记Stack的用法
在刷leetcode一道简单题的时候借助了栈的用法,发现在日常工作中很少会使用栈,因此复习一遍,以免后续遗忘
- 在leetcode中的题目是这样的

在解答这道题的时候,第一次尝试用了暴力解法,解是解开了,但是实在不美观,于是尝试了一下新的写法,就有了用了stack
点击查看代码
public static boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack();
Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put('[', 1);
map.put(']', -1);
map.put('(', 2);
map.put(')', -2);
map.put('{', 3);
map.put('}', -3);
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
Integer value = map.get(s.charAt(i));
if (!stack.empty()) {
Integer lastValue = stack.pop();
if (lastValue + value == 0 && lastValue > value) {
continue;
} else {
stack.push(lastValue);
stack.push(value);
}
}else {
stack.push(value);
}
}
if (stack.empty()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}

不得不说,刷题还有很多路要走,都是前面欠下的债/(ㄒoㄒ)/~~
回顾一下stack的特性
Stack是Vector类下面的一个子类,Vector是线程安全的,他除了继承Vetcor所有的方法以外,自己还定义了一些其他的方法
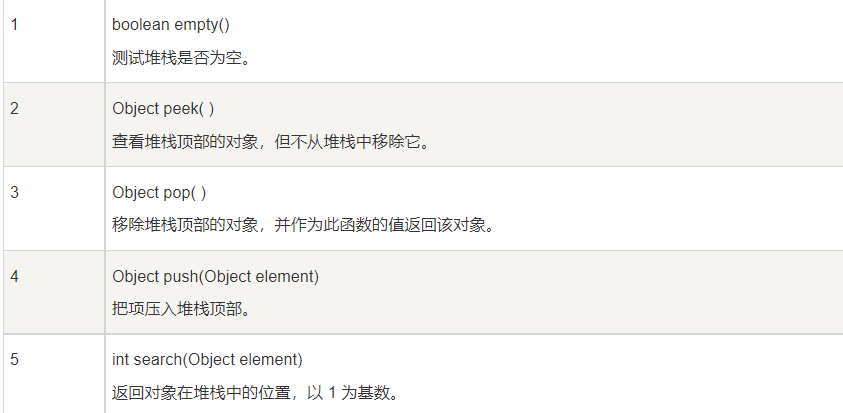
写一个简单的例子
点击查看代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
//压栈
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
//查看栈的顶部,但是不弹出
System.out.println("顶部数据:" + stack.peek());
//弹出最后一个进栈的数据
stack.pop();
//判断栈是否为空
boolean empty = stack.empty();
for (int i = 0; i < stack.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(stack.get(i));
}
System.out.println(empty);
}
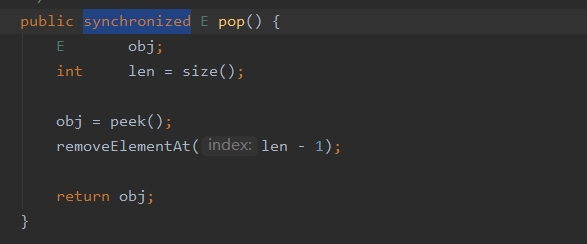
因为stack继承了Vector,所以它也是线程安全的,看Stack的源码可以看到,他的Pop方法被synchronized关键字修饰,保证在多线程的情况下不会有线程安全问题的发生


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号