1053 Path of Equal Weight(附测试点6思路)
题目:
Given a non-empty tree with root R, and with weight Wiassigned to each tree node Ti. The weight of a path from R to L is defined to be the sum of the weights of all the nodes along the path from R to any leaf node L.
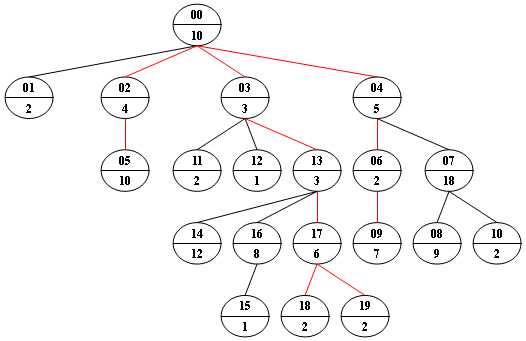
Now given any weighted tree, you are supposed to find all the paths with their weights equal to a given number. For example, let's consider the tree showed in the following figure: for each node, the upper number is the node ID which is a two-digit number, and the lower number is the weight of that node. Suppose that the given number is 24, then there exists 4 different paths which have the same given weight: {10 5 2 7}, {10 4 10}, {10 3 3 6 2} and {10 3 3 6 2}, which correspond to the red edges in the figure.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case starts with a line containing 0<N≤100, the number of nodes in a tree, M(<N), the number of non-leaf nodes, and 0<S<230, the given weight number. The next line contains N positive numbers where Wi (<1000) corresponds to the tree node Ti. Then Mlines follow, each in the format:
ID K ID[1] ID[2] ... ID[K]
where ID is a two-digit number representing a given non-leaf node, K is the number of its children, followed by a sequence of two-digit ID's of its children. For the sake of simplicity, let us fix the root ID to be 00.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print all the paths with weight S in non-increasing order. Each path occupies a line with printed weights from the root to the leaf in order. All the numbers must be separated by a space with no extra space at the end of the line.
Note: sequence {A1,A2,⋯,An} is said to be greater thansequence {B1,B2,⋯,Bm} if there exists 1≤k<min{n,m} such that Ai=Bi for i=1,⋯,k, and Ak+1>Bk+1.
Sample Input:
20 9 24
10 2 4 3 5 10 2 18 9 7 2 2 1 3 12 1 8 6 2 2
00 4 01 02 03 04
02 1 05
04 2 06 07
03 3 11 12 13
06 1 09
07 2 08 10
16 1 15
13 3 14 16 17
17 2 18 19
Sample Output:
10 5 2 7
10 4 10
10 3 3 6 2
10 3 3 6 2
思路:
1、为保证非增序输出,开始采用的方法是:对每个非叶子结点的子结点根据权值从大到小排序,从而保证在DFS遍历时,总是先遍历权值大的子节点,从而使得结果非增。
但是存在一个例外的情况,如下:
对应的树为:
1
/ \
2 2
/ \
2 3
/ \
3 2
按照现在的解法来处理这样就会导致输出为:
1 2 2 3
1 2 3 2
而实际上期望的正确输出为:
1 2 3 2
1 2 2 3
因此,对代码进行了改进。即将所有可能的情况都存在一个vector<vector<int>> paths 的二维容器内,再对容器内的结果按照字典序进行排序,最后按顺序输出即可。
代码:(29分:最后一个测试点答案错误)
#include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; int n, m, s; int w[105]; struct Node{ int w, id; }; bool cmp(Node s1, Node s2){ return s1.w > s2.w; } vector<Node> children[105]; vector<int> len; void dfs(int x, vector<int>&v, int l){ if(l == s && children[x].size() == 0){ bool flag = false; for(int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++){ if(!flag){ flag = true; }else{ printf(" "); } printf("%d", v[i]); } printf("\n"); } for(int i = 0; i < children[x].size(); i++){ int child = children[x][i].id; if(l + w[child] <= s){ v.push_back(w[child]); dfs(child, v, l + w[child]); v.pop_back(); } } } int main(){ scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &s); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ scanf("%d", &w[i]); } for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){ int id, num; scanf("%d%d", &id, &num); for(int j = 0; j < num; j++){ int child; scanf("%d", &child); Node node; node.w = w[child]; node.id = child; children[id].push_back(node); } sort(children[id].begin(), children[id].end(), cmp); } len.push_back(w[0]); dfs(0, len, w[0]); }
(满分)
#include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; int n, m, s; int w[105]; vector<int> children[105]; vector<int> path; vector<vector<int>> paths; void dfs(int x, vector<int>&v, int l){ if(l == s && children[x].size() == 0){ paths.push_back(v); return; } for(int i = 0; i < children[x].size(); i++){ int child = children[x][i]; if(l + w[child] <= s){ v.push_back(w[child]); dfs(child, v, l + w[child]); v.pop_back(); } } } int main(){ scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &s); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ scanf("%d", &w[i]); } for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){ int id, num; scanf("%d%d", &id, &num); for(int j = 0; j < num; j++){ int child; scanf("%d", &child); children[id].push_back(child); } } path.push_back(w[0]); dfs(0, path, w[0]); sort(paths.begin(), paths.end(), greater<vector<int>>()); for (int i = 0; i < paths.size(); i++) { printf("%d", paths[i][0]); for (int j = 1; j < paths[i].size(); j++) { printf(" %d", paths[i][j]); } printf("\n"); } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号