865. Smallest Subtree with all the Deepest Nodes
问题描述:
Given a binary tree rooted at root, the depth of each node is the shortest distance to the root.
A node is deepest if it has the largest depth possible among any node in the entire tree.
The subtree of a node is that node, plus the set of all descendants of that node.
Return the node with the largest depth such that it contains all the deepest nodes in its subtree.
Example 1:
Input: [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
Output: [2,7,4]
Explanation:
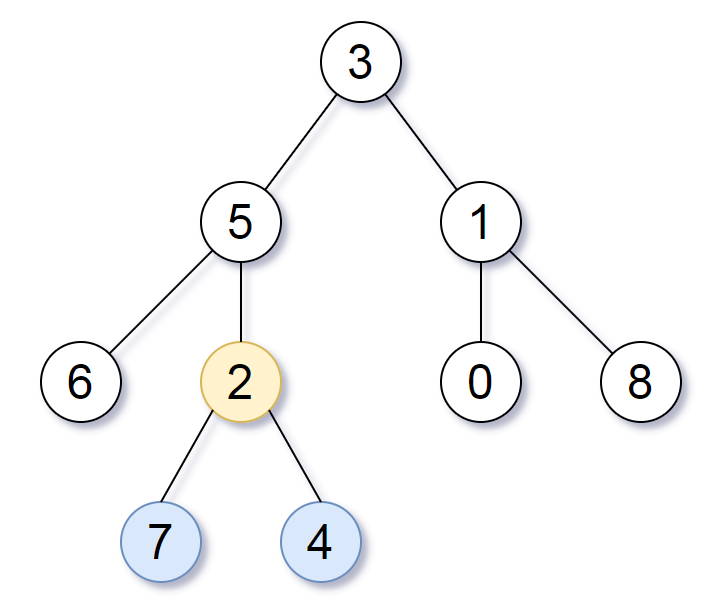 We return the node with value 2, colored in yellow in the diagram.
The nodes colored in blue are the deepest nodes of the tree.
The input "[3, 5, 1, 6, 2, 0, 8, null, null, 7, 4]" is a serialization of the given tree.
The output "[2, 7, 4]" is a serialization of the subtree rooted at the node with value 2.
Both the input and output have TreeNode type.
We return the node with value 2, colored in yellow in the diagram.
The nodes colored in blue are the deepest nodes of the tree.
The input "[3, 5, 1, 6, 2, 0, 8, null, null, 7, 4]" is a serialization of the given tree.
The output "[2, 7, 4]" is a serialization of the subtree rooted at the node with value 2.
Both the input and output have TreeNode type.
Note:
- The number of nodes in the tree will be between 1 and 500.
- The values of each node are unique.
解题思路:
参考了lee215的解法。
本质上也是后序遍历。
返回值是一个pair,pair.first是深度,pair.second当前包含最深的根节点。
当root不存在时,返回{0, NULL}
若存在,对左孩子和右孩子分别调用这个方法。
若左孩子和右孩子的深度相同,说明在做孩子和右孩子都有最深的节点,此时拥有所有最深节点的节点为当前节点。
若不相同,取深度最大的拥有最深节点的点。
代码:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode* root) { return deep(root).second; } pair<int, TreeNode*> deep(TreeNode* root){ if(!root) return {0, NULL}; pair<int, TreeNode*> l = deep(root->left), r = deep(root->right); int d1 = l.first, d2 = r.first; return {max(d1, d2)+1 , d1 == d2 ? root : d1 > d2 ? l.second : r.second}; } };




