pytorch的二维卷积torch.nn.functional.conv2d笔记
官方文档
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.functional.conv2d.html#torch.nn.functional.conv2d
H、W的输出计算也符合二维卷积的计算方式
https://www.cnblogs.com/yechangxin/articles/18390341
情况一:不使用groups(深度可分离卷积) 但是输出的batch_size变了!
结论:
1、第二个维度必须一模一样才能进行卷积,否则报错
2、batch_size 随便设置 无任何影响
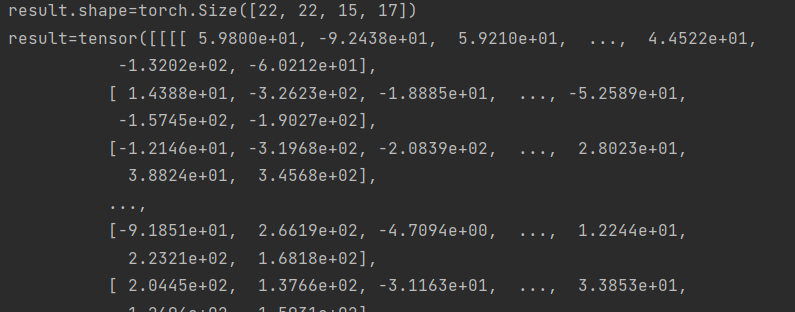
假设第二个维度设置一样
batch_size = 22
groups = 64
"""情况一 不使用groups(深度可分离卷积)
第二个维度必须一模一样才能进行卷积,否则报错
batch_size 随便设置 无任何影响
"""
fm_B = torch.randn(batch_size, 1024, 18, 19) # N*C*H*W fm torch.Size([batch_size, 1024, 14, 14])
fm_A_col = torch.randn(batch_size, 1024, 6, 3) # torch.Size([batch_size, 16, 14, 1])
result = F.conv2d(
input=fm_B,
weight=fm_A_col,
padding=(1, 0),
stride=1, # 添加步长
# groups=groups # 每个batch独立处理
)
print(f"result.shape={result.shape}")
print(f"result={result}")
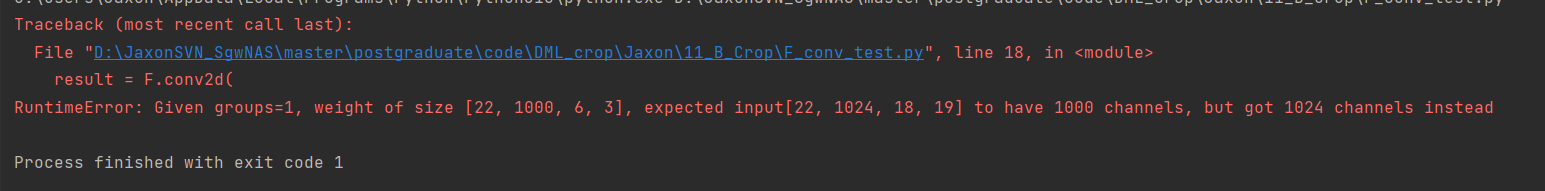
假设第二个维度设置不一样
fm_B = torch.randn(batch_size, 1024, 18, 19) # N*C*H*W fm torch.Size([batch_size, 1024, 14, 14])
fm_A_col = torch.randn(batch_size, 1000, 6, 3) # torch.Size([batch_size, 16, 14, 1])
报错
情况二:使用groups(深度可分离卷积)
结论:
1、根据官方文档,weight的第二个维度要满足in_channels/groups,且第一个维度batch_size都要和groups一样!
2、

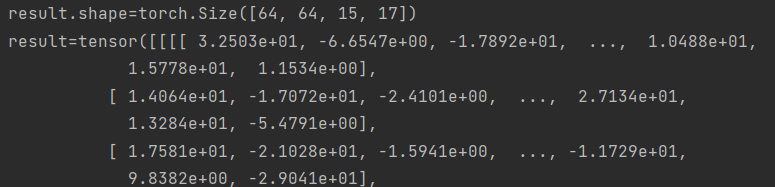
例如,weight的第二个维度为16=1024/64,batch_size=64,可正常跑通
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
batch_size = 64
groups = 64
fm_B = torch.randn(batch_size, 1024, 18, 19) # N*C*H*W fm torch.Size([batch_size, 1024, 14, 14])
fm_A_col = torch.randn(batch_size, 16, 6, 3) # torch.Size([batch_size, 16, 14, 1])
result = F.conv2d(
input=fm_B,
weight=fm_A_col,
padding=(1, 0),
stride=1, # 添加步长
groups=groups # 每个batch独立处理
)
print(f"result.shape={result.shape}")
print(f"result={result}")
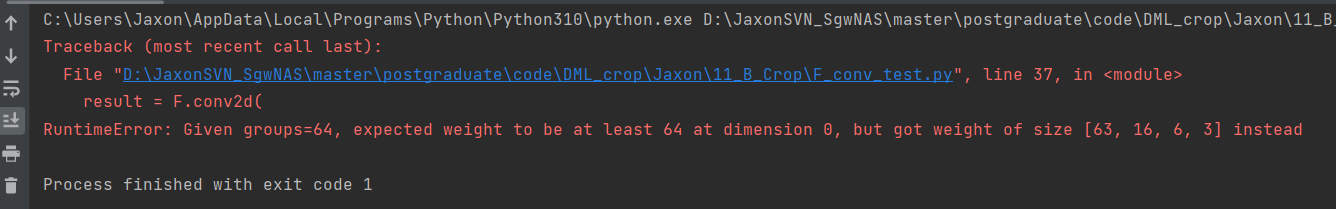
例如,weight的第二个维度为16=1024/64,batch_size=不等于groups,报错!
batch_size = 63
groups = 64
拆开操作即可
conv_outputs_raw = []
conv_outputs_col = []
for i in range(_batch_size):
fm_B_i = fm_B[i].unsqueeze(0) # Add batch dimension
fm_A_col_i = fm_A_col[i].unsqueeze(0)
fm_A_raw_i = fm_A_raw[i].unsqueeze(0)
conv_output_raw_i = F.conv2d(
fm_B_i,
fm_A_col_i,
padding=(1, 0),
stride=1
)
conv_output_col_i = F.conv2d(
fm_B_i,
fm_A_raw_i,
padding=(0, 1),
stride=1
)
conv_outputs_raw.append(conv_output_raw_i)
conv_outputs_col.append(conv_output_col_i)
conv_output_raw = torch.cat(conv_outputs_raw, dim=0) # torch.Size([batch_size, 1, 3, 14])
conv_output_col = torch.cat(conv_outputs_col, dim=0) # torch.Size([batch_size, 1, 14, 3])
不要加padding,计算出来和矩阵直接相乘就对得上了
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
batch_size = 100
groups = 64
fm_B = torch.randn(batch_size, 1024, 14, 14) # N*C*H*W fm torch.Size([batch_size, 1024, 14, 14])
fm_A_col = torch.randn(batch_size, 1024, 14, 1) # torch.Size([batch_size, 1024, 14, 1])
fm_A_raw = torch.randn(batch_size, 1024, 1, 14) # torch.Size([batch_size, 1024, 1, 14])
conv_outputs_raw = []
conv_outputs_col = []
for i in range(batch_size):
fm_B_i = fm_B[i].unsqueeze(0) # Add batch dimension
fm_A_col_i = fm_A_col[i].unsqueeze(0)
fm_A_raw_i = fm_A_raw[i].unsqueeze(0)
conv_output_raw_i = F.conv2d(
fm_B_i,
fm_A_col_i,
padding=(0, 0),
stride=1
)
conv_output_col_i = F.conv2d(
fm_B_i,
fm_A_raw_i,
padding=(0, 0),
stride=1
)
conv_outputs_raw.append(conv_output_raw_i)
conv_outputs_col.append(conv_output_col_i)
conv_output_raw = torch.cat(conv_outputs_raw, dim=0) # torch.Size([batch_size, 1, 3, 14])
conv_output_col = torch.cat(conv_outputs_col, dim=0) # torch.Size([batch_size, 1, 14, 3])
print(f"conv_output_raw.shape={conv_output_raw.shape}")
print(f"conv_output_col.shape={conv_output_col.shape}")
自己写的方法:
fm_A_col = torch.permute(fm_A_col, (0, 1, 3, 2)) # torch.Size([batch_size, 1024, 1, 14])
conv_output_raw = torch.matmul(fm_A_col, fm_B) # torch.Size([batch_size, 1024, 1, 14])
fm_A_row = torch.permute(fm_A_raw, (0, 1, 3, 2))
conv_output_col = torch.matmul(fm_B, fm_A_row)
这两个结果是一样的
本文来自博客园,作者:JaxonYe,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/yechangxin/articles/18400202
侵权必究


