第十六节:SpringMvc拦截器、全局异常处理、RestFul风格编程、文件上传
一. 拦截器
1. 简介
拦截器( Interceptor)是一种动态拦截方法调用的机制
作用:① 在指定的方法调用前后执行预先设定后的的代码 ②阻止原始方法的执行
核心原理: AOP思想
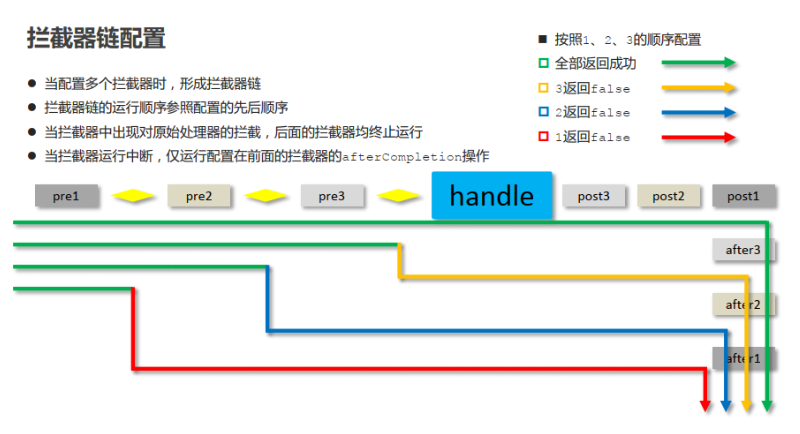
拦截器链:多个拦截器按照一定的顺序,对原始被调用功能进行增强
PS:拦截器 VS 过滤器

2. 实战开发-单拦截器
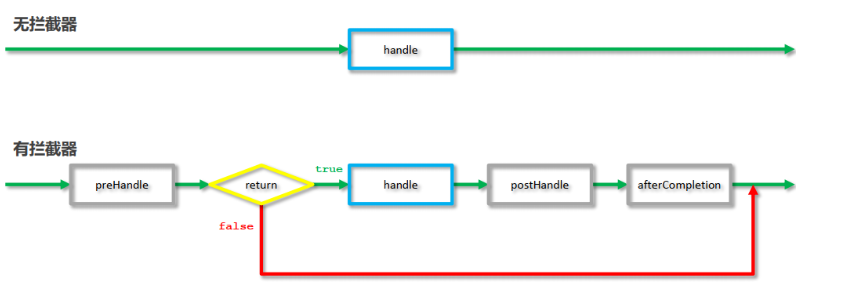
(1). 新建拦截器类 MyInterceptor1,实现 HandlerInterceptor接口,然后override三个方法,分别是:preHandle、postHandle、afterCompletion。
A. 前置处理方法preHandle
//处理器运行之前执行 @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { System.out.println("前置运行----a1"); //返回值为false将拦截原始处理器的运行 //如果配置多拦截器,返回值为false将终止当前拦截器后面配置的拦截器的运行 return true; }
参数剖析:
response:响应对象。 handler:被调用的处理器对象,本质上是一个方法对象,对反射中的Method对象进行了再包装。
返回值
返回值为true,继续往后执行。
B. 后置处理方法postHandle
//处理器运行之后执行 @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { System.out.println("后置运行----b1"); }
参数剖析:
modelAndView:如果处理器执行完成具有返回结果,可以读取到对应数据与页面信息,并进行调整。
C. 完成处理方法afterCompletion
//所有拦截器的后置执行全部结束后,执行该操作 @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { System.out.println("完成运行----c1"); }
参数剖析:
ex:如果处理器执行过程中出现异常对象,可以针对异常情况进行单独处理。
补充拦截器执行流程:
分享全部代码:

//拦截器1 //自定义拦截器需要实现HandlerInterceptor接口 public class MyInterceptor1 implements HandlerInterceptor { //处理器运行之前执行 @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { System.out.println("前置运行----a1"); //返回值为false将拦截原始处理器的运行 //如果配置多拦截器,返回值为false将终止当前拦截器后面配置的拦截器的运行 return true; } //处理器运行之后执行 @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { System.out.println("后置运行----b1"); } //所有拦截器的后置执行全部结束后,执行该操作 @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { System.out.println("完成运行----c1"); } //三个方法的运行顺序为 preHandle -> postHandle -> afterCompletion //如果preHandle返回值为false,三个方法仅运行preHandle }
(2). 开启拦截器配置
<mvc:interceptors> <mvc:interceptor> <!--拦截所有/User/开头的所有请求--> <mvc:mapping path="/User/*"/> <!--指定具体拦截器--> <bean class="com.ypf.interceptor.MyInterceptor1"/> </mvc:interceptor> </mvc:interceptors>
剖析:
<!--设置拦截器的拦截路径,支持*通配-->
<!--/** 表示拦截所有映射-->
<!--/* 表示拦截所有/开头的映射-->
<!--/User/* 表示拦截所有/User/开头的映射-->
<!--/User/add* 表示拦截所有/User/开头,且具体映射名称以add开头的映射-->
<!--/User/*All 表示拦截所有/User/开头,且具体映射名称以All结尾的映射-->
(3). 测试方法
@Controller @RequestMapping("User") public class UserController { @RequestMapping("/showMsg") @ResponseBody //http://localhost:8888/04_Interceptor_ErrorHandle/User/showMsg public String showMsg() { System.out.println("showMsg is running"); return "ok"; } }
运行结果:
A. preHandle中返回:true

B. preHandle中返回:false
3. 实战开发-多拦截器
(1). 准备三个拦截器: MyInterceptor1、MyInterceptor2、MyInterceptor3。

//拦截器1 //自定义拦截器需要实现HandlerInterceptor接口 public class MyInterceptor1 implements HandlerInterceptor { //处理器运行之前执行 @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { System.out.println("前置运行----a1"); //返回值为false将拦截原始处理器的运行 //如果配置多拦截器,返回值为false将终止当前拦截器后面配置的拦截器的运行 return true; } //处理器运行之后执行 @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { System.out.println("后置运行----b1"); } //所有拦截器的后置执行全部结束后,执行该操作 @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { System.out.println("完成运行----c1"); } //三个方法的运行顺序为 preHandle -> postHandle -> afterCompletion //如果preHandle返回值为false,三个方法仅运行preHandle } //拦截器2 //自定义拦截器需要实现HandlerInterceptor接口 public class MyInterceptor2 implements HandlerInterceptor { //处理器运行之前执行 @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { System.out.println("前置运行----a2"); //返回值为false将拦截原始处理器的运行 //如果配置多拦截器,返回值为false将终止当前拦截器后面配置的拦截器的运行 return true; } //处理器运行之后执行 @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { System.out.println("后置运行----b2"); } //所有拦截器的后置执行全部结束后,执行该操作 @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { System.out.println("完成运行----c2"); } //三个方法的运行顺序为 preHandle -> postHandle -> afterCompletion //如果preHandle返回值为false,三个方法仅运行preHandle } //拦截器1 //自定义拦截器需要实现HandlerInterceptor接口 public class MyInterceptor3 implements HandlerInterceptor { //处理器运行之前执行 @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { System.out.println("前置运行----a3"); //返回值为false将拦截原始处理器的运行 //如果配置多拦截器,返回值为false将终止当前拦截器后面配置的拦截器的运行 return true; } //处理器运行之后执行 @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { System.out.println("后置运行----b3"); } //所有拦截器的后置执行全部结束后,执行该操作 @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { System.out.println("完成运行----c3"); } //三个方法的运行顺序为 preHandle -> postHandle -> afterCompletion //如果preHandle返回值为false,三个方法仅运行preHandle }
(2). 配置多个拦截器
<!--4.2 开启多个拦截器--> <mvc:interceptors> <!--开启具体的拦截器的使用,可以配置多个--> <mvc:interceptor> <!--设置拦截器的拦截路径,支持*通配--> <!--/** 表示拦截所有映射--> <!--/* 表示拦截所有/开头的映射--> <!--/User/* 表示拦截所有/User/开头的映射--> <!--/User/add* 表示拦截所有/User/开头,且具体映射名称以add开头的映射--> <!--/User/*All 表示拦截所有/User/开头,且具体映射名称以All结尾的映射--> <mvc:mapping path="/*"/> <mvc:mapping path="/**"/> <!--设置拦截排除的路径,/User/showMsg2 不走MyInterceptor1拦截器--> <mvc:exclude-mapping path="/User/showMsg2"/> <!--指定具体的拦截器类--> <bean class="com.ypf.interceptor.MyInterceptor1"/> </mvc:interceptor> <!--配置多个拦截器,配置顺序即为最终运行顺序--> <mvc:interceptor> <mvc:mapping path="/**"/> <bean class="com.ypf.interceptor.MyInterceptor2"/> </mvc:interceptor> <mvc:interceptor> <mvc:mapping path="/**"/> <bean class="com.ypf.interceptor.MyInterceptor3"/> </mvc:interceptor> </mvc:interceptors>
(3). 测试
A. 三个拦截器中的preHandle都返回true。

B. MyInterceptor3中的preHander中返回false。

C. MyInterceptor2中的preHander中返回false。

D. MyInterceptor1中的preHander中返回false。

二. 全局异常处理
1. 通用异常过滤器1 (非注解形式)
/** * 通用异常过滤器1 (非注解形式) * 异常类实现HandlerExceptionResolver接口 * 注意:由于这个类实现了HandlerExceptionResolver接口,所以加上@Component后,springmvc就可以将他识别为异常处理器 */ @Component public class ExceptionResolver1 implements HandlerExceptionResolver { @Override public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o, Exception ex) { System.out.println("my exception is running ...."+ex); ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); if( ex instanceof NullPointerException){ modelAndView.addObject("msg","空指针异常"); }else if ( ex instanceof ArithmeticException){ modelAndView.addObject("msg","算数运算异常"); }else{ modelAndView.addObject("msg","未知的异常"); } modelAndView.setViewName("error.jsp"); return modelAndView; } }
注:
由于这个类实现了HandlerExceptionResolver接口,所以加上@Component后,springmvc就可以将他识别为异常处理器。不需要再做任何配置了。
2. 通用异常过滤器2(注解形式)
/** * 通用异常处理器2(注解的形式) * 加上@ControllerAdvice,使该类变为的通知类,声明后该类就会被加载成异常处理器,SpringMvc就会识别 * * 测试的时候需要注释掉:ExceptionResolver1中的@Component,从而使ExceptionResolver2单独生效 */ @Component @ControllerAdvice public class ExceptionResolver2 { //类中定义的方法携带@ExceptionHandler注解的会被作为异常处理器,后面添加实际处理的异常类型 @ExceptionHandler(NullPointerException.class) @ResponseBody public String doNullException(Exception ex){ return "空指针异常"; } @ExceptionHandler(ArithmeticException.class) @ResponseBody public String doArithmeticException(Exception ex){ return "ArithmeticException"; } @ExceptionHandler(Exception.class) @ResponseBody public String doException(Exception ex){ return "all error"; } }
注意:
加上@ControllerAdvice,使该类变为的通知类,声明后该类就会被加载成异常处理器,SpringMvc就会识别,不需要再做任何配置了。
以上两种异常处理器的测试类:
@RequestMapping("save1")
@ResponseBody
//http://localhost:8888/04_Interceptor_ErrorHandle/ExceptionTest/save1
public String save1(){
//模拟业务层发起调用产生了异常
int i = 1/0;
return "ok";
}
3. 自定义异常
(1). 两个基础异常处理器类

//自定义异常继承RuntimeException,覆盖父类所有的构造方法 public class SystemException extends RuntimeException { public SystemException() { } public SystemException(String message) { super(message); } public SystemException(String message, Throwable cause) { super(message, cause); } public SystemException(Throwable cause) { super(cause); } public SystemException(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace) { super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace); } } //自定义异常继承RuntimeException,覆盖父类所有的构造方法 public class BusinessException extends RuntimeException { public BusinessException() { } public BusinessException(String message) { super(message); } public BusinessException(String message, Throwable cause) { super(message, cause); } public BusinessException(Throwable cause) { super(cause); } public BusinessException(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace) { super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace); } }
(2). 一个主异常类

//异常处理器主类 //访问 /http://localhost:8888/04_Interceptor_ErrorHandle/ExceptionTest/save2?userName=ypf 进行测试 @Component @ControllerAdvice public class ProjectExceptionAdvice { @ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class) public String doBusinessException(Exception ex, Model m){ //使用参数Model将要保存的数据传递到页面上,功能等同于ModelAndView //业务异常出现的消息要发送给用户查看 m.addAttribute("msg",ex.getMessage()); return "error.jsp"; } @ExceptionHandler(SystemException.class) public String doSystemException(Exception ex, Model m){ //系统异常出现的消息不要发送给用户查看,发送统一的信息给用户看 m.addAttribute("msg","服务器出现问题,请联系管理员!"); //实际的问题现象应该传递给redis服务器,运维人员通过后台系统查看 //实际的问题显现更应该传递给redis服务器,运维人员通过后台系统查看 return "error.jsp"; } @ExceptionHandler(Exception.class) public String doException(Exception ex, Model m){ m.addAttribute("msg",ex.getMessage()); //将ex对象保存起来 return "error.jsp"; } }
(3). 测试方法
@RequestMapping("save2")
@ResponseBody
//http://localhost:8888/04_Interceptor_ErrorHandle/ExceptionTest/save2?userName=ypf
public String save2(String userName){
//模拟业务层发起调用产生了异常
//对用户的非法操作进行判定,并包装成异常对象进行处理,便于统一管理
if(userName.trim().length() < 8){
throw new BusinessException("对不起,用户名长度不满足要求,请重新输入!");
}else {
throw new SystemException("服务器连接失败,请尽快检查处理!");
}
}
三. RestFul风格编程
1. 相关注解介绍
(1). @RestController
通常加在控制器上,表示是rest风格的控制器。等价于: @ResponseBody 和 @Controller
(2). 请求类型的注解
A. @RequestMapping(value = "{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET) 等价 @GetMapping("{id}")
B. @RequestMapping(value = "{id}",method = RequestMethod.POST) 等价 @PostMapping("{id}")
C. @RequestMapping(value = "{id}",method = RequestMethod.PUT) 等价 @PutMapping("{id}")
D. @RequestMapping(value = "{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE) 等价 @DeleteMapping("{id}")
2. 代码实操
//设置rest风格的控制器 @RestController //(等价与 @ResponseBody 和 @Controller) //设置公共访问路径,配合下方访问路径使用 @RequestMapping("/RestTest/") public class RestTestController { //rest风格访问路径完整书写方式 @RequestMapping("/user/{id}") //使用@PathVariable注解获取路径上配置的具名变量,该配置可以使用多次 //http://localhost:8888/05_FileLoad_RestFul/RestTest/user/12 public Integer restLocation1(@PathVariable Integer id){ System.out.println("restful is running ...."); return id; } //接收GET请求配置方式 @RequestMapping(value = "{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET) //接收GET请求简化配置方式 // @GetMapping("{id}") //http://localhost:8888/05_FileLoad_RestFul/RestTest/12 public Integer get(@PathVariable Integer id){ System.out.println("restful is running ....get:"+id); return id; } //接收POST请求配置方式 @RequestMapping(value = "{id}",method = RequestMethod.POST) //接收POST请求简化配置方式 // @PostMapping("{id}") //http://localhost:8888/05_FileLoad_RestFul/RestTest/12 public Integer post(@PathVariable Integer id){ System.out.println("restful is running ....post:"+id); return id; } //接收PUT请求简化配置方式 //@RequestMapping(value = "{id}",method = RequestMethod.PUT) //接收PUT请求简化配置方式 @PutMapping("{id}") //http://localhost:8888/05_FileLoad_RestFul/RestTest/12 public Integer put(@PathVariable Integer id){ System.out.println("restful is running ....put:"+id); return id; } //接收DELETE请求简化配置方式 //@RequestMapping(value = "{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE) //接收DELETE请求简化配置方式 @DeleteMapping("{id}") //http://localhost:8888/05_FileLoad_RestFul/RestTest/12 public Integer delete(@PathVariable Integer id){ System.out.println("restful is running ....delete:"+id); return id; } }
四. 文件上传
1. 导入坐标
<dependency> <groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId> <artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId> <version>1.4</version> </dependency>
2. 核心配置
<!--5.配置文件上传--> <!--(注意:这里的id必须叫:multipartResolver)--> <bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver"> <property name="maxUploadSize" value="1024000000"/> </bean>
3. 前端代码
<form action="/05_FileLoad_RestFul/fileupload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <%--文件上传表单的name属性值一定要与controller处理器中方法的参数对应,否则无法实现文件上传--%> 上传LOGO:<input type="file" name="file"/><br/> 上传照片:<input type="file" name="file1"/><br/> 上传任意文件:<input type="file" name="file2"/><br/> <input type="submit" value="上传"/> </form>
4. 后台代码
//图片上传类 @Controller public class FileUploadController { @RequestMapping(value = "/fileupload") //参数中定义MultipartFile参数,用于接收页面提交的type=file类型的表单,要求表单名称与参数名相同 public String fileupload(MultipartFile file, MultipartFile file1, MultipartFile file2, HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException { System.out.println("file upload is running ..."+file); // MultipartFile参数中封装了上传的文件的相关信息 System.out.println(file.getSize()); System.out.println(file.getBytes().length); System.out.println(file.getContentType()); System.out.println(file.getName()); System.out.println(file.getOriginalFilename()); System.out.println(file.isEmpty()); //首先判断是否是空文件,也就是存储空间占用为0的文件 if(!file.isEmpty()){ //如果大小在范围要求内正常处理,否则抛出自定义异常告知用户(未实现) //获取原始上传的文件名,可以作为当前文件的真实名称保存到数据库中备用 String fileName = file.getOriginalFilename(); //设置保存的路径 String realPath = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("/images"); //保存文件的方法,指定保存的位置和文件名即可,通常文件名使用随机生成策略产生,避免文件名冲突问题 file.transferTo(new File(realPath,file.getOriginalFilename())); } //测试一次性上传多个文件 if(!file1.isEmpty()){ String fileName = file1.getOriginalFilename(); //可以根据需要,对不同种类的文件做不同的存储路径的区分,修改对应的保存位置即可 String realPath = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("/images"); file1.transferTo(new File(realPath,file1.getOriginalFilename())); } if(!file2.isEmpty()){ String fileName = file2.getOriginalFilename(); String realPath = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("/images"); file2.transferTo(new File(realPath,file2.getOriginalFilename())); } return "index.jsp"; } }
!
- 作 者 : Yaopengfei(姚鹏飞)
- 博客地址 : http://www.cnblogs.com/yaopengfei/
- 声 明1 : 如有错误,欢迎讨论,请勿谩骂^_^。
- 声 明2 : 原创博客请在转载时保留原文链接或在文章开头加上本人博客地址,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。





