pandas库dateframe介绍
javascript:void(0); ”的onclick =“ copyCnblogsCode(这)”标题=“复制代码”> <IMG SRC =” //common.cnblogs.com/images/copycode.gif” ALT =“复制代码”> </一> </跨度> </ div>
<span style =” color:rgb(0,0,255);--darkreader-inline-color:#337dff; ” data-darkreader-inline-color =“”>导入</ span> <span style =“ color:rgb(0,0,0); --darkreader-inline-color:#e8e6e3; ” data-darkreader-inline-color =“”> numpy as np </ span> <span style =” color:rgb(0,0,255);-darkreader-inline-color:#337dff; ” data-darkreader-inline-color =“”>导入</ span> <span style =“颜色:rgb(0,0,0);-darkreader-inline-color:#e8e6e3; “ data-darkreader-inline-color =””>熊猫作为pd
test_1 </ span> = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(4,4 <span style =” color:rgb(0,0,0); --darkreader-inline-color:#e8e6e3; ” data-darkreader -inline-color =“”>),索引</ span> =列表(<span样式=” color:rgb(128,0,0);-darkreader-inline-color:#ff7272; ” data-darkreader-inline-color =“”>'</ span> <跨度风格
=“ color:rgb(128,0,0); --darkreader-inline-color:#ff7272; ” data-darkreader-inline-color =“”> ABCD </ span> <span style =” color:rgb(128,0,0); --darkreader-inline-color:#ff7272; “ data-darkreader-inline-color =”“>'</ span>),列= list(<span style =” color:rgb(128,0,0); --darkreader-inline-color:#ff7272; “ data-darkreader-inline-color =“”>'</ span> <span style =” color:rgb(128,0,0); --darkreader-inline-color:#ff7272; “ data-darkreader-inline-color =””> 1234 </ span> <span style =” color:rgb(128,0,0);-darkreader-inline-color:#ff7272; “ data-darkreader-inline-color =”“>'</ span>))<span style =” color:rgb(0,128,0); --darkreader-inline-color:#72ff72;“ data-darkreader-inline-color =”“> =” color:rgb(0,128,0);--darkreader-inline-color:#72ff72;”> test_2 = pd。
]],
index=list('1234'), columns=list('ABCD')) # 自己输入
dic1 = {'name': ['小明', '小红', '狗蛋', '铁柱'],
'age': [17, 20, 5, 40], 'sex': ['男', '女', '女', '男']} # 使用字典进行输入
test_3 = pd.DataFrame(dic1, index=list('ABCD'))
print(test_1, '\n')
print(test_2, '\n')
print(test_3, '\n')

2.查看数据情况
print('查看数据类型:\n', test_3.dtypes, '\n') print('看前两行:\n', test_3.head(2), '\n') print('看后两行:\n', test_3.tail(2), '\n') print('index看行名:\n', test_3.index, '\n') print('columns看行名:\n', test_3.columns, '\n')

3.数据检索
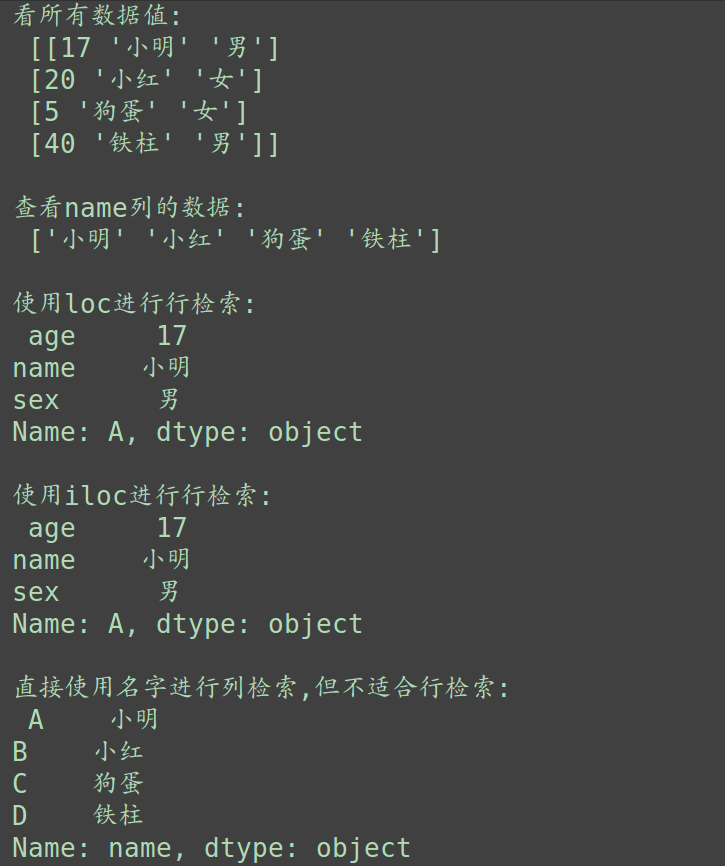
print('看所有数据值:\n', test_3.values, '\n') print('查看name列的数据:\n', test_3['name'].values, '\n') print('使用loc进行行检索:\n', test_3.loc['A'], '\n') print('使用iloc进行行检索:\n', test_3.iloc[0], '\n') print('直接使用名字进行列检索,但不适合行检索:\n', test_3['name'], '\n')
4.对表进行描述
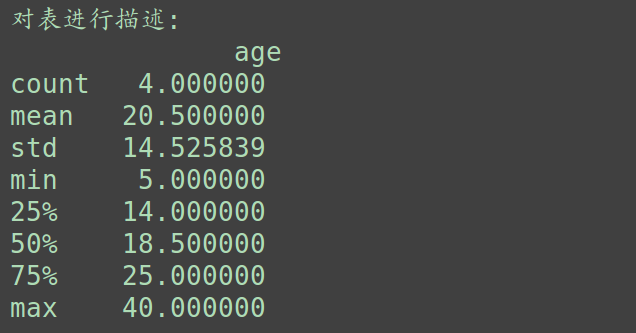
print('对表进行描述:\n', test_3.describe(), '\n')
5.表的合并
print('进行转置:\n', test_3.T, '\n') print('查看行数:', test_3.shape[0], '查看列数:', test_3.shape[1], '\n') # print('对表进行描述:\n', test_3.describe(), '\n') test_3.insert(3, 'skin', ['b', 'w', 'w', 'y']) print('对表用insert进行插入:\n', test_3, '\n')test_4 = pd.DataFrame(['T', 'E', 'W', 'A'], index=list('ABCD'), columns=list('N'))
# print('新建的DataFrame:\n', test_4, '\n')
print('合并DataFrame:\n', test_3.join(test_4), '\n')





