springboot系列05:redis使用
Redis 介绍
redis 是目前使用最为广泛的内存数据存储,支持丰富的数据结构,如hashes, lists, sets 等,同时支持数据持久化。除此之外,Redis 还提供一些类数据库的特性,比如事务,HA,主从库。
Redis 在springboot中的使用
-
引入依赖包
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId></dependency><dependency> <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId> <artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId></dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope></dependency> |
-
添加配置文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | # Redis数据库索引(默认为0)spring.redis.database=0 # Redis服务器地址spring.redis.host=localhost# Redis服务器连接端口spring.redis.port=6379 # Redis服务器连接密码(默认为空)spring.redis.password=# 连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制) 默认 8spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-active=8# 连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制) 默认 -1spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-wait=-1# 连接池中的最大空闲连接 默认 8spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-idle=8# 连接池中的最小空闲连接 默认 0spring.redis.lettuce.pool.min-idle=0 |
-
添加cache配置类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 | package com.example.redis.config;import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport;import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import java.lang.reflect.Method;@Configuration@EnableCaching //开启缓存public class RedisConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport { @Bean public KeyGenerator keyGenerator() { return new KeyGenerator() { @Override public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append(target.getClass().getName()); sb.append(method.getName()); for (Object obj : params) { sb.append(obj.toString()); } return sb.toString(); } }; }} |
-
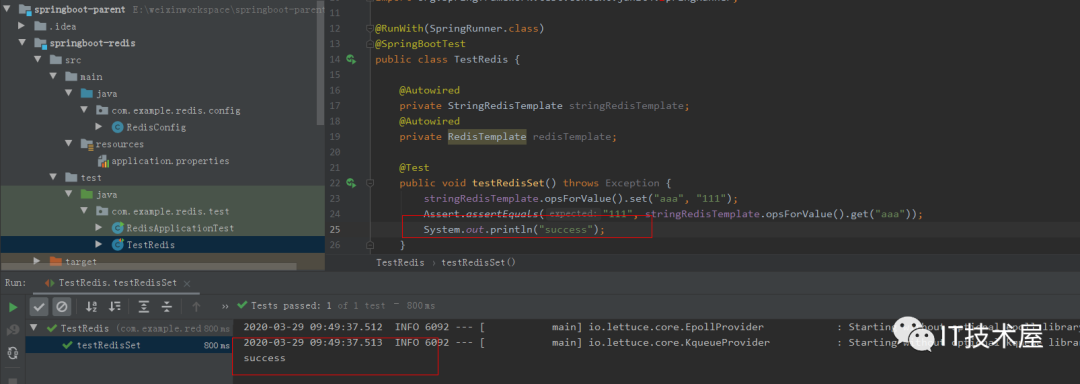
测试类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | package com.example.redis.test;import org.junit.Assert;import org.junit.Test;import org.junit.runner.RunWith;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)@SpringBootTestpublic class TestRedis { @Autowired private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate; @Autowired private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; @Test public void testRedisSet() throws Exception { stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("aaa", "111"); Assert.assertEquals("111", stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("aaa")); } } |
-
启动redis,运行TestRedis.testRedisSet 测试类报错信息:
1 2 3 4 | java.lang.IllegalStateException: Unable to find a @SpringBootConfiguration, you need to use @ContextConfiguration or @SpringBootTest(classes=...) with your test at org.springframework.util.Assert.state(Assert.java:73) at org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTestContextBootstrapper.getOrFindConfigurationClasses(SpringBootTestContextBootstrapper.java:233) |
-
解决方法:测试根目录编写测试启动类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | package com.example.redis.test;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;@SpringBootApplicationpublic class RedisApplicationTest { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(RedisApplicationTest.class,args); }} |
成功结果:
redis操作对象User
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | package com.example.domain;import lombok.Data;import java.io.Serializable;import java.util.Date;@Datapublic class User implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private Long id; private String userName; private String password; private String email; private String nickname; private Date regTime; |
测试对象是否存在
1 2 3 4 5 6 | @Test public void testUserExist() throws Exception { User user=new User(1L,"zhangl", "123456", "1796969389@qq.com", "zhangl",new Date()); redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("User::"+ user.getId(), user); Assert.assertEquals(true, redisTemplate.hasKey("User::"+ user.getId())); } |
测试获取对象属性
1 2 3 4 5 6 | @Test public void testUserName() throws Exception { User user=new User(1L,"zhangl", "123456", "1796969389@qq.com", "zhangl",new Date()); redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("User::"+ user.getId(), user); Assert.assertEquals("zhangl", ((User)redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("User::"+ user.getId())).getUserName()); } |
-
测试删除对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | @Test public void testUserDelete() throws Exception { User user=new User(1L,"zhangl", "123456", "1796969389@qq.com", "zhangl",new Date()); redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("User::"+ user.getId(), user); redisTemplate.delete("User::"+ user.getId()); Assert.assertEquals(false, redisTemplate.hasKey("User::"+ user.getId())); } |
-
测试过期时间
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | @Testpublic void testUserSetTime() throws Exception { User user=new User(1L,"zhangl", "123456", "1796969389@qq.com", "zhangl",new Date()); redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("User::"+ user.getId(), user,1, TimeUnit.SECONDS); Assert.assertEquals(true, redisTemplate.hasKey("User::"+ user.getId())); //等待1s Thread.sleep(1000L); Assert.assertEquals(false, redisTemplate.hasKey("User::"+ user.getId())); } |
分类:
spring boot
标签:
spring





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 写一个简单的SQL生成工具