23. 合并 K 个升序链表
题目描述
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
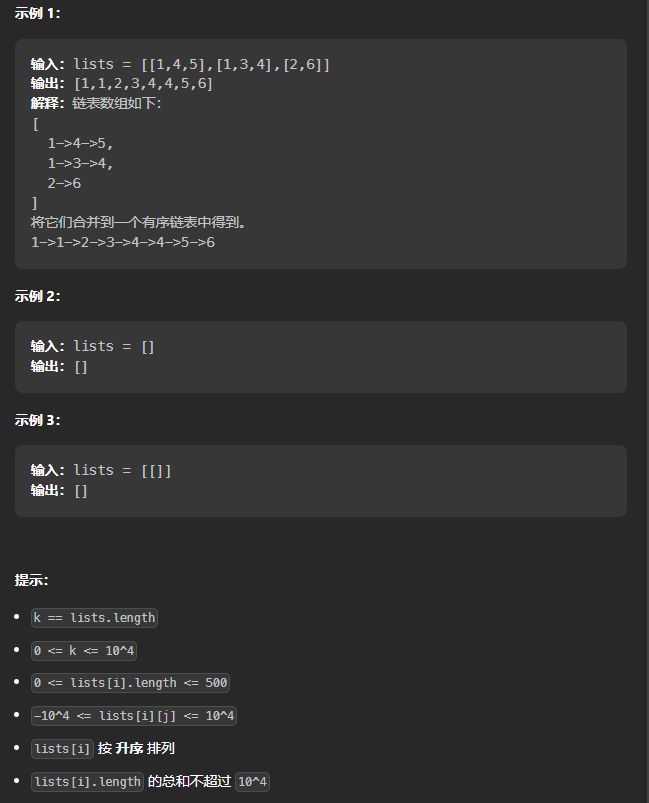
题解
1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * public class ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode next; 6 * ListNode() {} 7 * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } 8 * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } 9 * } 10 */ 11 class Solution { 12 // 思路1:利用java的PriorityQueue(推荐) 13 14 // 思路2:把集合中所有的数字加入到一个集合中,然后把集合按升序排序,然后按照顺序创建ListNode 15 16 // 思路3:采用合并两个有序链表的方法,两两合并,即让第一个依次和后面的链表合并 17 18 19 // 思路1 20 public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) { 21 // 将list中的listNode按照val从小到大的顺序加入到优先队列 22 PriorityQueue<ListNode> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o1.val - o2.val); 23 for (ListNode each : lists) { 24 if (each == null) { 25 continue; 26 } 27 priorityQueue.add(each); 28 } 29 30 ListNode head = new ListNode(); // 链表的头 31 ListNode cur = head; // 移动指针 32 while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()) { 33 ListNode tem = priorityQueue.poll(); // 从优先队列中弹出val最小的listNode 34 cur.next = tem; 35 cur = cur.next; 36 if (tem.next != null) { // 如果该链表的next不为空,继续把next加入到优先队列 37 priorityQueue.add(tem.next); 38 } 39 } 40 return head.next; 41 } 42 43 44 // 思路2 45 public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) { 46 if (lists.length == 0) { 47 return null; 48 } 49 List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); 50 for (ListNode each : lists) { // 将所有的数字加入到list集合中 51 while (each != null) { 52 list.add(each.val); 53 each = each.next; 54 } 55 } 56 Collections.sort(list); // 将集合中的数字从小到大排序 57 int listSize = list.size(); 58 ListNode head = new ListNode(); 59 ListNode cur = head; 60 for (int i = 0; i < listSize ; i++) { 61 ListNode node = new ListNode(list.get(i)); // 按照顺序从集合中拿数字,并创建新链表 62 cur.next = node; 63 cur = cur.next; 64 } 65 return head.next; 66 } 67 68 69 // 思路3 70 public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) { 71 // 当lists中的元素个数小于2个 72 if (lists.length == 0 || lists.length == 1) { 73 return lists.length == 0 ? null : lists[0]; 74 } 75 // 第一个ListNode逐渐与后面的每一个合并,n个元素需要合并n - 1次 76 ListNode first = lists[0]; 77 for (int i = 1; i < lists.length; i++) { 78 first = mergeTwoList(first, lists[i]); // 每合并一次first就会被更新 79 } 80 return first; 81 } 82 83 // 合并两个有序链表 84 ListNode mergeTwoList(ListNode listNode1, ListNode listNode2) { 85 ListNode head = new ListNode(); // 自定义一个头节点 86 ListNode cur = head; 87 while (listNode1 != null && listNode2 != null) { // 当listNode1和listNode2同时不为空进入循环 88 if (listNode1.val >= listNode2.val) { // cur的next指向val小的节点 89 cur.next = listNode2; 90 listNode2 = listNode2.next; 91 } else { 92 cur.next = listNode1; 93 listNode1 = listNode1.next; 94 } 95 cur = cur.next; // cur指针后移 96 } 97 98 // 两个链表连接过程中,总会有一个链表先被连接完,剩下的链表节点直接连接在后面即可 99 if (listNode1 == null) { 100 cur.next = listNode2; 101 } 102 if (listNode2 == null) { 103 cur.next = listNode1; 104 } 105 return head.next; 106 } 107 108 }


