceThread
1.1 BallRunnable类有什么用?为什么代码中需要调用Thread.sleep进行休眠?
答:BallRunnable类是支持多线程的类,开启了一个程序,使小球按照指定的规则移动,然后画出来获得小球的形状。代码中调用Thread.sleep进行休眠是为了延缓线程完成的时间,这样我们才能看到小球的移动,不然太快了看不到小球的移动轨迹。
1.2题:
a)Ball.java只做了两件事,这两件事分别是什么?
答:move()方法,实现小球的移动; getShape()方法,获取小球的坐标和大小。
b)BallComponent对象是干什么的?
答:添加小球;画出小球。
c)其内部的ArrayList有什么用?
答:用于存放添加的小球。
d)程序运行过程中,生成了几个BallComponent对象?
答:只有1个。
e)该程序使用了多线程技术,每个小球是分别在不同的线程中进行绘制吗?
答:是。每按一次start按钮,addBall方法都会启动一个新线程。
2. 实验总结:题集(多线程)
2.1 题目:Thread、PrintTask、Runnable与匿名内部类。并回答:
a)通过定义Runnable接口的实现类来实现多线程程序比通过继承自Thread类实现多线程程序有何好处?
答:Java中不支持多继承,只能继承一个父类,但可以继承多个接口,所以使用实现接口的方法可以避免继承的局限。使用Runnable实现多线程使多个线程一起完成多个任务。
b) 6-1,6-3,6-11实验总结。
- 6-1: 在构造该线程的时候,将要循环的次数num传入。然后重写run()方法。最后使用
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+isAlive())打印标识信息。 - 6-3:在Main方法中启动一个线程t1,该线程打印3行信息: 主线程名;线程t1的线程名 ;线程t1所实现的所有接口,使用
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getClass().getInterfaces()));打印。 - 6-11:这题主要是编写
PrintTask类实现Runnable接口,功能主要是输出从0到n-1的整数(n在创建PrintTask对象的时候初始化)。并在最后使用System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());输出标识信息。
2.2 使用Lambda表达式改写6-3
Thread t1 = new Thread(
() -> {
System.out.println(mainThreadName);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(Thread.class.getInterfaces()));
}
);
2.3 题目:6-2(Runnable与停止线程)。回答:需要怎样才能正确地停止一个运行中的线程?
- 6-2:这题的重点主要是run()方法的内容。对每个传入的word只检查一遍(检查完后将word置为null)。跳出无限循环后,使用
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " stop")打印标识信息。 - 答:一般使用一个boolean类型的变量用来终止线程。使用while语句,在运行中通过改变boolean标记值,退出循环以达到停止线程的作用。
3. 互斥访问
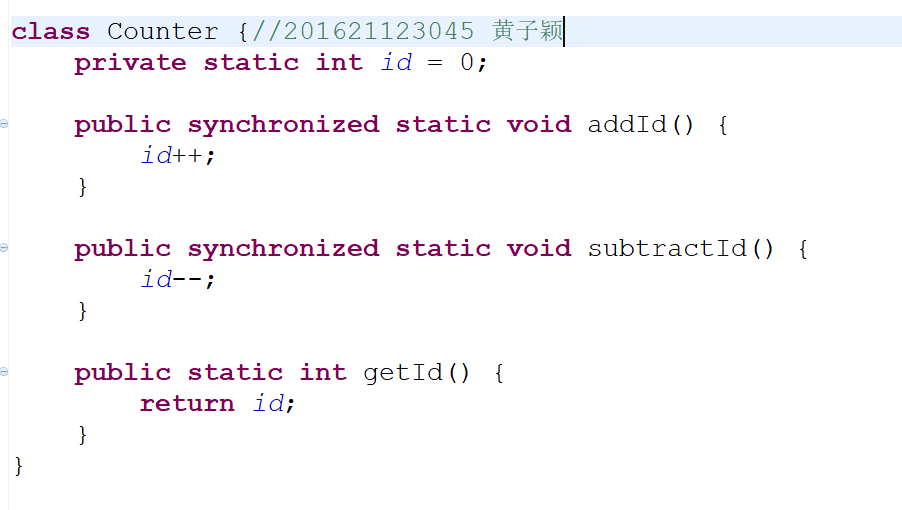
3.1 修改TestUnSynchronizedThread.java源代码使其可以同步访问。(关键代码截图,需出现学号)
截图如下:
4. 互斥访问与同步访问
完成题集6-4(互斥访问)与6-5(同步访问)
4.1 除了使用synchronized修饰方法实现互斥同步访问,还有什么办法可以使用synchronized实现互斥同步访问,使用代码说明(请出现相关代码及学号)?
- 可以使用
synchronized代码块:
public static void addId() {//黄子颖 201621123045
synchronized (Counter.class) {//代表Counter类型的对象
id++;
}
}
- 使用显式的
Lock和Condition对象:
class Account {//黄子颖 201621123045
private int balance;
public Account(int balance) {
super();
this.balance = balance;
}
public int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void deposit(int money) {
lock.lock();
try {
balance += money;
condition.signalAll();
} finally {
// TODO: handle finally clause
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void withdraw(int money) {
lock.lock();
try {
while (balance < money) {
try {
condition.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
balance -= money;
} finally {
// TODO: handle finally clause
lock.unlock();
}
}
private java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock lock = new java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock();
private java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
}
4.2 同步代码块与同步方法有何区别?
- 同步方法直接在方法上使用
synchronized修饰,实现加锁;而同步代码块在内部使用synchronized代码块。 - 同步代码块的性能更好些,但是同步方法的范围比较大。
4.3 实现互斥访问的原理是什么?请使用对象锁概念并结合相应的代码块进行说明。当程序执行synchronized同步代码块或者同步方法时,线程的状态是怎么变化的?
答:原理是当资源被一个任务使用时,其上加锁。现在在访问某项资源的任务必须锁定这种资源,这时其他任务无法访问它。其被解锁时,另一个任务可以锁定并且使用该资源了。例如:在下面的代码段中,可以获得对象“this”上的内部锁。当执行程序时,如果不能获得相对应的对象锁,那么将不能执行上述代码块中的内容,即synchronized同步代码块中的i++语句,就必须等待,等待获得对象锁。从而通过对象锁实现了互斥访问。
class MyCounter{
private int i = 0;
public void increment(){
//i++;
synchronized (this) {
i++;
}
}
……
}
线程的状态的变化为:如果没有获得对象锁就进入Look Pool状态,等待同步锁被释放;同步锁释放后,线程进入Runnable状态。
4.4 Java多线程中使用什么关键字实现线程之间的通信,进而实现线程的协同工作?
答:Java多线程中使用wait()和notify()/notifyAll()方法来实现线程之间的通信,进而实现线程的协同工作的。
5. 线程间的合作:生产者消费者问题
5.1 运行MyProducerConsumerTest.java。正常运行结果应该是仓库还剩0个货物。多运行几次,观察结果,并回答:结果正常吗?哪里不正常?为什么?
运行结果如下:



答:结果可能会不正常,剩余货物可能不为0,可能是其他的数量。因为生产者与消费者的存取速度不一致,可能出现了没有库存还在取货物的情况。
5.2 使用synchronized, wait, notify解决该问题(关键代码截图,需出现学号)
截图如下:

6. 面向对象设计作业-图书馆管理系统
6.1 系统的功能模块表格,表格中体现出每个模块的负责人。
| 负责人 | 学号 | 模块 |
|---|---|---|
| 黄子颖 | 201621123045 | 图书管理、菜单和主函数 |
| 翁华辉 | 201621123042 | 用户管理 |
6.2 运行视频

6.3 讲解自己负责的模块,并粘贴自己负责模块的关键代码(出现学号及姓名)。
我负责的是菜单和主函数还有图书管理模块的部分:
主函数Text:
public class Text {//201621123045 黄子颖
public static void main(String[] args) {
Menu menu=new Menu();
boolean flag=false;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while(!flag) {
System.out.println("\n\t ~~~图书馆借阅系统~~~");
System.out.println("\t欢迎使用本图书馆借阅系统!");
System.out.println("\t1.注册账号");
System.out.println("\t2.登录");
System.out.println("\t3.退出系统");
System.out.println("请输入序号:\n");
switch(sc.nextInt()) {
case 1: menu.register(); break;
case 2: menu.login(); break;
case 3: System.out.print("成功退出图书馆借阅系统!!!!"); flag=true; break;
default: System.out.println("请输入正确的操作序号"); break;
}
}
}
}
菜单Menu:
public class Menu {//201621123045 黄子颖
public User user;
public Student register() {
System.out.println("请输入您的注册信息:");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("姓名:\t");
String name=sc.nextLine();
System.out.print("学号:\t");
long ID=Long.parseLong(sc.nextLine()) ;
System.out.print("密码:\t");
String password=sc.nextLine();
Student s=new Student(name, ID, password);
if(UserUnit.isContain(s)) {
System.out.print("账户已存在!请重新注册!");
return register();
}
UserUnit.add(s);
user=s;
System.out.print("\t注册成功!!!!正在为您登陆!!请稍等。。。");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e+"\n\n");
e.printStackTrace();
}
run();
return s;
}
public User login() {
System.out.println("请输入您的登录信息:");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("学号:\t");
long ID=Long.parseLong(sc.next()) ;
System.out.print("登录密码:\t");
sc.nextLine();
String password=sc.nextLine();
if(UserUnit.peekUser(ID)==null) {
System.out.print("账号不存在!!!!");
return login();
}
if(!UserUnit.peekUser(ID).getPassword().equals(password)) {
System.out.println("密码错误!!!");
return login();
}
user=UserUnit.peekUser(ID);
System.out.println("登录成功!!!!");
run();
return user;
}
public void run() {
if(user==null) {
System.out.print("菜单显示错误:请先登录");
return;
}
Menu menu=new Menu();
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
Student stu=(Student)user;
boolean flag=false;
while(!flag) {
System.out.print("\n\t你好,"+user.getName()+"("+user.getID()+")\n" );
System.out.println("MENU:");
System.out.println("\t1.展示图书馆中的书籍");
System.out.println("\t2.借阅书籍");
System.out.println("\t3.归还书籍");
System.out.println("\t4.查询已借阅的书籍");
System.out.println("\t5.退出登录");
System.out.println("请输入序号:");
switch(sc.nextInt()) {
case 1:
Library.display();
System.out.println("\n\t。。。输入任意字符或者点击回车键返回上一级菜单。。。");
sc.nextLine();sc.nextLine();
break;
case 2:
Library.display();
System.out.println("\t请输入所借阅图书的ID:");
Book book=stu.borrow(sc.nextLong());
if(book==null)
System.out.println("借书失败!!!此书籍不存在或者无库存");
else if(stu.getBookLoan().containsKey(book))
System.out.println("借书成功!!! 请记得及时归还!!!");
else
System.out.println("借书成功!!! 请记得及时归还!!!");
System.out.println("\n\t。。。输入任意字符或者点击回车键返回上一级菜单。。。");
sc.nextLine();sc.nextLine();
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("\t请输入所归还图书的ID:");
Book book1=stu.giveback(sc.nextLong());
if(book1==null)
System.out.println("归还失败!!!您未借过本书");
else
System.out.println("归还成功!!!");
System.out.println("\n\t。。。输入任意字符或者点击回车键返回上一级菜单。。。");
sc.nextLine();sc.nextLine();
break;
case 4:
stu.displayloan();
System.out.println("\n\t。。。输入任意字符或者点击回车键返回上一级菜单。。。");
sc.nextLine();sc.nextLine();
break;
case 5:
flag=true;
System.out.println("\n\t。。。请稍后。。。");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e+"\n\n");
e.printStackTrace();
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("请输入正确的操作序号");
break;
}
}
}
}
图书馆Lib:
public class Lib {//201621123045 黄子颖
public enum LendOrBack{
LEND,BACK
}
private static Map<Book,Integer> books=new TreeMap<Books,Integer>();
static{
initializeBookStore();
}
private static void initializeBookStore(){
Book book1 = new Books("红",100,"文学");
Book book2 = new Books("橙",101,"艺术");
Book book3 = new Books("黄",102,"经济");
Book book4 = new Books("绿",103,"娱乐");
Book book5 = new Books("青",130,"杂志");
Book book6 = new Books("蓝",140,"报纸");
Book book7 = new Books("紫",300,"哲学");
books.put(book1, 33);
books.put(book2, 44);
books.put(book3, 66);
books.put(book4, 11);
books.put(book5, 22);
books.put(book6, 55);
books.put(book7, 44);
}
public static Map<Book, Integer> getBooks() {
return books;
}
public static Book peekBook(long ID) {
Iterator<Map.Entry<Books, Integer>> m = books.entrySet().iterator();
while(m.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<Books, Integer> e = m.next();
if(e.getKey().getID()==ID&&e.getValue()>0)
return e.getKey();
}
return null;
}
public static ArrayList<Book> peekBooks(String name) {
ArrayList<Book> bookList=new ArrayList<Books> ();
Iterator<Map.Entry<Books, Integer>> m = books.entrySet().iterator();
while(m.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<Books, Integer> e = m.next();
if(e.getKey().getName()==name&&e.getValue()>0)
bookList.add(e.getKey());
}
return bookList;
}
public static void add(Books book,int num){
if(books.get(book)==null){
books.put(book, num);
}
else{
books.put(book, books.get(book)+num);
}
}
public static void remove(Books book){
books.remove(book);
}
public static void lendOrBack(Book book,LendOrBack action){
switch(action) {
case LEND:{
books.put(book, books.get(book)-1);
break;
}
case BACK:{
books.put(book, books.get(book)+1);
break;
}
}
}
public static void display(){
Iterator<Map.Entry<Book, Integer>> m = books.entrySet().iterator();
System.out.println(" 书名 \t\tID\t\t类别\t\t数量");
while(m.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<Book, Integer> e = m.next();
if(e.getValue()>0)
System.out.println(e.getKey().toString()+"\t\t"+e.getValue());
}
System.out.println();
}
}
图书Books:
public class Bs implements Comparable<Books>{//201621123045 黄子颖
private String name;
private long ID;
private String category;
public Books(String name,long ID,String category){
this.name = name;
this.ID = ID;
this.category = category;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public long getID() {
return ID;
}
public void setID(long iD) {
ID = iD;
}
public String getCategory() {
return category;
}
public void setCategory(String category) {
this.category = category;
}
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + (int) (ID ^ (ID >>> 32));
result = prime * result + ((category == null) ? 0 : category.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Book other = (Book) obj;
if (ID != other.ID)
return false;
if (category == null) {
if (other.category != null)
return false;
} else if (!category.equals(other.category))
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
public int compareTo(Books o) {
return (int) (ID-o.ID);
}
public String toString() {
return "《"+name+"》 \t\t"+ID+"\t\t"+category;
}
}
三.码云及PTA
题目集:多线程
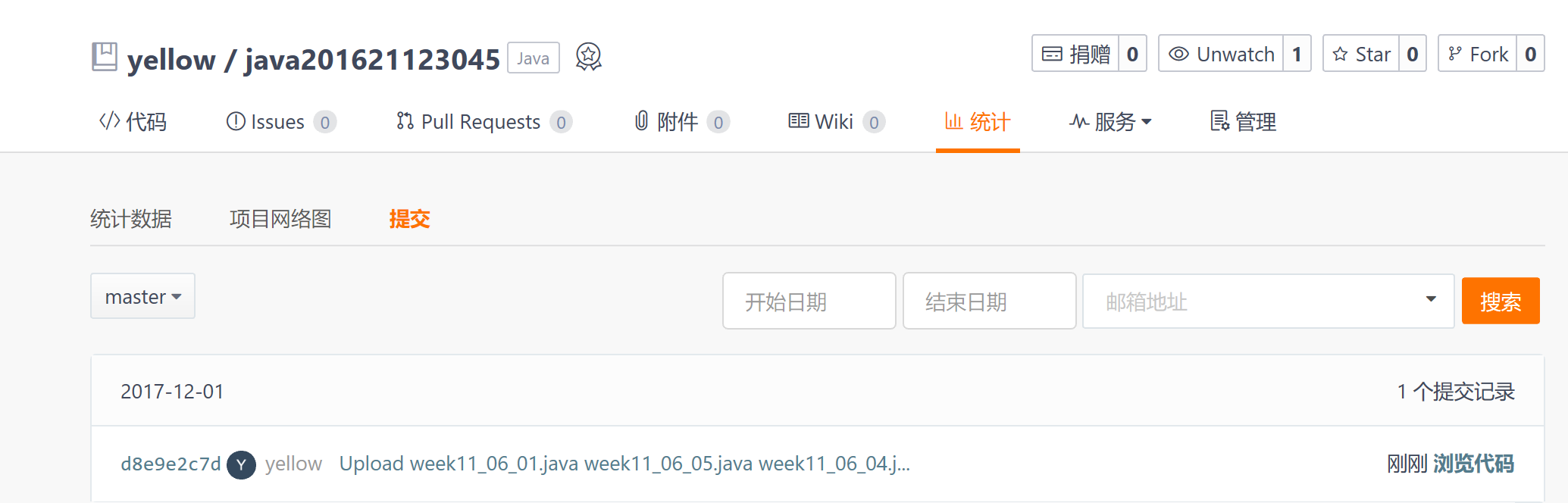
3.1. 码云代码提交记录
在码云的项目中,依次选择“统计-Commits历史-设置时间段”, 然后搜索并截图
必须出现几个要素:提交日期-用户名(姓名与学号)-不提交说明
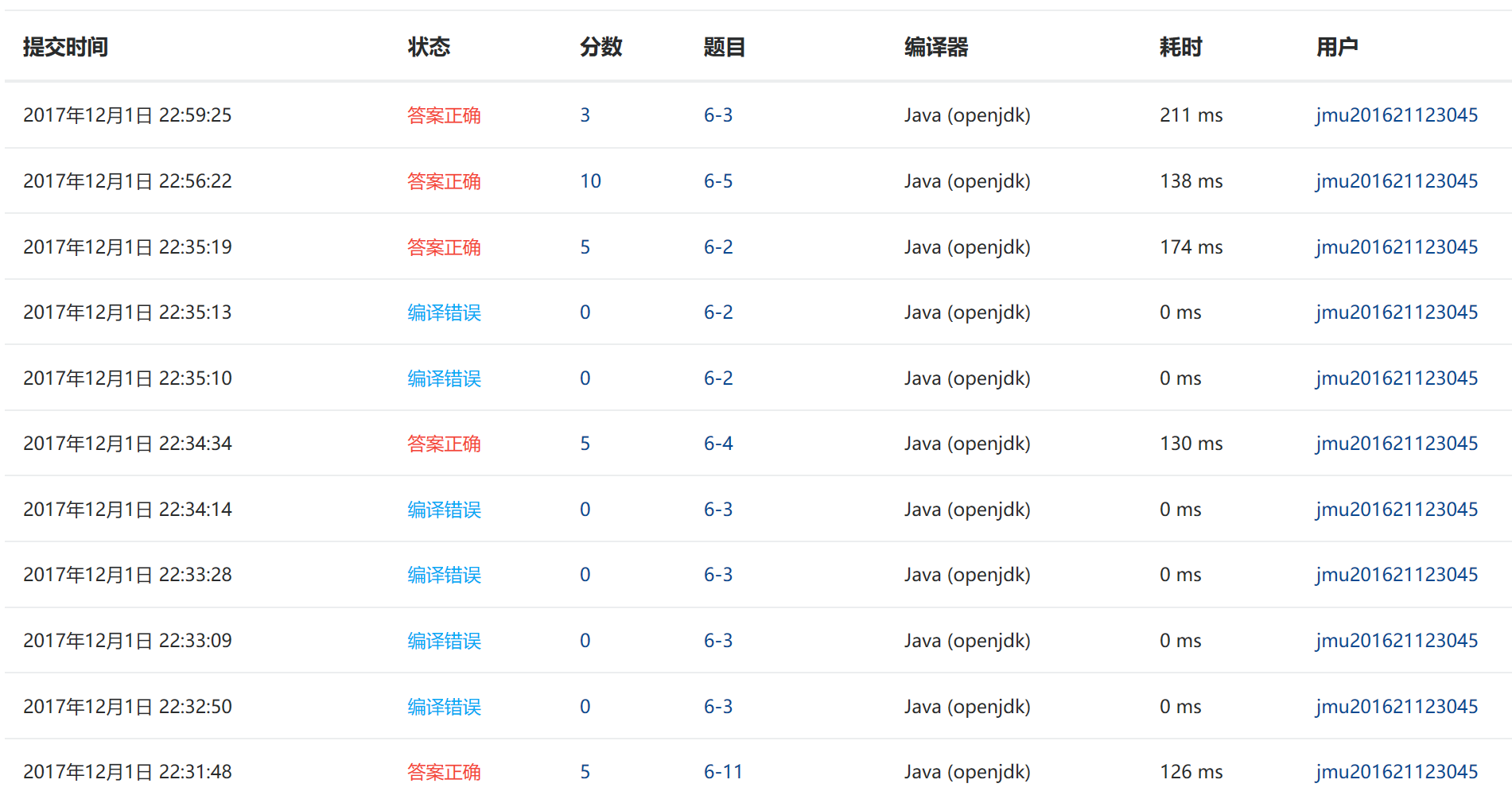
3.2 截图"多线程"PTA提交列表
需要有两张图(1. 排名图。2.PTA提交列表图)


3.3 统计本周完成的代码量
需要将每周的代码统计情况融合到一张表中。
| 周次 | 行数 | 新增行数 | 文件数 | 新增文件数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 115 | 115 | 17 | 17 |
| 2 | 421 | 306 | 24 | 7 |
| 3 | 698 | 277 | 30 | 6 |
| 5 | 1085 | 387 | 38 | 8 |
| 6 | 1497 | 412 | 48 | 10 |
| 7 | 2033 | 536 | 57 | 9 |
| 8 | 2265 | 232 | 60 | 3 |
| 9 | 2728 | 522 | 65 | 5 |
| 10 | 3360 | 632 | 73 | 8 |
| 11 | 3958 | 598 | 83 | 10 |
| 12 | 4591 | 633 | 93 | 10 |



