第二十二节:进程/线程、node事件机制、微任务/宏任务、相关面试题剖析
一. 进程/线程
(进程、线程、时间片相关概念详见:https://www.cnblogs.com/yaopengfei/p/12504514.html)
1. 概念
(1). 进程和线程是操作系统中的两个概念:
进程(process):计算机已经运行的程序,是操作系统管理程序的一种方式;
线程(thread):操作系统能够运行运算调度的最小单位,通常情况下它被包含在进程中;
(2). 通俗的理解:
进程:我们可以认为,启动一个应用程序,就会默认启动一个进程(也可能是多个进程);
线程:每一个进程中,都会启动至少一个线程用来执行程序中的代码,这个线程被称之为主线程;所以我们也可以说进程是线程的容器;
(3). 再用一个形象的例子解释:
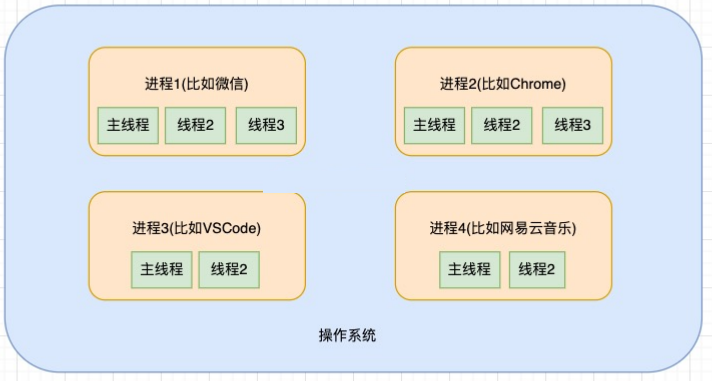
操作系统类似于一个大工厂;
工厂中里有很多车间,这个车间就是进程;
每个车间可能有一个以上的工人在工厂,这个工人就是线程;
2. 操作系统-进程-线程
3. 操作系统的工作方式
(1). 操作系统是如何做到同时让多个进程(边听歌、边写代码、边查阅资料)同时工作呢?
这是因为CPU的运算速度非常快,它可以快速的在多个进程之间迅速的切换;
当我们进程中的线程获取到时间片时,就可以快速执行我们编写的代码;
对于用户来说是感受不到这种快速的切换的;
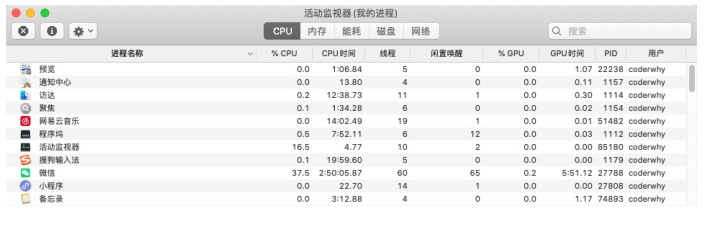
(2). 你可以在Mac的活动监视器或者Windows的资源管理器中查看到很多进程:
二. 浏览器的事件机制
1. 浏览器中的JavaScript线程
(1). 我们经常会说JavaScript是单线程的,但是JavaScript的线程应该有自己的容器进程:浏览器或者Node。
(2). 浏览器是一个进程吗,它里面只有一个线程吗?
A. 目前多数的浏览器其实都是多进程的,当我们打开一个tab页面时就会开启一个新的进程,这是为了防止一个页面卡死而造成所有页面无法响应,整个浏览器需要强制退出;
B. 每个进程中又有很多的线程,其中包括执行JavaScript代码的线程;
(3). JavaScript的代码执行是在一个单独的线程中执行的:
A. 这就意味着JavaScript的代码,在同一个时刻只能做一件事;
B. 如果这件事是非常耗时的,就意味着当前的线程就会被阻塞;
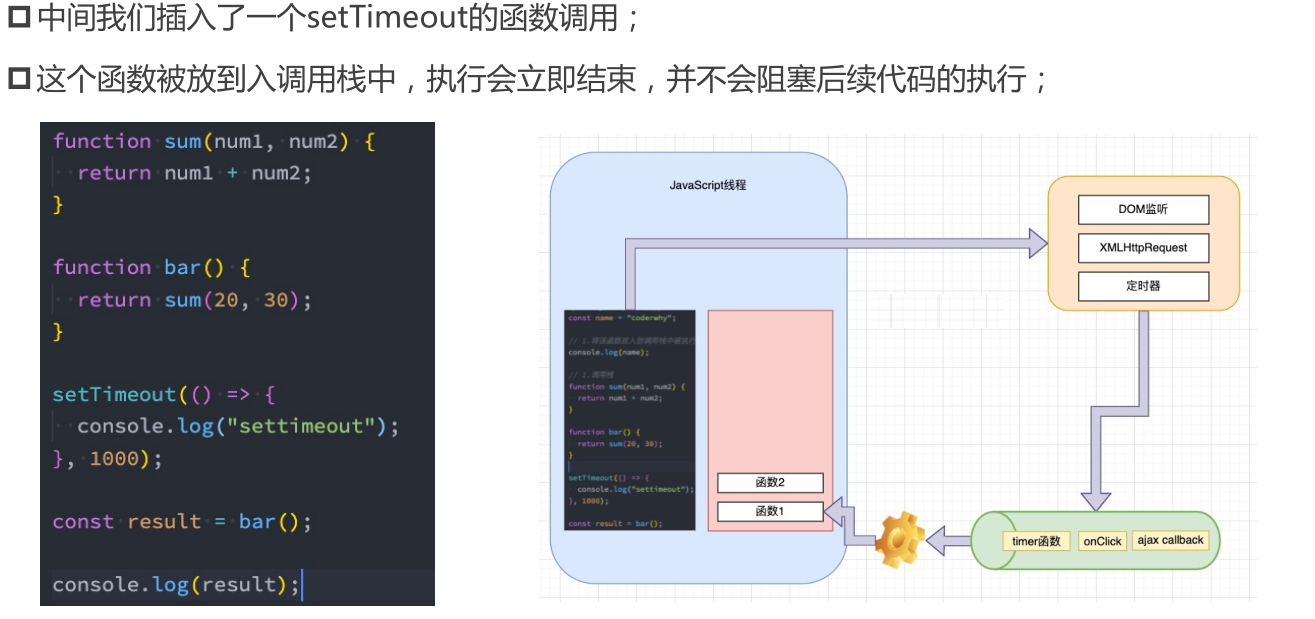
(4). 所以真正耗时的操作,实际上并不是由JavaScript线程在执行的:
A. 浏览器的每个进程是多线程的,那么其他线程可以来完成这个耗时的操作;
B. 比如网络请求、定时器,我们只需要在特性的时候执行应该有的回调即可;
三. 微任务/宏任务
1. 事件循环中并非只维护着一个队列,事实上是有两个队列:
宏任务队列(macrotask queue):ajax、setTimeout、setInterval、DOM监听、UI Rendering等
微任务队列(microtask queue):Promise的then回调、 Mutation Observer API、queueMicrotask()等
2. 那么事件循环对于两个队列的优先级是怎么样的呢?
(1). main script中的代码优先执行(编写的顶层script代码);
(2). 在执行任何一个宏任务之前(不是队列,是一个宏任务),都会先查看微任务队列中是否有任务需要执行也就是宏任务执行之前,必须保证微任务队列是空的;
如果不为空,那么就优先执行微任务队列中的任务(回调);
四. 相关面试题剖析
试题1

setTimeout(function () {
console.log("setTimeout1");
new Promise(function (resolve) {
resolve();
}).then(function () {
new Promise(function (resolve) {
resolve();
}).then(function () {
console.log("then4");
});
console.log("then2");
});
});
new Promise(function (resolve) {
console.log("promise1");
resolve();
}).then(function () {
console.log("then1");
});
setTimeout(function () {
console.log("setTimeout2");
});
console.log(2);
queueMicrotask(() => {
console.log("queueMicrotask1")
});
new Promise(function (resolve) {
resolve();
}).then(function () {
console.log("then3");
});
// promise1
// 2
// then1
// queueMicrotask1
// then3
// setTimeout1
// then2
// then4
// setTimeout2
试题2

// async function bar() {
// console.log("22222")
// return new Promise((resolve) => {
// resolve()
// })
// }
// async function foo() {
// console.log("111111")
// await bar()
// console.log("33333")
// }
// foo()
// console.log("444444")
async function async1 () {
console.log('async1 start')
await async2();
console.log('async1 end')
}
async function async2 () {
console.log('async2')
}
console.log('script start')
setTimeout(function () {
console.log('setTimeout')
}, 0)
async1();
new Promise (function (resolve) {
console.log('promise1')
resolve();
}).then (function () {
console.log('promise2')
})
console.log('script end')
// script start
// async1 start
// async2
// promise1
// script end
// async1 end
// promise2
// setTimeout
试题3

Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log(0);
// 1.直接return一个值 相当于resolve(4)
// return 4
// 2.return thenable的值
return {
then: function(resolve) {
// 大量的计算
resolve(4)
}
}
// 3.return Promise
// 不是普通的值, 多加一次微任务
// Promise.resolve(4), 多加一次微任务
// 一共多加两次微任务
return Promise.resolve(4)
}).then((res) => {
console.log(res)
})
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log(1);
}).then(() => {
console.log(2);
}).then(() => {
console.log(3);
}).then(() => {
console.log(5);
}).then(() =>{
console.log(6);
})
// 1.return 4
// 0
// 1
// 4
// 2
// 3
// 5
// 6
// 2.return thenable
// 0
// 1
// 2
// 4
// 3
// 5
// 6
// 3.return promise
// 0
// 1
// 2
// 3
// 4
// 5
// 6
试题4

async function async1() {
console.log('async1 start')
await async2()
console.log('async1 end')
}
async function async2() {
console.log('async2')
}
console.log('script start')
setTimeout(function () {
console.log('setTimeout0')
}, 0)
setTimeout(function () {
console.log('setTimeout2')
}, 300)
setImmediate(() => console.log('setImmediate'));
process.nextTick(() => console.log('nextTick1'));
async1();
process.nextTick(() => console.log('nextTick2'));
new Promise(function (resolve) {
console.log('promise1')
resolve();
console.log('promise2')
}).then(function () {
console.log('promise3')
})
console.log('script end')
// script start
// async1 start
// async2
// promise1
// promise2
// script end
// nexttick1
// nexttick2
// async1 end
// promise3
// settimetout0
// setImmediate
// setTimeout2
!
- 作 者 : Yaopengfei(姚鹏飞)
- 博客地址 : http://www.cnblogs.com/yaopengfei/
- 声 明1 : 如有错误,欢迎讨论,请勿谩骂^_^。
- 声 明2 : 原创博客请在转载时保留原文链接或在文章开头加上本人博客地址,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· .NET周刊【3月第1期 2025-03-02】