第八节:高阶链表详解(循环链表、双向链表)
一. 循环链表简介
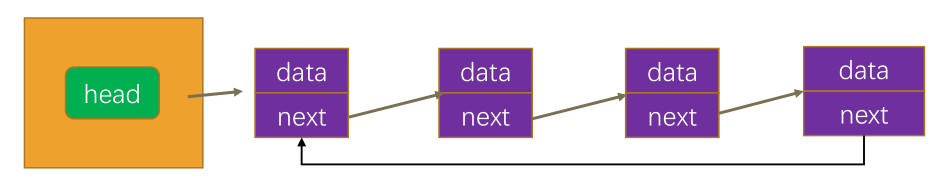
1. 什么是循环链表?
在普通链表的基础上,最后一个节点的下一个节点不再是 null,而是指向链表的第一个节点。
这样形成了一个环,使得链表能够被无限遍历。
这样,我们就可以在单向循环链表中从任意一个节点出发,不断地遍历下一个节点,直到回到起点。
二. 单项链表改造
1. 目的
便于后面的双向链表和循环链表继承
2. 重构思路
链表类LinkedList新增tail属性,指向尾节点
/**
* 单链表类
*/
class LinkedList<T> implements ILinkedList<T> {
head: Node<T> | null = null; //就是头节点!!!(就是第一个节点)
protected size: number = 0; //内部使用
// 新增tail属性,表示指向尾节点
tail: Node<T> | null = null;
}3. 重构的位置
append:直接简化了while循环,代码简洁了很多
/**
* 1. 向尾部插入元素
* @param val 插入的元素
*
*/
append(val: T): void {
let newNode = new Node(val);
//1.链表本身为空
if (!this.head) {
this.head = newNode;
}
//2.链表不为空
else {
this.tail!.next = newNode;
}
//3.tail都需要指向这个新节点
this.tail = newNode;
//4.最后数量+1
this.size++;
}insert:只有在尾部插入的时候,才需要处理tail,中间位置或头部不需处理
/**
* 3. 任意位置插入
* @param val 插入的元素
* @param position 插入位置,索引从0开始(0时插入在最前面,1时插入在1节点和2节点之间,2时插入在2节点和3节点之间)
* 重点区分:A=B 表示A和B都是相同的,可以理解成A和B在内存中指向同一个区域
* A.next=B 表示A是B的前一个节点
*
*/
insert(val: T, position: number): boolean {
// 非法位置,越界了
if (position < 0) return false;
let newNode = new Node(val); // 创建新节点
// 向头位置插入
if (position == 0) {
newNode.next = this.head; //这里head节点就是第一个节点
this.head = newNode;
}
// 向中间位置或者最后位置插入
else {
let previous = this.getNode(position - 1);
newNode.next = previous!.next; //previous.next 相当于current
previous!.next = newNode;
//最后位置插入,需要处理tail指向
if (position === this.size) {
this.tail = newNode;
}
}
this.size++;
return true;
}removeAt:当只有一个节点 和 删除的是最后一个节点的时候需要处理
/**
* 4. 删除指定位置节点
* @param position 删除的位置,索引从0开始(0时删除在第1个节点,1时表示删除第2个节点,索引的最大值比length小1)
* @returns 返回删除的节点值 或者 null
* 几个注意的点:
* (1). 找到正确位置后,就可以直接将上一项的next指向current项的next,这样中间的项就没有引用指向它,也就不再存在于链表后,会面会被回收掉
* (2). while遍历完后,只操作了previous节点,此时current还指向一个节点,但它是局部遍历,完成后就消失了
*/
removeAt(position: number): T | null {
//1.越界处理
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null;
//2.正常的索引
let current = this.head;
//2.1 删除第1个节点
if (position === 0) {
//这里要考虑是否总共1个节点
// this.head = this.length === 1 ? null : current!.next;
//等价于
this.head = current?.next ?? null;
//只有一个节点,需要处理tail (还没到下面的size--,所以是1,不是0)
if (this.size === 1) {
this.tail = null;
}
}
//2.2 删除中间节点(即第二个 或 以后的节点)
else {
let previous = this.getNode(position - 1);
previous!.next = previous?.next?.next ?? null;
//删除的是最后一个节点
if (position == this.size - 1) {
this.tail = previous;
}
}
this.size--;
return current?.value ?? null;
}4. 新增方法:isTail
用来判断当前节点是否是最后一个节点
/**
* 10. 判断该节点是否是尾节点
* @param node 需要判断的节点
* @returns true or false
*/
isTail(node: Node<T>): Boolean {
return this.tail === node;
}5. 针对循环链表需要改造
(1) traverse
当循环到尾节点的时候,需要停止,否则就无限循环了
循环列表特有的输出格式(aa→bb→cc→aa)
/**
* 2. 遍历链表
* 以string拼接的形式输出
*/
traverse(): string {
let array: T[] = []; //用数组来存储
let current = this.head;
while (current) {
array.push(current.value);
//当是尾节点的时候,current滞空,则退出循环
if (this.isTail(current)) {
current = null;
} else {
current = current.next;
}
}
//下面是循环列表特有的输出格式(aa→bb→cc→aa)
if (this.head && this.tail?.next == this.head) {
array.push(this.head.value);
}
return array.join("->");
}(2). indexOf
当是尾节点的时候需要中断循环
/**
* 6. 根据内容值返回索引
* @param val 内容值
* @returns 返回的所以,不存在则返回-1
*/
indexOf(val: T): number {
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
while (current) {
if (current.value === val) return index;
//当是尾节点的时候需要中断循环
if (this.isTail(current)) {
current = null;
} else {
current = current.next; //向后移位
}
index++;
}
return -1; //返回-1,表示不存在
}
三. 循环链表实操
1. append方法重写
在单链表的append方法的基础上,只需要处理一下tail的next指向即可
class CircularLinkList<T> extends LinkedList<T> {
/**
* 01-向尾部追加节点
* @param val 内容
*/
append(val: T): void {
super.append(val);
//处理tail的指向问题
this.tail!.next = this.head;
}
}2. insert
在单链表的insert方法的基础上,只需要处理一下tail的next指向即可
因为tail的next指向head,所以tail的next指向只有在插入头部 或 尾部的时候才需要处理
/**
* 02. 任意位置插入
* @param val 插入的元素
* @param position 插入位置,索引从0开始(0时插入在最前面,1时插入在1节点和2节点之间,2时插入在2节点和3节点之间)
*/
insert(val: T, position: number): boolean {
const isSuccess = super.insert(val, position);
//只有头部或尾部的时候才需要修改
if (isSuccess && (position === 0 || position === this.length - 1)) {
this.tail!.next = this.head;
}
return isSuccess;
}3. removeAt
在单链表的insert方法的基础上,只需要处理一下tail的next指向即可
因为tail的next指向head,所以tail的next指向只有在删除头部 或 尾部的时候才需要处理
注:这里是length而不是length-1,因为前面调用super.removeAt内部已经 -1了
/**
* 03. 删除指定位置节点
* @param position 删除的位置,索引从0开始(0时删除在第1个节点,1时表示删除第2个节点,索引的最大值比length小1)
* @returns 返回删除的节点值 或者 null
*/
removeAt(position: number): T | null {
const result = super.removeAt(position);
//只有删除头部或尾部的时候才需要修改
//注:这里是length而不是length-1,因为前面调用super.removeAt内部已经 -1了
if (result && (position === 0 || position === this.length)) {
this.tail!.next = this.head;
}
return result;
}4. traverse
直接在父类单向链表中修改
5. indexOf
直接在父类单向链表中修改
四. 双向链表简介
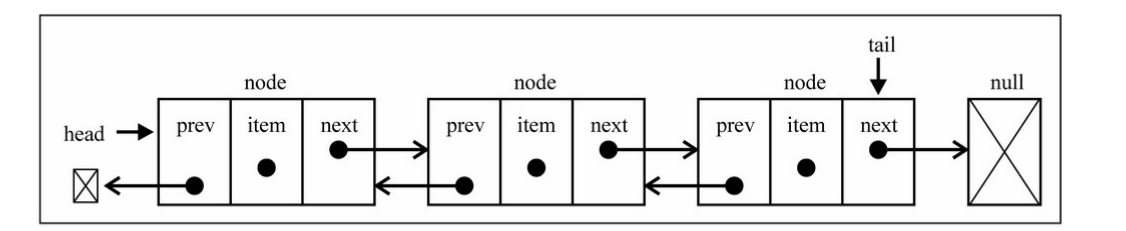
1. 定义
既可以从头遍历到尾, 又可以从尾遍历到头。一个节点既有向前连接的引用prev, 也有一个向后连接的引用next.
特别注意:双向链表不是循环链表!! 这是两个维度
2. 缺点
(1).每次在插入或删除某个节点时, 需要处理四个引用, 而不是两个. 也就是实现起来要困难一些
(2).相对于单向链表, 必然占用内存空间更大一些.
但是这些缺点和我们使用起来的方便程度相比, 是微不足道的.
五. 双向链表实操
1. 节点封装
声明DoublyNode双向链表节点类,继承Node节点类,新增prev属性,重写next属性,二者都是DoublyNode类型。
/**
* 双向链表
*/
class DoublyLinkedList<T> extends LinkedList<T> {
// 重写head和tail属性,目的:否则会导致append中的newNode.prev = this.tail无法赋值
head: DoublyNode<T> | null = null;
tail: DoublyNode<T> | null = null;
}2. append方法
在尾部追加元素
/**
* 01-在尾部追加元素
* @param val 添加的元素
*/
append(val: T): void {
let newNode = new DoublyNode<T>(val);
//1. 链表为空
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}
//2. 链表非空
else {
this.tail!.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
}
//3. 长度+1
this.size++;
}3. prepend方法
在头部添加元素
/**
* 02-在头部追加元素
* @param val 添加的元素
*/
prepend(val: T): void {
let newNode = new DoublyNode<T>(val);
//1. 链表为空
if (!this.head) {
this.head = this.tail = newNode;
}
//2. 链表非空
else {
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head.prev = newNode;
this.head = newNode;
}
//3. 长度+1
this.size++;
}4. postTraverse方法
从尾部遍历所有节点
/**
* 03-从尾部遍历所有节点
*/
postTravese() {
let current = this.tail;
let array: T[] = [];
while (current) {
array.push(current.value);
current = current.prev;
}
return array.join("=>");
}5. insert方法
根据索引插入元素
分三种情况,分别是从头部、尾部、中间插入,其中头部、尾部直接调用封装好的prepend、append方法即可,中间插入,则需要处理两个next 和 两个prev
/**
* 04-根据索引插入元素
* @param value 元素值
* @param position 索引,从0开始
* @returns 插入成功true,失败false
*/
insert(value: T, position: number): boolean {
//1. 边界判断
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) return false;
//2. 头部插入
if (position === 0) {
this.prepend(value);
}
//2.尾部插入
else if (position === this.length) {
this.append(value);
}
//3.中间插入
else {
/*
获取索引位置的节点,该节点将变成newNode的后面一个节点
*/
let newNode = new DoublyNode(value);
let current = this.getNode(position) as DoublyNode<T>;
//需要处理两个next
newNode.next = current;
current.prev!.next = newNode;
//需要处理两个prev
newNode.prev = current.prev;
current.prev = newNode;
this.size++;
}
return true;
}6. removeAt方法
根据索引删除元素,分三种情况,分别是从头部、尾部、中间删除,都需要对current进行赋值,用于返回
(1).其中头部删除,需要区分是否只有一个节点
(2).头部删除、尾部删除,都需要进行对应的置空操作,
(3).尾部删除,处理一下前后节点的 next 和 prev就行了
/**
* 05-根据索引位置删除元素
* @param position 索引位置
* @returns 返回删除的元素,删除失败返回null
*/
removeAt(position: number): T | null {
//1.边界判断
if (position < 0 || position > this.length - 1) return null;
let current = this.head; //默认值,即删除头部位置的时候不需要处理了
//2.删除头部位置
if (position === 0) {
//2.1 只有一个元素
if (this.length === 1) {
this.head = this.tail = null;
}
//2.2 多个元素
else {
this.head = this.head!.next;
//置空操作
this.head!.prev = null;
}
}
//3.删除尾部位置
else if (position === this.length - 1) {
current = this.tail;
this.tail = this.tail!.prev;
//置空操作
this.tail!.next = null;
}
//4.删除中间位置
else {
current = this.getNode(position) as DoublyNode<T>;
current.prev!.next = current.next;
current.next!.prev = current.prev;
// 不需要处理,内存机制也能清空
// current.next = null;
// current.prev = null;
}
this.size--;
return current?.value ?? null;
}注:其它方法都是可以直接继承使用的
!
- 作 者 : Yaopengfei(姚鹏飞)
- 博客地址 : http://www.cnblogs.com/yaopengfei/
- 声 明1 : 如有错误,欢迎讨论,请勿谩骂^_^。
- 声 明2 : 原创博客请在转载时保留原文链接或在文章开头加上本人博客地址,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· DeepSeek如何颠覆传统软件测试?测试工程师会被淘汰吗?
2018-01-02 第三节:ThreadPool的线程开启、线程等待、线程池的设置、定时功能