Java使用线程池和缓存提高接口QPS
1.什么是QPS?
- QPS:Queries Per Second意思是“每秒查询率”,是一台服务器每秒可以相应的查询次数,是对一个特定的查询服务器在规定时间内所处理流量多少的衡量标准。互联网中,做为域名系统服务器的机器的性能常常用每秒查询率来衡量。
2.准备三个接口,使用jmeter对三个接口各发10000个并发请求
product接口:/rpc/inner/product/findCategoryPath/50:直接操作数据库的接口
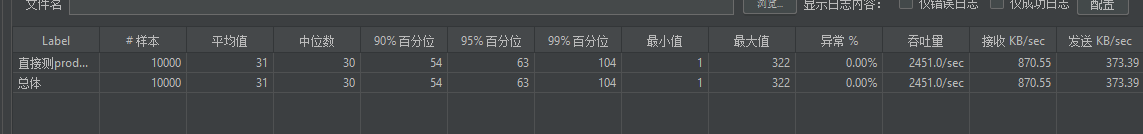
// 商品详情页,的业务逻辑如下
/**
* 根据skuId查询商品详情
*
* @param skuId
* @return
*/
@Override
public SkuItemTo findSkuItem(Long skuId) {
// 创建商品详情To对象,远程调用封装数据
SkuItemTo skuItemTo = new SkuItemTo();
// 查询三级分类路径
Result<BaseCategoryView> categoryViewResult = productFeignClient.findCategoryPath(skuId);
if (categoryViewResult.isOk()) {
BaseCategoryView categoryView = categoryViewResult.getData();
skuItemTo.setBaseCategoryView(categoryView);
}
// 查询skuInfo
Result<SkuInfo> skuInfoResult = productFeignClient.findSkuInfoById(skuId);
if (skuInfoResult.isOk()) {
SkuInfo skuInfo = skuInfoResult.getData();
skuItemTo.setSkuInfo(skuInfo);
}
// 查询价格
Result<BigDecimal> bigDecimalResult = productFeignClient.findPriceBySkuId(skuId);
if (bigDecimalResult.isOk()) {
BigDecimal price = bigDecimalResult.getData();
skuItemTo.setPrice(price);
}
// 查询skuId对应的销售属性列表
Result<List<SpuSaleAttr>> spuSaleAttrResult = productFeignClient.findSpuSaleAttrListBySkuId(skuId);
if (spuSaleAttrResult.isOk()) {
List<SpuSaleAttr> spuSaleAttrList = spuSaleAttrResult.getData();
skuItemTo.setSpuSaleAttrList(spuSaleAttrList);
}
// 查询valuesSkuJson
Result<Map<String, String>> valuesSkuJsonResult = productFeignClient.findValuesSkuJsonBySkuId(skuId);
if (valuesSkuJsonResult.isOk()) {
Map<String, String> resultData = valuesSkuJsonResult.getData();
String jsonStr = JsonUtils.objectToJson(resultData);
skuItemTo.setValuesSkuJson(jsonStr);
}
return skuItemTo;
}
/admin/product/test:简单的接口
@GetMapping("/test")
public String test() {
return "qmall hello";
}

/rpc/inner/item/findSkuItem/50:远程调用上面的product接口,然后通过product操作数据库,可以发现数据吞吐量直接降到了200多
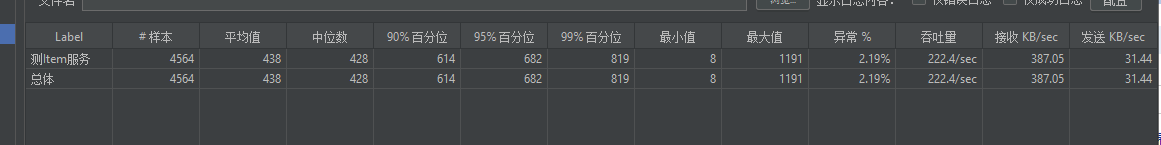
3.优化方案
(1)先把内存加上去试试-Xmx100m -Xms100m ===> -Xmx500m -Xms500m,测试
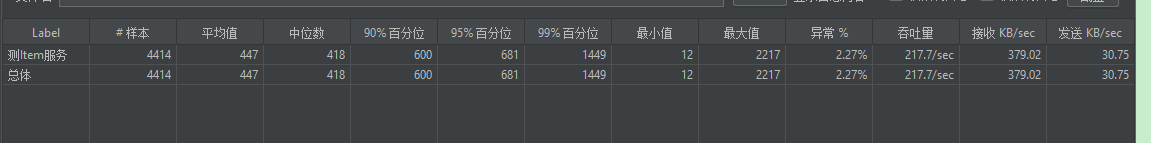
并没有什么改变
(2)由于前面的product接口查询涉及到了查询多张表,使用了链表查询,所以我在从表的主键上加了索引

快了一点
(3)使用线程池异步处理数据
- 由于使用到了线程池,所以根据alibaba开发手册,强制规定线程池由程序员手动创建,所以先自定义二个线程池
package com.qbb.qmall.service.config.thread;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* @author QiuQiu&LL (个人博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/qbbit)
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022-05-24 18:37
* @Description:自定义线程池
*/
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ThreadPoolProperties.class)
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class ThreadPoolAutoConfiguration {
// @Qualifier("corePoolExecutor")
// @Autowired
// private ThreadPoolExecutor corePoolExecutor;
@Autowired
private ThreadPoolProperties threadPoolProperties;
/**
* 核心线程池
*
* @return
*/
@Primary // 优先注入核心线程池
@Bean
public ThreadPoolExecutor corePoolExecutor(@Value("${spring.application.name:defaultName}") String name) {
/**
* int corePoolSize,核心线程数
* int maximumPoolSize,最大线程数
* long keepAliveTime,线程存活时间
* TimeUnit unit,线程存活时间单位
* BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,阻塞队列
* ThreadFactory threadFactory,线程工厂,创建线程
* RejectedExecutionHandler handler拒绝策略
*/
log.info("线程池配置文件:{}", threadPoolProperties);
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(
threadPoolProperties.getCorePoolSize(),
threadPoolProperties.getMaximumPoolSize(),
threadPoolProperties.getKeepAliveTime(),
threadPoolProperties.getUnit(),
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(threadPoolProperties.getQueueSize()),
new QmallThreadFactory("[" + name + "]-core"),
threadPoolProperties.getHandler());
}
/**
* 其他线程池
*
* @param threadPoolProperties
* @param name
* @return
*/
@Bean
public ThreadPoolExecutor otherPoolExecutor(ThreadPoolProperties threadPoolProperties,
@Value("${spring.application.name:defaultName}") String name) {
/**
* int corePoolSize,核心线程数
* int maximumPoolSize,最大线程数
* long keepAliveTime,线程存活时间
* TimeUnit unit,线程存活时间单位
* BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,阻塞队列
* ThreadFactory threadFactory,线程工厂,创建线程
* RejectedExecutionHandler handler拒绝策略
*/
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(threadPoolProperties.getCorePoolSize(),
threadPoolProperties.getMaximumPoolSize(),
threadPoolProperties.getKeepAliveTime(),
threadPoolProperties.getUnit(),
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(threadPoolProperties.getQueueSize()),
new QmallThreadFactory("[" + name + "]-other"),
threadPoolProperties.getHandler());
}
class QmallThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
private String appName;
private AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(1);
public QmallThreadFactory(String appName) {
this.appName = appName;
}
/**
* 自定义线程工厂
*
* @param r
* @return
*/
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread thread = new Thread(r);
thread.setName(appName + count.getAndIncrement());
return thread;
}
}
}
- 线程池7大参数配置对象(当然写死也是可以的,但是最好还是写成可配置的,利于后面的优化)
package com.qbb.qmall.service.config.thread;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionHandler;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author QiuQiu&LL (个人博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/qbbit)
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022-05-24 21:20
* @Description:
*/
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "qbb.threadpool")
public class ThreadPoolProperties {
private Integer corePoolSize;
private Integer maximumPoolSize;
private Long keepAliveTime;
private TimeUnit unit = TimeUnit.MINUTES;
private Integer queueSize;
private RejectedExecutionHandler handler = new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy();
}
- 将我们创建的线程池加入ioc容器,方便后面注入使用
@Autowired
private ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor;
- 测试一下
package com.qbb.qmall.item;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
/**
* @author QiuQiu&LL (个人博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/qbbit)
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022-05-25 0:43
* @Description:
*/
@SpringBootTest
public class ThreadPoolTest {
@Autowired
private ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor;
@Test
public void testRunAsync() {
System.out.println("threadPoolExecutor = " + threadPoolExecutor);
}
}

下面我用Completable+上面自定义的线程池执行任务
(1)Completable常用的方法
- static runAsync: 执行一个任务,不带返回值
/**
* 启动一个不带返回值的任务
*/
@Test
public void startRunAsync() {
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(
"使用Completable+自定义线程池启动一个不带返回值的任务"
);
}, threadPoolExecutor);
}
- static supplyAsync: 执行一个任务,带返回值
/**
* 启动一个带返回值的任务
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void startRunSupplyAsync() throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<Double> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("使用Completable+自定义线程池启动一个带返回值的任务");
return Math.random();
}, threadPoolExecutor);
Double result = future.get();
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}
(2)Completable常用Api测试
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* 1、new Thread
* <p>
* 2、异步(CompletableFuture)+线程池(ThreadPoolExecutor)
* CompletableFuture:
*
*
* 使用线程池
* 1、准备自定义一个线程池
* 2、CompletableFuture 给线程池中提交任务
* 3、对提交的任务进行编排、组合、容错处理
*/
@SpringBootTest //这是一个SpringBoot测试
public class AppThreadPoolTest {
// @Qualifier("corePool")
@Autowired
ThreadPoolExecutor poolExecutor;
@Test
public void zuheTest() throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<Void> async1 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("打印A");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("A");
}, poolExecutor);
CompletableFuture<Void> async2 =CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
System.out.println("查询B");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("B");
},poolExecutor);
CompletableFuture<Void> async3 =CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
System.out.println("保存C");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("C");
},poolExecutor);
//多任务组合
// CompletableFuture.allOf(async1,async2,async3)
// .whenComplete((a,b)->{
// System.out.println("结果:"+a);
// System.out.println("异常:"+b);
// System.out.println("D");
// });
//只是一个等不到拉倒
try {
CompletableFuture.anyOf(async1,async2,async3).get(100, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
System.out.println("正常逻辑");
}catch (TimeoutException e){
System.out.println("超时逻辑");
}
// //1、这三个任务全部完成以后 打印D
// long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// System.out.println("start....");
// //其实等了最长时间
// async2.get(); //1s
// async3.get(); //2s
// async1.get(); //3s
//
// long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
// System.out.println("D:"+(end-start)/1000);
}
/**
* then系列进行任务编排
* 1、thenRun: 传入 Runnable 启动一个无返回值的异步任务,
* thenRun
* thenRunAsync
* thenRunAsync(带线程池)
* 2、thenAccept: 传入 Consumer void accept(T t); 接参数,但是也无返回值
* thenAccept
* thenAcceptAsync
* thenAcceptAsync(带线程池)
* 3、thenApply: 传入 Function: R apply(T t); 而且有返回值
*
*/
@Test
public void thenTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//1、计算
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":正在计算");
int i = 1 + 1;
return i;
}, poolExecutor).thenApplyAsync((result) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":正在转换");
return result + 10;
}, poolExecutor).thenApplyAsync((result) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":变成字母");
return result + "A";
});
String s = future.get();
System.out.println("结果:"+s);
//2、数据转换 +10 12
//3、变成字母 12A
}
/**
* CompletableFuture future
* 1、thenXXX: 前一个任务结束以后,继续做接下来的事情
* 2、whenXxx: when的事件回调
* whenComplete: 完成后干啥
* 前一个任务.whenComplete((t,u)->{ 处理t[上一步结果],u[上一步异常] })
* xxxxAsync: 带了Async代表这些方法运行需要开新线程
* 指定线程池: 就在指定线程池中开新线程
* 3、exceptionally: 前面异常以后干什么
*/
@Test
public void lianshidiaoyong() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":正在计算");
Double random = Math.random() * 100;
return random.intValue();
}, poolExecutor)
.exceptionally((t) -> {
System.out.println("zhale:" + t);
return 222;
});
System.out.println("结果:" + future.get());
}
@Test
public void exceptionTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> aaa = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":正在计算");
Double random = Math.random() * 100;
return random.intValue() / 0;
}, poolExecutor);
//异常才会运行 RPC 熔断
CompletableFuture<Integer> exceptionally = aaa.exceptionally((exception) -> {
System.out.println("上一步炸了:" + exception);
return 1;
});
Integer integer = exceptionally.get();
System.out.println("结果:" + integer);
}
@Test
public void bianpaiTest() {
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("哈哈");
int i = 10 / 0;
}, poolExecutor);
// void accept(T t, U u);
future.whenComplete((t, u) -> {
System.out.println("t:" + t);
System.out.println("u:" + u);
});
// R apply(T t); 异常回调
future.exceptionally((t) -> {
System.out.println("上次的异常:" + t);
return null;
});
// Void unused = future.get();
CompletableFuture<Integer> aaa = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":正在计算");
Double random = Math.random() * 100;
return random.intValue();
}, poolExecutor);
aaa.whenCompleteAsync((a, b) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": when");
if (b != null) {
//异常不为null
System.out.println("b:" + b);
} else {
System.out.println("a:" + a);
}
}, poolExecutor);
//get就是阻塞等待
// future.get();
// System.out.println("///");
//xxxxxxxx
}
/**
* 启动一个任务: 返回一个 CompletableFuture
*/
@Test
public void startAsyncTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "哈哈啊...");
}, poolExecutor);
/**
* @FunctionalInterface
* public interface Supplier<T> {
*
*
* * Gets a result.
* *
* * @return a result
*
* T get ();
* }
*/
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":正在计算");
Double random = Math.random() * 100;
return random.intValue();
}, poolExecutor);
Integer result = future.get(); //阻塞等待
System.out.println("结果:" + result);
}
/**
* 验证线程池
*/
// @Transactional //所有测试期间的数据会被自动回滚
@Test
public void poolExecutorTest() {
System.out.println("线程池:" + poolExecutor);
int corePoolSize = poolExecutor.getCorePoolSize();
System.out.println(poolExecutor.getQueue().remainingCapacity());
}
}
总结:
- 使用线程池
- 1、准备自定义一个线程池
- 2、CompletableFuture 给线程池中提交任务
- 3、对提交的任务进行编排、组合、容错处理
(3)使用上面的线程池改造一下前面的product商品详情接口
使用了线程池,并且把参数调整到我电脑的最优8核16线程,会发现并没有提升太大的吞吐量
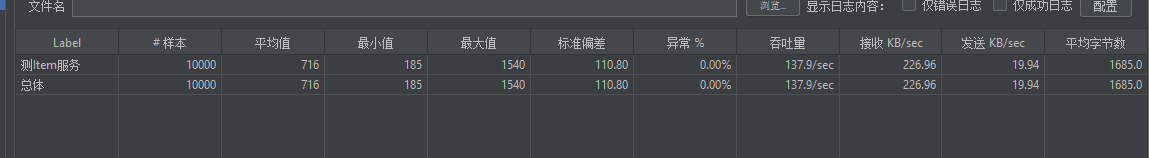
(4)使用缓存(本地缓存|分布式缓存)
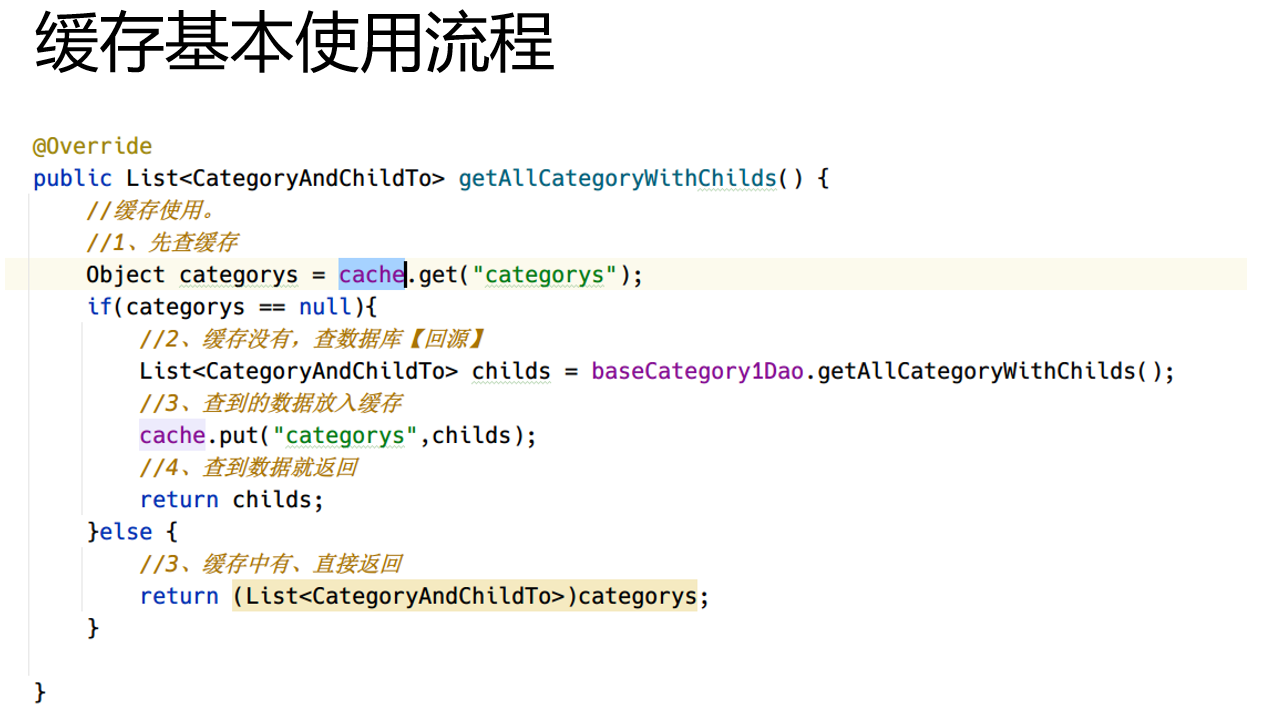
(1)先使用本地缓存
// 先从缓存中获取一下
SkuItemTo cacheItem = (SkuItemTo) cacheMap.get("skuItemTo");
if (cacheItem != null) {
// 缓存有值
return cacheItem;
}
......
// 保存到本地缓存一份
cacheMap.put("skuItemTo", skuItemTo);
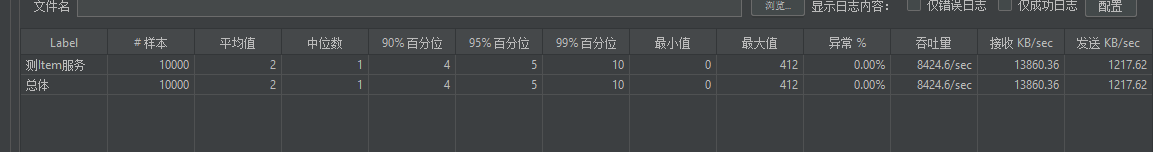
好家伙,直接奔到了8000多
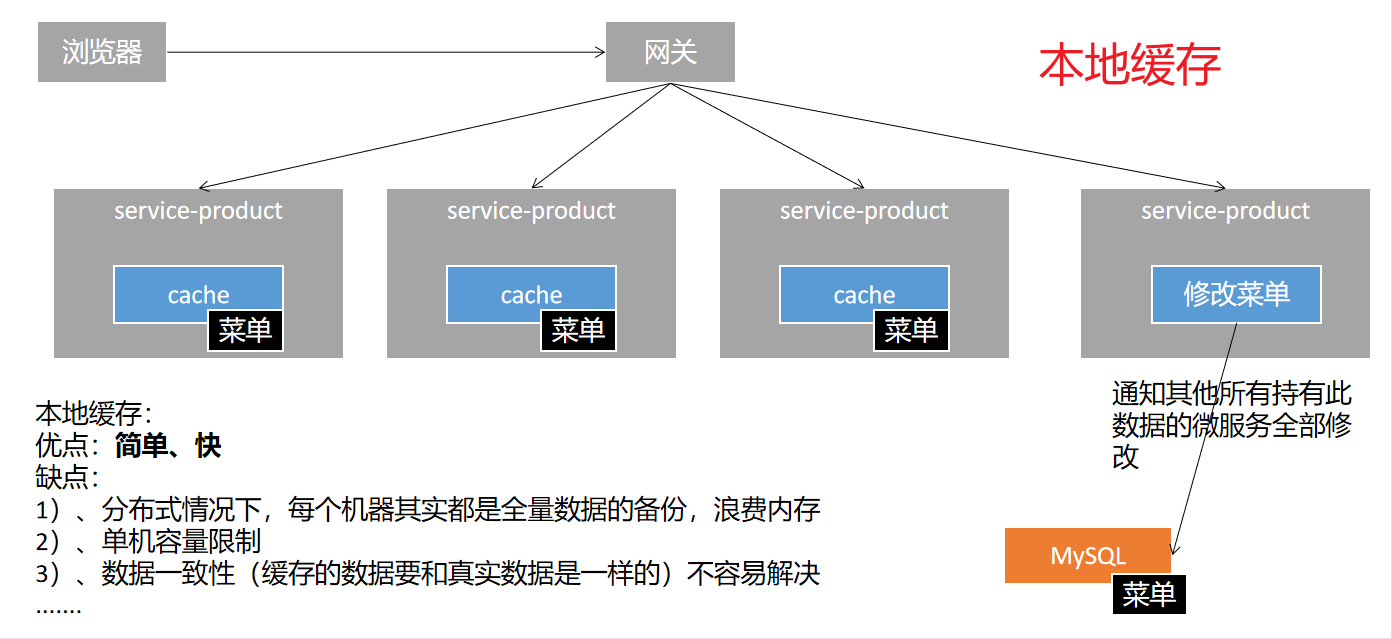
本地缓存优缺点
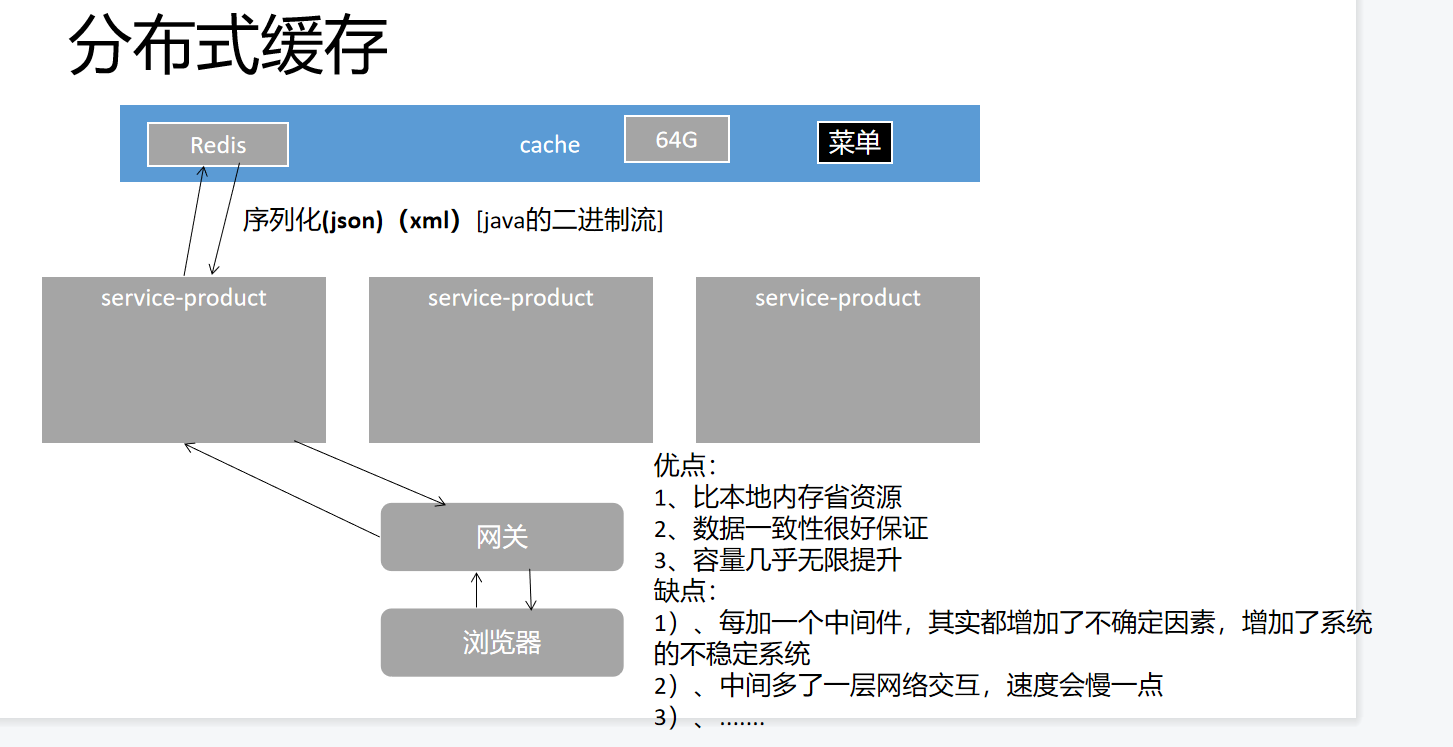
(2)使用分布式缓存Redis
分布式缓存优缺点
- 导入redis的starter依赖
<!-- redis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- spring2.X集成redis所需common-pool2-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
<version>2.6.0</version>
</dependency>
- yml配置文件中配置相应的连接信息
spring:
redis:
host: 192.168.137.137
password: qbb
lettuce:
pool:
max-active: 8
min-idle: 0
- DI注入相应的组件
RedisTemplate:操作redis中的任意类型
StringRedisTemplate:操作Redis中的String类型
@SpringBootTest
public class RedisTemplateTest {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Test
public void test01(){
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue()
.set("name", "qbb");
}
}
- 使用分布式缓存Redis处理我们的业务方法
package com.qbb.qmall.service.cache.impl;
import com.qbb.qmall.common.util.JsonUtils;
import com.qbb.qmall.model.product.to.CategoryTreeTo;
import com.qbb.qmall.service.cache.CacheService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author QiuQiu&LL (个人博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/qbbit)
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022-05-25 19:58
* @Description:
*/
@Service
public class CacheServiceImpl implements CacheService {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
/**
* 查询缓存
*
* @param category3Tree
* @return
*/
@Override
public List<CategoryTreeTo> getData(String category3Tree) {
// 先查询缓存
String categoryStr = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(category3Tree);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(category3Tree)) {
return null;
}
// 缓存中有
List<CategoryTreeTo> categoryTreeToList = JsonUtils.jsonToList(categoryStr, CategoryTreeTo.class);
return categoryTreeToList;
}
/**
* 添加数据到缓存
*
* @param category3Tree
*/
@Override
public void saveData(List<CategoryTreeTo> category3Tree) {
String json = JsonUtils.objectToJson(category3Tree);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("category3Tree", json);
}
}
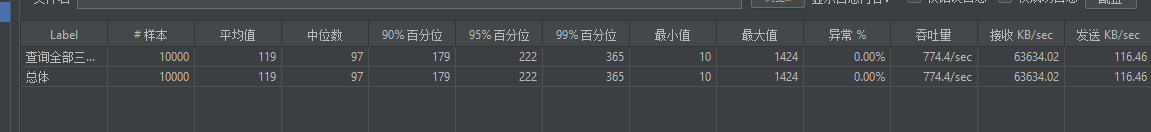
数据吞吐量虽说没有本地缓存那么高,但还是比不使用缓存好很多的,而且未来项目中也会大量使用到分布式缓存


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号