第十二节:Spring注解用法剖析、整合MyBatis和Junit、自定义用法(过滤器、导入器、注册器等等)
一. Spring注解用法剖析
1. 开启注解扫描
(1). 通过XML的形式
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!--1. 启动注解驱动,指定对应扫描的路径,也就是资源所在的包--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.ypf"/> </beans>
使用:
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); UserService uS1 = (UserService) ctx.getBean("userService1"); uS1.save();
剖析:
在进行包所扫描时,会对配置的包及其子包中所有文件进行扫描
扫描过程是以文件夹递归迭代的形式进行的
扫描过程仅读取合法的java文件
扫描时仅读取spring可识别的注解
扫描结束后会将可识别的有效注解转化为spring对应的资源加入IoC容器
注意:
无论是注解格式还是XML配置格式,最终都是将资源加载到IoC容器中,差别仅仅是数据读取方式不同
从加载效率上来说注解优于XML配置文件
(2). 借助一个类加注解
@Configuration @ComponentScan("com.ypf") public class SpringConfig0 { }
使用
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig0.class); UserService uS1 = (UserService) ctx.getBean("userService1"); uS1.save();
2. bean相关
(1). bean定义
相关注解:@Component @Controller @Service @Repository,作用在类上;@Controller、@Service 、@Repository是@Component的衍生注解,功能同@Component。
A. 可以设置参数,即定义bean的访问id
@Component("userDao1")
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{}
注入的写法:
@Autowired @Qualifier("userDao1") private UserDao userDao;
B. 也可以不设置参数
@Component @Primary //提高优先级(当@Component不指定id的时候,提高优先级) public class UserDaoImpl2 implements UserDao2 {} @Component public class UserDaoImpl21 implements UserDao2{}
剖析:
当同一个接口的两个实现类定义bean的注解上都没有指定bean的id,那么在注入的时候则不知道要注入哪个了,这个时候可以通过添加@Primary提高优先级,即哪个实现类加了@Primary,则注入就是哪个。
注入的写法(@Autowired默认按类型装配,指定@Qualifier后可以指定自动装配的bean的id)
@Autowired private UserDao2 userDao2;
(2). bean作用域
相关注解:@Scope
@Component("userService1")
@Scope("singleton") //默认是singleton,也可以设置非单例prototype
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {}
(3). bean生命周期
作用在方法上,相关注解:@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy
@PostConstruct public void init() { System.out.println("init..."); }
3. 注入相关
(1). 引用类型注入
A. 通过定义bean的id值识别注入,使用注解为:@Autowired、@Qualifier
@Autowired @Qualifier("userDao1") private UserDao userDao;
PS:可以通过 @Autowired(required = false) 来配置该属性是否允许为null
B. 默认通过类型进行装配,使用注解为:@Autowired
@Autowired private UserDao2 userDao2;
扩展:@Primary优先装配的问题,详见上面定义bean出的说明。
(2). 非引用类型注入
使用注解@Value进行注入,可以作用在属性 和 方法上。
注:@value注解如果添加在属性上方,可以省略set方法(set方法的目的是为属性赋值)
@Value("66666")
private int num;
@Value("V1.2.1")
private String version;
补充:加载properties文件,使用 @PropertySource注解,注:该注解不支持*通配格式,一旦加载,所有spring控制的bean中均可使用对应属性值,可以通过逗号写多个配置文件。
-
value(默认):设置加载的properties文件名
-
@Component @PropertySource(value={"classpath:jdbc.properties","classpath:xxx.properties"},ignoreResourceNotFound = true) //可以关联多个配置文件 public class UserDaoImpl2 implements UserDao2 { @Value("${jdbc.userName}") private String userName; @Value("${jdbc.password}") private String password; @Override public void save() { System.out.println("UserDaoImpl2 is running...."); System.out.println("userName:"+userName); System.out.println("password:"+password); } }
jdbc.properties代码如下:
jdbc.userName=root
jdbc.password=123456
4. 扩展 @Inject、@Named、@Resource
@Inject与@Named是JSR330规范中的注解,功能与@Autowired和@Qualifier完全相同,适用于不同架构场景
@Resource是JSR250规范中的注解,可以简化书写格式
@Resource相关属性
name:设置注入的bean的id
type:设置注入的bean的类型,接收的参数为Class类型
5. 纯注解格式-干掉xml
可以通过@Configuration、@ComponentScan 纯注解的形式设置Spring核心配置类,从而干掉xml配置
作用:设置当前类为spring核心配置加载类。
说明:
配置类:
@Configuration @ComponentScan("com.ypf") public class SpringConfig0 {}
调用:
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig0.class); UserService uS1 = (UserService) ctx.getBean("userService1"); uS1.save();
6. 加载第三方资源
使用@Bean注解,加在方法定义上方,从而该方法的返回值作为spring管理的bean,可以直接调用该方法,获得返回值。
参数:value(默认),定义bean的访问id。
说明:
-
-
该注解用于替代XML配置中的静态工厂与实例工厂创建bean,不区分方法是否为静态或非静态
-
@Configuration @ComponentScan("com.ypf")
public class JDBCConfig { @Bean("dataSource") public static DruidDataSource getDataSource(){ DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource(); ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db"); ds.setUsername("root"); ds.setPassword("123456"); return ds; } }
调用:
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(JDBCConfig.class); //相当于直接调用 getDataSource 方法 DruidDataSource dataSource = (DruidDataSource) ctx.getBean("dataSource"); System.out.println(dataSource);
7. 类导入模式 @Import
使用@Import注解,加载类上面,导入第三方bean作为spring控制的资源。(通俗的将:把类A导入到类B中,那么在加载类B的时候,就可以使用类A中的方法)
说明:
-
-
在被导入的类中可以继续使用@Import导入其他资源(了解)
-
样例:下面是把JDBCConfig导入到SpringConfig1和SpringConfig2中。
public class JDBCConfig { @Bean("dataSource") public static DruidDataSource getDataSource(){ DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource(); ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db"); ds.setUsername("root"); ds.setPassword("123456"); return ds; } } @Configuration @ComponentScan("com.ypf") @Import({JDBCConfig.class}) public class SpringConfig1 { @Bean("b1") public String getB1(){ System.out.println("b1 is running"); return ""; } } @Configuration @ComponentScan("com.ypf") @Import({JDBCConfig.class}) public class SpringConfig2 { @Bean("b2") public String getB2(){ System.out.println("b2 is running"); return ""; } }
调用:

ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig1.class, SpringConfig2.class); //直接调用方法 DruidDataSource dataSource = (DruidDataSource) ctx.getBean("dataSource"); System.out.println(dataSource); String result1=(String)ctx.getBean("b1"); String result2=(String)ctx.getBean("b2"); System.out.println(result1); System.out.println(result2);

8. 依赖加载
(1). @DependsOn
-
-
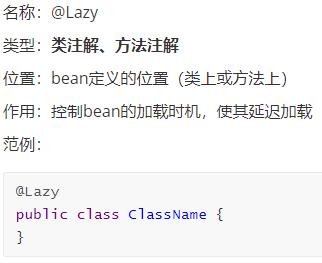
类型:类注解、方法注解
-
位置:bean定义的位置(类上或方法上)
-
作用:控制bean的加载顺序,使其在指定bean加载完毕后再加载
-
范例:
-
说明:
-
配置在方法上,使@DependsOn指定的bean优先于@Bean配置的bean进行加载
-
配置在类上,使@DependsOn指定的bean优先于当前类中所有@Bean配置的bean进行加载
-
配置在类上,使@DependsOn指定的bean优先于@Component等配置的bean进行加载
-
-
相关属性
-
(2). @Order

(3). @Lazy
场景应用:

二. 整合MyBatis
1. 整体剖析
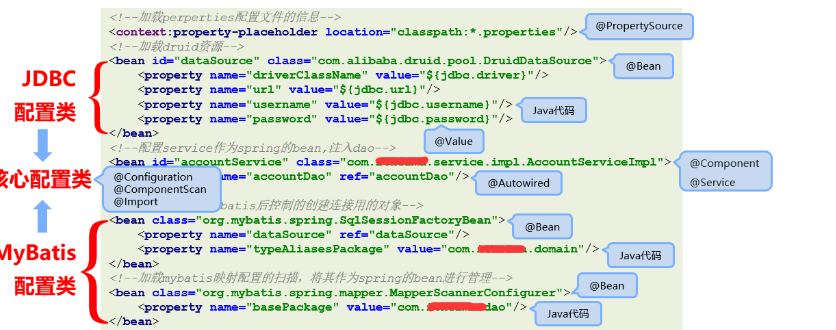
(2). 建立独立的配置管理类,分类管理外部资源,根据功能进行分类,并提供对应的方法获取bean
(3). 使用注解形式启动bean扫描,加载所有注解配置的资源(bean)
2. 案例实操
(1). 在pom.xml导入相应的坐标

<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.6</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <version>3.5.7</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.3.7</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.2.6</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId> <version>5.3.7</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId> <version>2.0.6</version> </dependency> <!-- Spring整合Junit --> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.13.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId> <version>5.3.7</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
(2). 新建JDBCConfig配置类,在里面注入连接数据库的相关方法属性,如:url、userName、password。 最后以方法的形式+@Bean的展示。

public class JDBCConfig { @Value("${jdbc.driver}") private String driver; @Value("${jdbc.url}") private String url; @Value("${jdbc.username}") private String userName; @Value("${jdbc.password}") private String password; @Bean("dataSource") public DataSource getDataSource(){ DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource(); ds.setDriverClassName(driver); ds.setUrl(url); ds.setUsername(userName); ds.setPassword(password); return ds; } }
jdbc.properties文件如下(注:该文件需要在核心配置类中配置路径识别,否则找不到)

#远程链接 jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://xxx:3306/db1?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&rewriteBatchedStatements=true jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=xxx
(3). 新建MyBatisConfig类, 在里面配置spring连接用的对象、和spring对bean的管理
public class MyBatisConfig { //spring整合mybatis后控制的创建连接用的对象 @Bean public SqlSessionFactoryBean getSqlSessionFactoryBean(@Autowired DataSource dataSource){ SqlSessionFactoryBean ssfb = new SqlSessionFactoryBean(); ssfb.setTypeAliasesPackage("com.ypf.domain"); //通用的设置别名 ssfb.setDataSource(dataSource); //设置数据源 return ssfb; } //加载mybatis映射配置的扫描,将其作为spring的bean进行管理 // 所以 StudentServiceImpl中的 @Autowired 直接就可以注入userDao,userDao本身不需要实现@Compontent @Bean public MapperScannerConfigurer getMapperScannerConfigurer(){ MapperScannerConfigurer msc = new MapperScannerConfigurer(); msc.setBasePackage("com.ypf.dao"); return msc; } }
(4). 新建Student、StudenDao、StudentServie及其实现类。
代码1

public class Student { private Integer id; private String name; private Integer age; public Student(){ } public Student(Integer id, String name, Integer age) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.age = age; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } } public interface StudentDao { //查询全部 @Select("SELECT * FROM student") public abstract List<Student> selectAll(); //新增操作 @Insert("INSERT INTO student VALUES (#{id},#{name},#{age})") public abstract Integer insert(Student stu); //修改操作 @Update("UPDATE student SET name=#{name},age=#{age} WHERE id=#{id}") public abstract Integer update(Student stu); //删除操作 @Delete("DELETE FROM student WHERE id=#{id}") public abstract Integer delete(Integer id); }
代码2

public interface StudentService { //查询全部 public abstract List<Student> selectAll(); //新增数据 public abstract Integer insert(Student stu); //修改数据 public abstract Integer update(Student stu); //删除数据 public abstract Integer delete(Integer id); } @Component("StudentService1") public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService{ //注入 @Autowired private StudentDao studentDao; @Override public List<Student> selectAll() { return studentDao.selectAll(); } @Override public Integer insert(Student stu) { return studentDao.insert(stu); } @Override public Integer update(Student stu) { return studentDao.update(stu); } @Override public Integer delete(Integer id) { return studentDao.delete(id); } }
(5). 代码测试
public class Test1 { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig1.class); StudentService studentService = (StudentService) ctx.getBean("StudentService1"); //1.测试 查询 List<Student> list=studentService.selectAll(); for (Student stu : list) { System.out.println(stu); } } }
三. 整合Junit
1. 说明
(2). 为Junit测试用例设定对应的spring容器:
-
从Spring5.0以后,要求Junit的版本必须是4.12及以上
-
2. 案例实操
(1). 在Pom.xml中导入相关坐标, sping-context、junit、spring-test。
<dependencies> <!--Spring标准库--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.3.7</version> </dependency> <!-- Spring整合Junit --> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.13.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId> <version>5.3.7</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
(2). 准备Spring配置类
PS:如果测试中不涉及注入,仅仅是单独的业务测试,@ComponentScan("com.ypf") 扫描注册bean可以省略。
//该类主要用于测试Spring整合Junit @Configuration @ComponentScan("com.ypf") public class SpringConfig2 {}
(3). 测试调用
A. 测试类上必须加标签 @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class),表示Spring接管Junit
B. @ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfig2.class),表示加载Spring核心配置。 (此处可以换成加载xml文件)
C. 测试方法上需要加@Test
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfig2.class) public class Test2Junit { @Autowired @Qualifier("StudentService1") private StudentService studentService; @Test public void testSave(){ //1.测试 查询 List<Student> list=studentService.selectAll(); for (Student stu : list) { System.out.println(stu); } } @Test public void testSave2(){ System.out.println("hello testsave2"); } }
扩展:
也可以用xml代替SpringConfig2类,如下applicationContext.xml,同样道理,如果不需要注入,则可以省略下面的开启注解扫描那一句。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd "> <!--开启注解——组件扫描--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.ypf.aop"/> </beans>
调用:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml") public class AopAnnoTest { @Autowired @Qualifier("UserService1") public UserService userService; @Test public void test1(){ userService.save(); } }
四. 过滤器、导入器、注册器等等
1. 自定义过滤器
(1). 排除规则为注解
@Configuration //1.设置排除bean,排除规则为注解修饰,具体的注解喂@Service修饰 //excludeFilters表示排除 //FilterType.ANNOTATION ,表示排除规则为注解 //Service.class,表示注解的形式为 @Service //结果:No qualifying bean of type 'com.ypf.service.UserService' available, 说明成功的被排除了 @ComponentScan(value = "com.ypf", excludeFilters = @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, classes = Service.class)) public class SpringConfig1 {}
(2). 自定义排除规则
@Configuration //2.设置排除bean,自定义类排除规则 //结果:No qualifying bean of type 'com.ypf.service.UserService' available, 说明成功的被排除了 @ComponentScan(value = "com.ypf", excludeFilters = @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = MyTypeFilter.class)) public class SpringConfig1 {}
自定义过滤类

public class MyTypeFilter implements TypeFilter { @Override //加载的类满足要求,匹配成功 public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) throws IOException { //通过参数获取加载的类的元数据 ClassMetadata classMetadata = metadataReader.getClassMetadata(); //通过类的元数据获取类的名称 String className = classMetadata.getClassName(); //如果加载的类名满足过滤器要求,返回匹配成功 if(className.equals("com.ypf.service.UserServiceImpl")){ //返回true表示匹配成功,返回false表示匹配失败。此处仅确认匹配结果,不会确认是排除还是加入,排除/加入由配置项决定,与此处无关 return true; } return false; } }
2. 自定义导入器
//3.自定义导入器 //一种快速高效配置大量bean的方式,不需要写xml和在类上加注解即可 // 效果就是:AccountDaoImpl、BookDaoImpl上面不需要加任何注解,就可以被识别,被注入 // 运行 testsave2方法进行测试 @ComponentScan("com.ypf") @Import(MyImportSelector.class) public class SpringConfig1 {}
自定义导入类:

public class MyImportSelector implements ImportSelector { @Override public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) { // 1.编程形式加载一个类 // return new String[]{"com.ypf.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl","com.ypf.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl"}; // 2.加载import.properties文件中的单个类名 // ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("import"); // String className = bundle.getString("className"); // 3.加载import.properties文件中的多个类名 ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("import"); String className = bundle.getString("className"); return className.split(","); } }
配置文件
#1.加载import.properties文件中的单个类名 #className=com.ypf.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl #2.加载import.properties文件中的多个类名 className=com.ypf.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl,com.ypf.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl path=com.ypf.test.impl.*
3. 自定义注册器
@Configuration //4.自定义注册器 //结果:UserService is Running,正常运行 @Import(MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class) public class SpringConfig1 {}
自定义类:

public class MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar { @Override public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { //自定义注册器 //1.开启类路径bean定义扫描器,需要参数bean定义注册器BeanDefinitionRegistry,需要制定是否使用默认类型过滤器 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(registry,false); //2.添加包含性加载类型过滤器(可选,也可以设置为排除性加载类型过滤器) scanner.addIncludeFilter(new TypeFilter() { @Override public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) throws IOException { //所有匹配全部成功,此处应该添加实际的业务判定条件 return true; } }); //设置扫描路径 scanner.scan("com.ypf"); } }
4. 自定义工厂后处理bean,bean定义前处理后处理bean
//5.自定义工厂后处理bean,bean定义前处理后处理bean //运行testsave1测试 @ComponentScan("com.ypf") @Import({CustomeImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class, MyBeanFactory.class, MyBean.class}) public class SpringConfig1 {}
自定义类:

public class CustomeImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar { private String expression; public CustomeImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar(){ try { //初始化时指定加载的properties文件名 Properties loadAllProperties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadAllProperties("import.properties"); //设定加载的属性名 expression = loadAllProperties.getProperty("path"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { //1.定义扫描包的名称 String[] basePackages = null; //2.判断有@Import注解的类上是否有@ComponentScan注解 if (importingClassMetadata.hasAnnotation(ComponentScan.class.getName())) { //3.取出@ComponentScan注解的属性 Map<String, Object> annotationAttributes = importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(ComponentScan.class.getName()); //4.取出属性名称为basePackages属性的值 basePackages = (String[]) annotationAttributes.get("basePackages"); } //5.判断是否有此属性(如果没有ComponentScan注解则属性值为null,如果有ComponentScan注解,则basePackages默认为空数组) if (basePackages == null || basePackages.length == 0) { String basePackage = null; try { //6.取出包含@Import注解类的包名 basePackage = Class.forName(importingClassMetadata.getClassName()).getPackage().getName(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } //7.存入数组中 basePackages = new String[] {basePackage}; } //8.创建类路径扫描器 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(registry, false); //9.创建类型过滤器(此处使用切入点表达式类型过滤器) TypeFilter typeFilter = new AspectJTypeFilter(expression,this.getClass().getClassLoader()); //10.给扫描器加入类型过滤器 scanner.addIncludeFilter(typeFilter); //11.扫描指定包 scanner.scan(basePackages); } } public class MyBean implements BeanPostProcessor { @Override //所有bean初始化前置操作 public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("-----------bean之前-----------"); System.out.println(beanName); return bean; } @Override //所有bean初始化后置操作 public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("-----------bean之后-----------"); return bean; } } public class MyBeanFactory implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor { @Override //工厂后处理bean接口核心操作 public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { System.out.println("----------------bean工厂制作好了,还有什么事情需要处理----------------"); } }
!
- 作 者 : Yaopengfei(姚鹏飞)
- 博客地址 : http://www.cnblogs.com/yaopengfei/
- 声 明1 : 如有错误,欢迎讨论,请勿谩骂^_^。
- 声 明2 : 原创博客请在转载时保留原文链接或在文章开头加上本人博客地址,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。





