第十一节:Spring简介、IOC和DI的各种XML配置、整合MyBatis
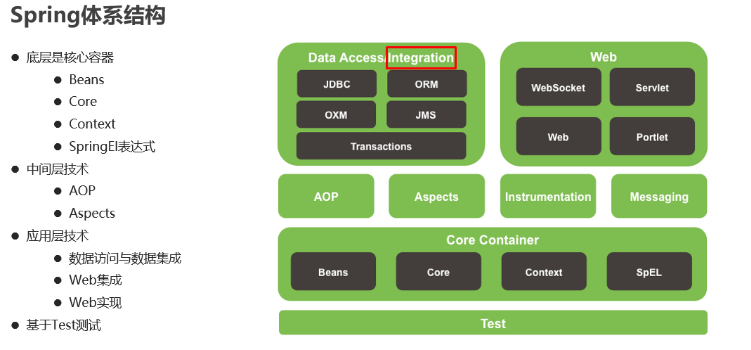
一. Spring简介
1. Spring简介
(官网:https://spring.io/)
Spring是分层的JavaSE/EE应用full-stack轻量级开源框架。
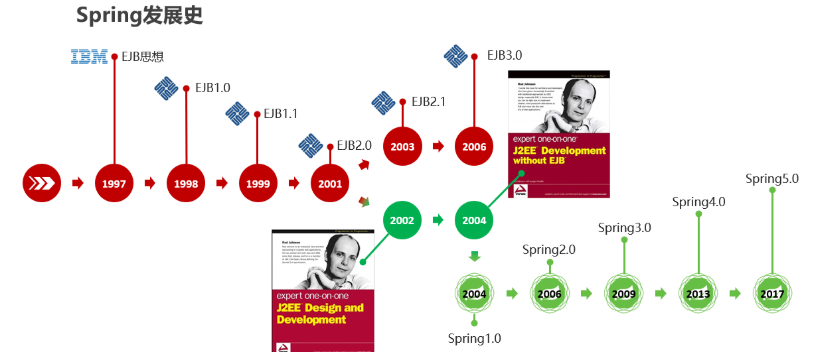
2. Spring发展史
3. IOC简介
(1). 工厂模式发展史


(2). Spring的演化
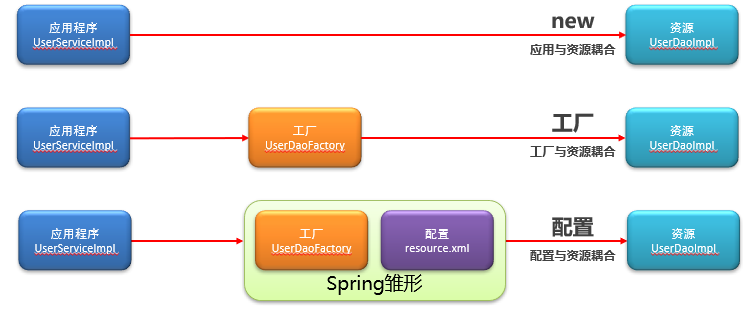
(3). IOC

二. IOC和DI的各种xml配置
前提:
(1). 通过maven导入所需要的所有坐标。

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>org.example</groupId> <artifactId>SpringDemo3</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target> </properties> <dependencies> <!--spring --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.3.7</version> </dependency> <!--第三方资源配置(阿里数据源方案Druid)--> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.2.6</version> </dependency> <!-- Spring整合mybaits相关坐标--> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.6</version> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <version>3.5.7</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId> <version>5.3.7</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId> <version>2.0.6</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
(2). 分享一个1个全的spring配置文件的命名空间

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> </beans>
复习:什么是IOC和DI
1. IOC入门
目标:通过注入的方式获取UserService对象,并调用save方法。
(1). 创建UserService接口 和 UserServicedImpl实现类

public interface UserService { //业务方法 void save(); } public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { public void save() { System.out.println("user service running..."); } }
(2). 配置文件中进行声明
PS:处理通过id标识,还可以通过name起别名以供调用
<!--1.创建spring控制的资源--> <!--id:bean的名称,通过id值获取bean class:bean的类型--> <bean id="userService1" class="com.ypf.service.UserServiceImpl"></bean> <!--2.利用name属性起别名 --> <!--name:bean的名称,可以通过name值获取bean,用于多人配合时给bean起别名 --> <bean id="userService2" name="uS1,uS2" class="com.ypf.service.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
(3). 直接调用
可以通过id获取bean,也可以通过name别名获取bean。
public static void main(String[] args) { //1. 加载配置文件 ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //2. 获取资源(根据id获取该对象) UserService userService = (UserService) ctx.getBean("userService1"); //3. 运行 userService.save(); //也可以根据name别名来获取对象 UserService uS1 = (UserService) ctx.getBean("uS1"); UserService uS2 = (UserService) ctx.getBean("uS2"); uS1.save(); uS2.save(); }
2. bean设置是否单例
通过scope属性来设置,常用的有singleton单例、prototype非单例,默认是单例的。
<!--默认是单例模式 --> <bean id="uScope1" class="com.ypf.service.UserServiceImpl"></bean> <!--单例--> <bean id="uScope2" scope="singleton" class="com.ypf.service.UserServiceImpl"></bean> <!--非单例--> <bean id="uScope3" scope="prototype" class="com.ypf.service.UserServiceImpl"></bean>3
3. bean生命周期测试
主要通过 init-method,destroy-method 来设置。
<!--2. init-method,destroy-method 以下两个要分开注释掉,单独使用,否则覆盖 --> <bean id="ts1" scope="singleton" init-method="TestInit" destroy-method="TestDestory" class="com.ypf.service.UserServiceImpl"></bean> <bean id="ts2" scope="prototype" init-method="TestInit" destroy-method="TestDestory" class="com.ypf.service.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
-
当scope=“singleton”时,spring容器中有且仅有一个对象,init方法在创建容器时仅执行一次
-
当scope=“prototype”时,spring容器要创建同一类型的多个对象,init方法在每个对象创建时均执行一次
-
当scope=“singleton”时,关闭容器会导致bean实例的销毁,调用destroy方法一次
-
4. bean对象创建方式
(1). 静态方法类和实例方法类

//静态方法 public class UserFactory1 { public static UserService GetService(){ System.out.println("Static Factory is running"); return new UserServiceImpl(); } } //实例方法 public class UserFactory2 { public UserService GetService(){ System.out.println("Instance Factory is running"); return new UserServiceImpl(); } }
(2). xml配置
<!-- 三. 创建bean对象 了解 以下两个要分开注释掉,单独使用,否则覆盖 --> <!--1. 静态方法--> <bean id="staticFactory" class="com.ypf.service.UserFactory1" factory-method="GetService"></bean> <!--2. 实例方法--> <bean id="instanceFactory" class="com.ypf.service.UserFactory2"></bean> <bean id="us5" factory-bean="instanceFactory" factory-method="GetService"></bean>
(3). 调用

public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //1. 静态方法 // UserService u1= (UserService) ctx.getBean("staticFactory"); // u1.save(); //2. 实例方法 UserService u2= (UserService) ctx.getBean("us5"); u2.save(); }
5. set属性注入
语法:需要给哪个bean注入,就配置在哪个bean下面,使用<property>标签 。
<property name="propertyName" value="propertyValue" ref="beanId"/>
剖析:
name:对应bean中的属性名,要求该属性必须提供可访问的set方法(严格规范为此名称是set方法对应名称)
value:设定非引用类型属性对应的值,不能与ref同时使用
(1). xml配置样例
给UserServiceImpl类注入UserDao、num、version, 其中后面两个直接赋值,UserDao通过ref链接。
<bean id="userDao1" class="com.ypf.dao.UserDaoImpl"></bean> <!--2.注册 UserServiceImpl --> <bean id="userService1" class="com.ypf.service.UserServiceImpl"> <!--3.下面表示要在 UserServiceImpl注入userDao、num、version--> <!--这里的name中的userDao必须和注入的private UserDao userDao的属性名相同--> <property name="userDao" ref="userDao1"></property> <!--同上下面的name也是要和注入的属性名相同!!!!--> <property name="num" value="10"></property> <property name="version" value="v1.2.3"></property> </bean>
(2). set属性注入模式
如下,即可注入成功。
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { //注入以下3个对象(userDao、num、version)--set注入模式 private UserDao userDao; private int num; private String version; public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) { this.userDao = userDao; } public void setNum(int num) { this.num = num; } public void setVersion(String version) { this.version = version; } @Override public void save() { System.out.println("userService is running"); System.out.println("num:" + num); System.out.println("version:" + version); userDao.save(); } }
(3). 调用测试
//1.测试set注入 ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); UserService userService = (UserService) ctx.getBean("userService1"); userService.save();
6. 构造函数注入
语法:通过<constructor-arg>标签控制。
<constructor-arg name="argsName" value="argsValue /> <constructor-arg index="arg-index" type="arg-type" ref="beanId"/>
剖析:
A. 格式1
B. 格式2
ref:设定引用类型构造方法参数对应bean的id ,不能与value同时使用。
type :设定构造方法参数的类型,用于按类型匹配参数或进行类型校验。
index :设定构造方法参数的位置,用于按位置匹配参数,参数index值从0开始计数。
(1). xml配置样例
给UserDaoImpl2类注入三个值,给UserServiceImpl2注入
<!--二. 构造函数注入 了解 --> <!--1.注册 UserDaoImpl2 --> <bean id="userDao2" class="com.ypf.dao.UserDaoImpl2"> <constructor-arg index="1" value="12356"/> <constructor-arg index="0" value="root"/> <constructor-arg index="2" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> </bean> <!--2.注册 UserServiceImpl2 --> <bean id="userService2" class="com.ypf.service.UserServiceImpl2"> <!--使用构造方法进行注入,需要保障注入的属性与bean中定义的属性一致--> <!--一致指顺序一致或类型一致或使用index解决该问题--> <constructor-arg name="userDao2" ref="userDao2" index="0"/> <constructor-arg name="num" value="666666" index="1"/> <constructor-arg name="version" value="v2.0.0" index="2"/> </bean>
(2). 两个注入类

public class UserDaoImpl2 implements UserDao2 { private String username; private String pwd; private String driver; public UserDaoImpl2(String username, String pwd, String driver) { this.username = username; this.pwd = pwd; this.driver = driver; } @Override public void save() { System.out.println("userDaoImpl2 is running, userName:" + username + ",pwd:" + pwd + ",driver:" + driver); } } public class UserServiceImpl2 implements UserService2 { private UserDao2 userDao2; private int num; private String version; public UserServiceImpl2(UserDao2 userDao2, int num, String version) { this.userDao2 = userDao2; this.num = num; this.version = version; } @Override public void save() { System.out.println("UserServiceImpl2 is running. num:" + num + ",version:" + version); userDao2.save(); } }
7. 各种数据类型注入
(1). 五种数据类型的注入:array,list,set,map,props 。

<!--三.集合类型数据注入 --> <bean id="userService3" class="com.ypf.service.UserServiceImpl3"> <property name="al"> <list> <value>ypf</value> <value>66666</value> </list> </property> <property name="properties"> <props> <prop key="name">ypf</prop> <prop key="value">666666</prop> </props> </property> <property name="arr"> <array> <value>123456</value> <value>66666</value> </array> </property> <property name="hs"> <set> <value>ypf</value> <value>66666</value> </set> </property> <property name="hm"> <map> <entry key="name" value="ypf"/> <entry key="value" value="6666666666"/> </map> </property> </bean>
(2). 被注入的类

public class UserServiceImpl3 implements UserService3 { private ArrayList al; private Properties properties; private int[] arr; private HashSet hs; private HashMap hm ; public void setAl(ArrayList al) { this.al = al; } public void setProperties(Properties properties) { this.properties = properties; } public void setArr(int[] arr) { this.arr = arr; } public void setHs(HashSet hs) { this.hs = hs; } public void setHm(HashMap hm) { this.hm = hm; } @Override public void save() { System.out.println("ArrayList:"+al); System.out.println("Properties:"+properties); for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { System.out.println(arr[i]); } System.out.println("HashSet:"+hs); System.out.println("HashMap:"+hm); } }
8. 使用P命名空间简化配置
<!--四.使用p命名空间简化配置 了解 --> <!-- 需要添加 xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" --> <bean id="userServiceTest" class="com.ypf.service.UserServiceImpl" p:userDao-ref="userDao1" p:num="123456" p:version="V2.0.1" />
9. SpEL
Spring提供了对EL表达式的支持,统一属性注入格式。所有属性值不区分是否引用类型,统一使用value赋值
-
-
引用bean #{beanId}
-
引用bean属性 #{beanId.propertyName}
-
引用bean方法 beanId.methodName().method2()
-
引用静态方法 T(java.lang.Math).PI
-
运算符支持 #{3 lt 4 == 4 ge 3}
-
正则表达式支持 #{user.name matches‘[a-z]{6,}’}
-
<bean id="userServiceSpElTest" class="com.ypf.service.UserServiceImpl"> <!-- 所有属性值不区分是否引用类型,统一使用value赋值--> <property name="userDao" value="#{userDao1}"></property> <property name="num" value="#{10}"></property> <property name="version" value="#{'v1.2.3'}"></property> </bean>
10. 加载外部properties文件
(1). 新增1个 data.properties配置文件
username=root
pwd=12345
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
(2). 在Spring配置文件中引入下面代码,即可使用上面配置文件。
<!-- 加载外部properties文件的机制 --> <!--1.在开头添加命名空间 --> <!-- xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"--> <!--2.加载配置文件--> <!-- <context:property-placeholder location="classpath*:*.properties"/>--> <!-- 或者只加载对应文件即可 --> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath*:data.properties"/> <!--3.使用加载数据 --> <bean id="userService4" class="com.ypf.service.UserServiceImpl4"> <property name="username" value="${username}"/> <property name="pwd" value="${pwd}"/> <property name="driver" value="${driver}"/> </bean>
11. 导入其它的Spring配置文件
<!--导入其它配置文件中的项 --> <import resource="applicationContextC1.xml"/> <import resource="applicationContextC2.xml"/>
测试代码:
//7. 导入其它配置文件中的项 //7.1 加载主文件的模式 ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); UserService userServiceC1 = (UserService) ctx.getBean("userServiceC1"); userServiceC1.save(); System.out.println("------------------------------------------------"); UserService userServiceC2 = (UserService) ctx.getBean("userServiceC2"); userServiceC2.save(); System.out.println("------------------------------------------------"); //7.2 加载多个子文件 ApplicationContext ctx1 = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContextC1.xml","applicationContextC2.xml"); UserService userServiceC11 = (UserService) ctx.getBean("userServiceC1"); userServiceC11.save(); System.out.println("------------------------------------------------"); UserService userServiceC22 = (UserService) ctx.getBean("userServiceC2"); userServiceC22.save();
12. 第三方资源配置
(1). 首先导入坐标
<dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.2.6</version> </dependency>
(2). Spring的xml配置
<!--八 整合第三方配置 阿里数据源方案Druid --> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_ioc"></property> <property name="username" value="root"></property> <property name="password" value="root"></property> </bean>
(3). 调用
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); DruidDataSource dataSource = (DruidDataSource) ctx.getBean("dataSource"); System.out.println(dataSource);
三. 整合MyBatis
1. 导入相应坐标

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>org.example</groupId> <artifactId>SpringDemo3</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target> </properties> <dependencies> <!--spring --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.3.7</version> </dependency> <!--第三方资源配置(阿里数据源方案Druid)--> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.2.6</version> </dependency> <!-- Spring整合mybatis相关坐标--> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.6</version> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <version>3.5.7</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId> <version>5.3.7</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId> <version>2.0.6</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
2. 在com.ypf.domain下新建Account实体类

public class Account implements Serializable { private Integer id; private String name; private Double money; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Double getMoney() { return money; } public void setMoney(Double money) { this.money = money; } @Override public String toString() { return "Account{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", money=" + money + '}'; } }
3. 在com.ypf.dao下新建AccountDao接口
注:该接口中的命名空间要和下面的sql配置的xml的命名空间相同,且方法名也要和sql配置的xml中的id值相同。

public interface AccountDao { void save(Account account); void delete(Integer id); void update(Account account); List<Account> findAll(); Account findById(Integer id); }
4. 在com.ypf.service下新建AccountService接口 和 在com.ypf.servcie.impl新建AccountServiceImpl实现类

public interface AccountService { void save(Account account); void delete(Integer id); void update(Account account); List<Account> findAll(); Account findById(Integer id); } public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { private AccountDao accountDao; public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) { this.accountDao = accountDao; } public void save(Account account) { accountDao.save(account); } public void update(Account account){ accountDao.update(account); } public void delete(Integer id) { accountDao.delete(id); } public Account findById(Integer id) { return accountDao.findById(id); } public List<Account> findAll() { return accountDao.findAll(); } }
5. 在recources资源文件夹下的com.ypf.dao包下新建AccountDao.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.ypf.dao.AccountDao"> <!--配置根据id查询--> <select id="findById" resultType="account" parameterType="int"> select * from account where id = #{id} </select> <!--配置查询所有--> <select id="findAll" resultType="account"> select * from account </select> <!--配置保存--> <insert id="save" parameterType="account"> insert into account(name,money)values(#{name},#{money}) </insert> <!--配置删除--> <delete id="delete" parameterType="int"> delete from account where id = #{id} </delete> <!--配置更新--> <update id="update" parameterType="account"> update account set name=#{name},money=#{money} where id=#{id} </update> </mapper>
注:
(1). com.ypf.dao 应该是一层层往下的三个文件夹,而不是一个文件夹
(2). xml文件的名称必须和AccountDao接口名称相同。
(3). xml的命名空间需要和AccountDao的相同,而且xml中每个sql对应的id需要和AccountDao接口中的方法名相同。
6. 在recources资源文件夹下新建applicationContext1.xml 和 jdbc.properties
jdbc.properties
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver # 下面配置防止中文乱码 jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://xxx:3306/db1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&rewriteBatchedStatements=true jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=xxxx
applicationContext1.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!--加载properties配置文件的信息--> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath*:*.properties"/> <!--加载druid资源--> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> </bean> <!--配置service作为spring的bean,注入dao 由spring管理,所以ref中不需要单独配置--> <bean id="accountService" class="com.ypf.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"> <property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/> </bean> <!--spring整合mybatis后控制的创建连接用的对象--> <bean class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean"> <!--数据源 --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> <!--通用别名配置 --> <property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.ypf.domain"/> </bean> <!--加载mybatis映射配置的扫描,将其作为spring的bean进行管理--> <bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer"> <property name="basePackage" value="com.ypf.dao"/> </bean> </beans>
7. 测试
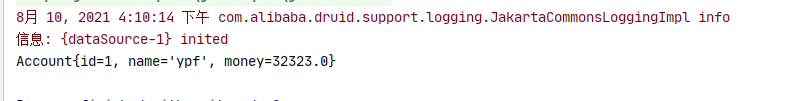
public class Test1 { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext1.xml"); AccountService accountService = (AccountService) ctx.getBean("accountService"); Account ac = accountService.findById(1); System.out.println(ac); } }
8. 运行结果
!
- 作 者 : Yaopengfei(姚鹏飞)
- 博客地址 : http://www.cnblogs.com/yaopengfei/
- 声 明1 : 如有错误,欢迎讨论,请勿谩骂^_^。
- 声 明2 : 原创博客请在转载时保留原文链接或在文章开头加上本人博客地址,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。




