Spring原理与源码分析系列(二)- Spring IoC容器启动过程分析(上)
前言
Spring的IoC容器是一个提供IoC支持的轻量级容器。
Spring提供了两种容器:BeanFactory和ApplicationContext。
两者的继承关系图如下:
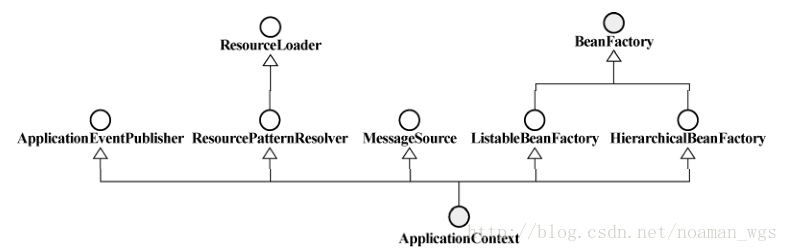
• BeanFactory:基本的IoC容器,默认采用延迟初始化策略(lazy-load),即只有当客户端对象需要访问容器中某个bean对象的时候,才会对该bean对象进行初始化以及依赖注入操作。 所以BeanFactory容器的特点是启动初期速度快,所需资源有限,适合于资源有限功能要求不严格的场景。
• ApplicationContext: ApplicationContext在BeanFactory基础上构建,支持其他的高级特性,如国际化,事件发布等。
相对于BeanFactory容器来说,ApplicationContext在启动的时候即完成资源的初始化,所以启动时间较长,适合于系统资源充足,需要更多功能的场景。
关于Spring容器启动过程的分析,本章节分为两篇文章进行叙述:
第一篇主要介绍Spring中Bean的相关概念以及IoC容器类型;
第二篇开始详细介绍IoC容器的启动过程。
本篇详述Spring中Bean的相关概念以及IoC容器类型。
一、Spring Bean
在介绍IoC容器之前,我们需要知道什么是Bean以及相关概念。
1、Bean定义
Java 中Bean的定义:
类中所有的属性都必须封装,即:使用private声明;
封装的属性如果需要被外部所操作,则必须编写对应的setter、getter方法;
一个JavaBean中至少存在一个无参构造方法。
如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | package com.wgs.spring.bean;/** * @author GenshenWang.nomico * @date 2017/11/23. */public class User { private String name; private int age; public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getName() { return name; } public int getAge() { return age; }} |
而Spring IoC容器就是管理bean的工厂。
Spring中bean 是一个被实例化,组装,并通过 Spring IoC 容器所管理的对象。这些 bean 是由用容器提供的配置元数据创建的。
Spring可以采用XML配置文件的方式来管理和配置Bean信息,如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"><bean id="user" class="com.wgs.spring.bean.User"></bean></beans> |
<beans>是XML配置文件中根节点,下面可包含多个<bean>子节点。
Spring的XML配置文件中的配置与<bean>元素是一一对应的。
下面来看看bean定义的常见属性:
(1)id属性
通常,注册到容器的对象都有一个唯一的id值,如id="user",这个id值使其表示的bean与其他bean区分开来,当然也可以用以下的name属性值进行标识;
(2)name属性
可以用name属性来指定bean的别名。
如:
1 | <bean id="user" name="beanname/user" class="com.wgs.spring.bean.User"></bean> |
name可以使用逗号、空格或冒号等分割指定多个name,而id就不可以。
(3)class属性
每个注册到容器的bean都需要通过class属性指定其类型。(部分情况例外 )
其余常见属性:

2、Bean的类型
• XML
• Annotation
• Class
• Properties、YML
3、Bean的注入方式
在XML配置中,常用的是构造方法注入与setter注入两种方式。
(1)构造方法注入
构造方法注入是通过有参构造器方法来注入属性值,在XML中通过<constructor-arg type="" value="">为其赋值。
如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | public class User { private String name; private int age; public User(String name){ this.name = name; } public User(int age){ this.age = age; } public User(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; }} |
这样在Xml中,就可以通过type属性来指定要传入的参数类型。
比如:
如果给name赋值,就只需要传入一个type=”String”类型的值即可:
1 2 3 4 5 | <bean id="user" class="com.wgs.spring.bean.User"> <constructor-arg type="java.lang.String"> <value>wgs</value> </constructor-arg></bean> |
如果给age赋值,就只需要传入一个type=”int”类型的值即可:
1 2 3 4 5 | <bean id="user" class="com.wgs.spring.bean.User"> <constructor-arg type="int"> <value>25</value> </constructor-arg></bean> |
如果给age,name同时赋值,就可以通过index来指定传入参数的顺序:
1 2 3 4 | <bean id="user" class="com.wgs.spring.bean.User"> <constructor-arg index="0" value="wgs"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg index="1" value="25"></constructor-arg></bean> |
这样index=”0”的value值就赋值给构造器User(String name, int age)第1个参数值;
index=”1”的value值就赋值给构造器第2个参数值.
如果在构造器中有别的对象的依赖,可以通过ref属性来赋值。
(2)setter方法注入
setter方法注入需要Bean类提供setter方法和无参构造器,在XML配置文件中通过<property name = "" value="">为其赋值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | public class User { private String name; private int age; public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; }} |
在XML中为setter方法提供了<property >元素。<property >元素有个name属性,用来指定对应bean类中的属性值。
如下:
1 2 3 4 | <bean id="user" class="com.wgs.spring.bean.User"> <property name="age" value="25"></property> <property name="name" value="wgs"></property></bean> |
4、Bean的scope
scope常被叫做“作用域”,声明容器中该对象的存活时间。超过这个scope,对象即将被销毁。
bean常见的scope有:
• singleton
• prototype
• request
• session
• global session
容器默认的scope是singleton。
常用的是如下两种类型:
(1)singleton
声明为singleton类型的bean在容器中有如下特性:
一个对象实例:singleton类型的bean在一个容器中只存在一个共享实例,所有对该类型bean的引用,都会共享这单一实例。
对象实例存活时间:从容器启动到它第一次被请求而实例化开始,将一直存活到容器退出。即与IoC容器的生命周期相同。
IoC容器中默认的scope即是singleton,在XML中也可以设置为false:
1 | <bean id="user" name="beanname/user" class="com.wgs.spring.bean.User" scope="singleton"></bean> |
(2) prototype
声明为prototype类型的bean在容器中有如下特性:
• 对象实例:容器在接到该类型对象的请求的时候,每次都会重新创建一个新的对象实例给请求方;
• 生命周期:容器每次返回请求方一个新的对象实例后,就不再拥有该对象的引用;该对象的生死均由请求方负责。
对于那些请求方不能共享使用的对象类型,应该将其bean定义的scope设置为prototype。
1 | <bean id="user" name="beanname/user" class="com.wgs.spring.bean.User" scope="prototype"></bean> |
这样每个请求方都可以得到自己对应的一个对象实例。
singleton与prototype的区别:
(1)singleton类型的对象在容器只会存在一个对象实例,被共享;
而prototype类型的对象会每次创建新的对象实例。
(2)singleton类型的对象的生命周期由容器管理;
而prototype类型的对象的生命周期由请求方管理。
5、BeanDefinition接口(BD)
Spring IoC是管理Bean的容器,负责创建,装配,销毁Bean。
在IoC容器中,BeanDefinition抽象了Bean的定义,保存了Bean的必要信息,
如在xml配置中,BeanDefinition就保存了与<bean>相关的id,name,aliases等属性,
封装了很多与Bean相关的基本数据(在XML配置中这些数据都是通过诸如<bean id="" name="">等标签进行配置的),
是容器实现依赖反转功能的核心数据结构。
下面是BeanDefinition的源码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 | public interface BeanDefinition extends AttributeAccessor, BeanMetadataElement { String SCOPE_SINGLETON = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON; String SCOPE_PROTOTYPE = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE;<br> int ROLE_APPLICATION = 0; int ROLE_SUPPORT = 1; int ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE = 2;<br> String getParentName(); void setParentName(String parentName);<br> String getBeanClassName(); void setBeanClassName(String beanClassName);<br> String getFactoryBeanName(); void setFactoryBeanName(String factoryBeanName);<br> String getFactoryMethodName(); void setFactoryMethodName(String factoryMethodName);<br> String getScope(); void setScope(String scope);<br> boolean isLazyInit(); void setLazyInit(boolean lazyInit);<br> String[] getDependsOn(); void setDependsOn(String... dependsOn);<br> boolean isAutowireCandidate(); void setAutowireCandidate(boolean autowireCandidate);<br> boolean isPrimary();<br> void setPrimary(boolean primary);<br> ConstructorArgumentValues getConstructorArgumentValues();<br> MutablePropertyValues getPropertyValues();<br> boolean isSingleton(); boolean isPrototype(); boolean isAbstract();<br> int getRole();<br> String getDescription(); String getResourceDescription();<br> BeanDefinition getOriginatingBeanDefinition();} |
可以看到BeanDefinition接口中定义了很多bean相关的属性和方法,
如类名,scope,属性,构造参数列表,是否单例,是否软加载等。
这样对bean的操作实际上就是直接对BeanDefinition进行操作。
BeanDefinition接口继承了AttributeAccessor接口,说明它拥有处理属性的能力;
BeanDefinition接口继承了BeanMetadataElement 接口,说明它拥有bean元素的属性。
BeanDefinition只是一个接口,最主要的一个子实现类:AbstractBeanDefinition; 常用的孙实现类有:
• ChildBeanDefinition
• RootBeanDefinition
• GenericBeanDefinition
二、Spring IoC容器-->BeanFactory容器
1、BeanFactory容器职责-->对象注册与依赖绑定
BeanFactory就是生成Bean的工厂,作为Spring提供的基本的IoC容器,其主要职责是:
• 业务对象的注册
• 对象间依赖关系的绑定
BeanFactory的源码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 | package org.springframework.beans.factory;import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;import org.springframework.core.ResolvableType;public interface BeanFactory { String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&"; Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException; <T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException; Object getBean(String name, Object... args) throws BeansException; <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType, Object... args) throws BeansException; boolean containsBean(String name); boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; boolean isPrototype(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; boolean isTypeMatch(String name, ResolvableType typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; boolean isTypeMatch(String name, Class<?> typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; Class<?> getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; String[] getAliases(String name);} |
可以看出,BeanFactory接口中定义了一系列管理Bean的方法,如:
• getBean:在容器中根据Bean name取得某个Bean;
• containsBean:判断容器中是否存在某个Bean;
• isSingleton:判断Bean是否是Singleton类型的Bean;
• isPrototype:判断Bean是否是Prototype类型的Bean;
• isTypeMatch:判断Bean的Class类型与指定的Class类型是否匹配;
• getType:查询Bean的Class类型;
• getAliases:查询Bean的别名。
…
BeanFactory只是一个接口,而DefaultListableBeanFactory是其一个较为通用的实现类。
下图是BeanFactory容器对象注册与依赖绑定过程中涉及到的接口:
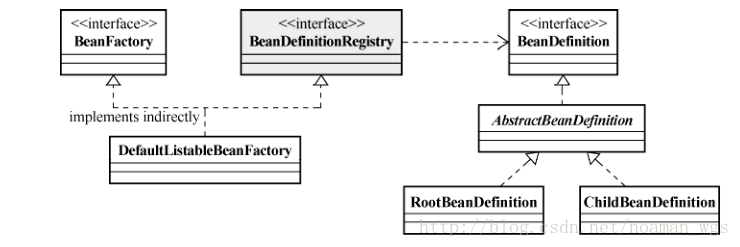
如图所示,DefaultListableBeanFactory除了间接实现BeanFactory接口,还实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口。
BeanDefinitionRegistry接口定义抽象了Bean的注册逻辑,担当Bean注册管理的角色,而BeanDefinitionRegistry将Bean注册到容器当中,是以BeanDefinition保存的。
在容器当中每一个受管理的Bean都有一个与之对应的BeanDefinition,BeanDefinition保存对象的所有必要信息。
总结:
• BeanFactory:该接口只定义如何访问容器内管理的Bean的方法;
• BeanDefinitionRegistry:该接口充当Bean注册管理的角色;
• DefaultListableBeanFactory:上述两接口的具体实现类,负责Bean注册以及管理的管理。
2. 对象注册与依赖绑定方式
上小节描述了BeanFactory的功能与职责主要是对象注册与依赖绑定。
Spring提供了三种方式来实现对象注册与依赖绑定过程。
(1)直接编码方式
首先: 需要通过BeanFactory来创建一个IoC容器,
然后: 通过BeanDefinitionRegistry将bean注册到容器当中(而DefaultListableBeanFactory是上述两接口的具体实现类),
最后: 可通过构造注入或者setter注入方式完成对象间关系的依赖绑定。
代码实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 | package com.wgs.spring.registry;import org.springframework.beans.MutablePropertyValues;import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValue;import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConstructorArgumentValues;import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinition;import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry;import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory;import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition;public class BeanFactoryRegistryDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { DefaultListableBeanFactory beanRegistry = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); BeanFactory beanFactory = bindBeanByCode(beanRegistry); //3 完成上述步骤后即可从容器获取Bean实例 CommentService service = (CommentService) beanFactory.getBean("commentService"); System.out.println(service.getCount()); } public static BeanFactory bindBeanByCode(BeanDefinitionRegistry beanRegistry){ //先将Bean抽象成BeanDefinition AbstractBeanDefinition commentService = new RootBeanDefinition(CommentService.class); AbstractBeanDefinition commentDao = new RootBeanDefinition(CommentDao.class); //1 注册:beanRegistry是BeanDefinitionRegistry实现类,可以实现Bean注册功能 beanRegistry.registerBeanDefinition("commentService", commentService); beanRegistry.registerBeanDefinition("commentDao", commentDao); //2 依赖绑定:将commnetDao绑定到commnetService当中 // (1)通过构造方法注入 /* ConstructorArgumentValues argumentValues = new ConstructorArgumentValues(); argumentValues.addIndexedArgumentValue(0, commentDao); commentService.setConstructorArgumentValues(argumentValues);*/ // (2)通过setter方法注入 MutablePropertyValues propertyValues = new MutablePropertyValues(); propertyValues.addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue("commentDao", commentDao)); commentService.setPropertyValues(propertyValues); return (BeanFactory)beanRegistry; }} |
(2)外部配置文件方式
Spring的IoC容器支持两种配置文件格式:
• Properties文件格式
• XML文件格式
在这个过程中有个很重要的接口:BeanDefinitionReader。
该接口负责读取配置文件内容并映射到BeanDefinition,然后将BeanDefinition交由BeanDefinitionRegistry 完成Bean的注册与加载。
本文通过XML文件格式来描述这个功能,代码实现如下:
xml配置文件:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <bean id="commentDao" class="com.wgs.spring.registry.CommentDao"/> <bean id="commentService" class="com.wgs.spring.registry.CommentService"> <property name="commentDao"> <ref bean="commentDao"></ref> </property> </bean></beans> |
Spring中提供了BeanDefinitionReader的实现类XmlBeanDefinitionReader来读取文件内容,并加载到容器中:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | package com.wgs.spring.registry;import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.*;import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader;/** * @author GenshenWang.nomico * @date 2017/11/17 */public class BeanFactoryRegistryDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { DefaultListableBeanFactory beanRegistry = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); BeanFactory container = bindBeanByXML(beanRegistry); CommentService commentService = (CommentService) container.getBean("commentService"); System.out.println(commentService.getCount()); } public static BeanFactory bindBeanByXML(BeanDefinitionRegistry beanRegistry){ //读取配置文件内容,解析文件格式,并映射到对应的BeanDefinition,完成注册 XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanRegistry); reader.loadBeanDefinitions("classpath:/spring.xml"); return (BeanFactory) beanRegistry; }} |
(3)注解方式
注解方式需要使用@Autowired和@Component对对象进行标记。
@Component:配合<context:component-scan base-package=""/>使用,
<context:component-scan package=""/>会扫描指定的包(package)下标注有 @Component的类,并将他们作为Bean添加到容器当中进行管理;
@Autowired:通知容器,将依赖对象注入到当前对象中。
代码实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | @Componentpublic class CommentDao {...}@Componentpublic class CommentService { @Autowired private CommentDao commentDao; public int getCount(){ commentDao = new CommentDao(); return commentDao.getCommentCount(); }}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="com.wgs.spring.registry"/></beans> |
三、Spring IoC容器—ApplicationContext容器
ApplicationContext是高级IoC容器的实现,除了拥有BeanFactory支持的所有功能外,还进一步拓展了基本容器的功能,包括:
• BeanFactoryPostProcessor
• 特殊类型的bean的自动识别
• 容器启动后bean实例的自动初始化
• 国际化
• 容器内时间发布
Spring为BeanFactory提供了XmlBeanFactory实现;相应地为ApplicationContext类型容器提供如下几个常用实现:
(1)FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:从文件系统加载bean定义以及相关资源的ApplicationContext实现;
(2)ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:从classpath下加载bean定义以及相关资源的ApplicationContext实现;
(3)XmlWebApplicationContext:从Web应用程序中加载bean定义以及相关资源的ApplicationContext实现。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理