DeBug Python代码全靠print函数?换用这个一天2K+Star的工具吧,改进版
pysnooper是代码debug神器,比无限low print好很多和也比日志debug好一些,比断点调试也好一些,这个很犀利的装饰器。
https://www.toutiao.com/a6682957535856558606/
DeBug Python代码全靠print函数?换用这个一天2K+Star的工具吧
对其修改了2点。
1、由于部署一般是linux,开发是windows,所以可以禁止linux上使用调试,相同的代码在linux上运行,调试装饰器自动失效,因为忘了注释掉装饰器,在生产调试会消耗性能。
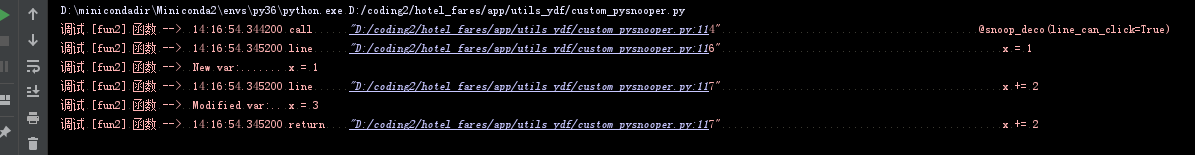
2、将代码运行轨迹修改成可以点击的,点击控制台的行号即可跳转到pycharm对应的代码行。
3、提供一个猴子补丁,使用猴子补丁修改三方包的模块级全局变量MAX_VARIABLE_LENGTH ,最大变量默认是100,但对调试对接方json时候,往往很大,可以加大到最大显示10万个字母。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @Author : ydf import datetime import os from functools import wraps import decorator import pysnooper # 需要安装 pip install pysnooper==0.0.11 from pysnooper.pysnooper import get_write_function from pysnooper.tracer import Tracer, get_local_reprs, get_source_from_frame os_name = os.name class TracerCanClick(Tracer): """ 使运行轨迹可点击。 """ def trace(self, frame, event, arg): if frame.f_code is not self.target_code_object: if self.depth == 1: return self.trace else: _frame_candidate = frame for i in range(1, self.depth): _frame_candidate = _frame_candidate.f_back if _frame_candidate is None: return self.trace elif _frame_candidate.f_code is self.target_code_object: indent = ' ' * 4 * i break else: return self.trace else: indent = '' self.frame_to_old_local_reprs[frame] = old_local_reprs = \ self.frame_to_local_reprs[frame] self.frame_to_local_reprs[frame] = local_reprs = \ get_local_reprs(frame, variables=self.variables) modified_local_reprs = {} newish_local_reprs = {} for key, value in local_reprs.items(): if key not in old_local_reprs: newish_local_reprs[key] = value elif old_local_reprs[key] != value: modified_local_reprs[key] = value newish_string = ('Starting var:.. ' if event == 'call' else 'New var:....... ') for name, value_repr in newish_local_reprs.items(): self.write('{indent}{newish_string}{name} = {value_repr}'.format( **locals())) for name, value_repr in modified_local_reprs.items(): self.write('{indent}Modified var:.. {name} = {value_repr}'.format( **locals())) now_string = datetime.datetime.now().time().isoformat() source_line = get_source_from_frame(frame)[frame.f_lineno - 1] # print(frame) # print(dir(frame.f_code)) # print(frame.f_code.co_filename) file_name_and_line = f'{frame.f_code.co_filename}:{frame.f_lineno}' # print(file_name_and_line) # self.write('{indent}{now_string} {event:9} ' # '{frame.f_lineno:4} {source_line}'.format(**locals())) file_name_and_line2 = f'"{file_name_and_line}"' self.write('{indent}{now_string} {event:9} ' # REMIND 主要是修改了这一行,使debug可点击。 '{file_name_and_line2:100} {source_line}'.format(**locals())) return self.trace def _snoop_can_click(output=None, variables=(), depth=1, prefix=''): write = get_write_function(output) # noinspection PyShadowingBuiltins @decorator.decorator def decorate(function, *args, **kwargs): target_code_object = function.__code__ with TracerCanClick(target_code_object=target_code_object, write=write, variables=variables, depth=depth, prefix=prefix): return function(*args, **kwargs) return decorate def snoop_deco(output=None, variables: tuple = (), depth=1, prefix='', do_not_effect_on_linux=True, line_can_click=True): # REMIND 对装饰器再包装一次,不使用上面的和官方的。 def _snoop(func): nonlocal prefix if prefix == '': prefix = f'调试 [{func.__name__}] 函数 --> ' @wraps(func) def __snoop(*args, **kwargs): if os_name == 'posix' and do_not_effect_on_linux: # 不在linux上debug return func(*args, **kwargs) else: if line_can_click: return _snoop_can_click(output, variables, depth, prefix)(func)(*args, **kwargs) else: return pysnooper.snoop(output, variables, depth, prefix)(func)(*args, **kwargs) return __snoop return _snoop def patch_snooper_max_variable_length(max_lenth=100000): """ 提供一个猴子补丁,三方包默认是变量最大显示100个字母,对于我这种经常debug对接方json的,要加到10万才能显示一个josn。 最好是放在__name__ == main中去执行此补丁,否则由于模块是单例的永远只导入一次,如果本文件被其他地方导入,也会改变当前python解释器的其他也使用snooper地方的运行表现也加到10万了。 :param max_lenth: :return: """ from pysnooper import tracer tracer.MAX_VARIABLE_LENGTH = max_lenth if __name__ == '__main__': @snoop_deco(line_can_click=True) def fun2(): x = 1 x += 2 fun2()
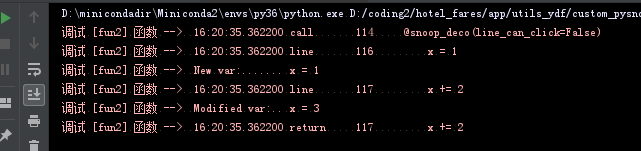
原版是上面这样,不能点击,修改后,直接点击链接可以跳转到代码对应地方。不用加很多print来确定代码运行了什么分支。
反对极端面向过程编程思维方式,喜欢面向对象和设计模式的解读,喜欢对比极端面向过程编程和oop编程消耗代码代码行数的区别和原因。致力于使用oop和36种设计模式写出最高可复用的框架级代码和使用最少的代码行数完成任务,致力于使用oop和设计模式来使部分代码减少90%行,使绝大部分py文件最低减少50%-80%行的写法。






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」