第八节:队列简介、手撸顺序队列、手撸链队列和队列的应用
一. 队列简介
1. 什么是队列
队列(Queue)只允许在一端进行插入,在另一端进行删除的线性表。(队尾入队,队头出队),可见队列具有先进先出(First In First Out)或后进后出( Last In Last Out)的特性。
C#中提供Queue队列类,它不是线程安全的; 如需要使用线程安全的队列类,则使用:ConcurrentQueue
2. 名词
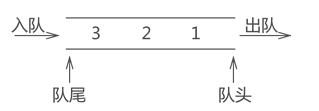
队头( Front):队列中允许数据删除的那一端。
队尾( Rear):队列中允许数据插入的那一端。
队上溢(Full):存储空间已满,仍希望入队操作,会产生上溢出,是一种空间不足的出错状态。
队下溢(Empty):队内空间无数据,仍希望出队操作,会产生下溢出,是一种数据不足的出错状态。
空队列(Empty Queue):队列中没有数据元素.
入队(Enqueue):将一个数据插入到队尾的操作。
出队(Dequeue):读取队头节点并删除该节点的操作
3. 常用Api
Enqueue()入队(放在队尾)
Dequeue()出队(移除队首元素,并返回被移除的元素)
Peek()取得队首的元素,不移除
Clear()清空元素
Count获取队列中元素的个数
测试代码:

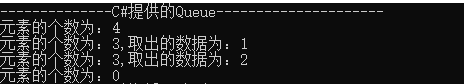
{ Console.WriteLine("--------------C#提供的Queue---------------------"); Queue<int> s1 = new Queue<int>(); s1.Enqueue(1); s1.Enqueue(2); s1.Enqueue(3); s1.Enqueue(4); Console.WriteLine($"元素的个数为:{s1.Count}"); int p1 = s1.Dequeue(); //取出并删除 Console.WriteLine($"元素的个数为:{s1.Count},取出的数据为:{p1}"); int p2 = s1.Peek(); //取出不删除 Console.WriteLine($"元素的个数为:{s1.Count},取出的数据为:{p2}"); s1.Clear(); Console.WriteLine($"元素的个数为:{s1.Count}"); }
运行结果:
4. 分类
队列存储结构的实现有以下两种方式:
顺序队列:在顺序表的基础上实现的队列结构。
链队列:在链表的基础上实现的队列结构。
两者的区别仅是顺序表和链表的区别,即在实际的物理空间中,数据集中存储的队列是顺序队列,分散存储的队列是链队列。
二. 顺序队列
1. 顺序队列
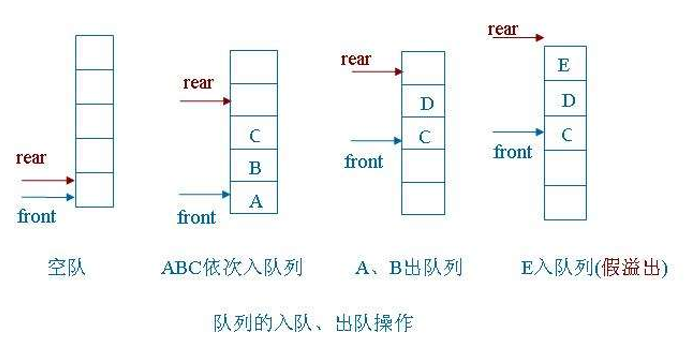
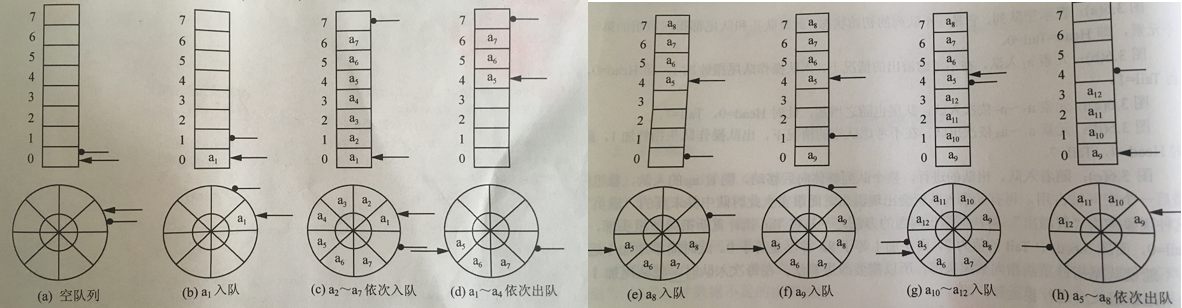
顺序队列(Sequence Queue)用一片连续的存储空间来存储队列中的数据元素.用一维数组来存放顺序队列中的数据元素。队头位置设在数组下标为 0 的端,用 front 表示;队尾位置设在数组的另一端,用 tail 表示。 front 和 tail 随着插入和删除而变化。当队列为空时, front=tail=0。因为在出队列(删除元素)的时候,需要花费大量的时间移动大量元素,速度很慢,所以很少有实际应用.
2. 顺序循环队列
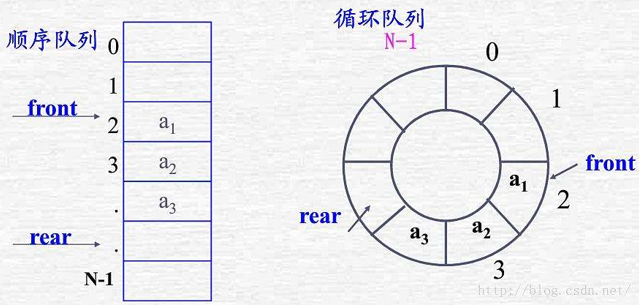
为了避免大量数据的移动,通常将一维数组的各个元素看成一个收尾相接的封闭的圆环,即第一个元素是最后一个元素的下一个元素,这种形式的顺序队列称为循环顺序队列(Circular sequence Queue)。
注:C#为我们提供的Queue类就是循环队列。
3. 手撸循环队列
接口
/// <summary> /// 声明队列接口 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam> public interface IQueue<T> { int Count { get; }//获取元素个数 bool IsEmpty(); //是否为空队列 void Clear(); //清空队列 void Enqueue(T item); //入队 T Dequeue(); //出队 T Peek(); //取队头元素 }
代码

/// <summary> /// 循环队列 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam> public class SeqQueue<T> : IQueue<T> { //存放元素的数组 public T[] _array; //增长因子 1-10之间 private int _growfactor; //最小增长值 private const int _MinimumGrow = 4; //默认队列空间的大小 private const int _defaultCapacity = 8; //元素的个数 private int _size = 0; //队头指针 指向队头的第一个元素 private int _head; //队尾指针 指向队尾的最后一个元素索引+1 private int _tail; public SeqQueue() : this(_defaultCapacity, 2) { } public SeqQueue(int capacity, float growFactor) { if (capacity < 0) { throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("capacity", "初识容量不能小于0"); } if (capacity < _defaultCapacity) { capacity = _defaultCapacity; } if (growFactor < 1.0 || growFactor > 10.0) { throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("growFactor", "增长因子必须在1-10之间"); } this._array = new T[capacity]; //初始化数组 this._head = this._tail = 0; this._size = 0; this._growfactor = (int)(growFactor * 100f); } //获取元素个数 public int Count { get { return this._size; } } public void Clear() { this._head = this._tail = this._size = 0; } //出队操作 public T Dequeue() { if (this._size == 0) { throw new InvalidOperationException("队列下溢,队里里没有数据"); } T obj = this._array[_head]; //出队数据 this._array[_head] = default(T); //在数组里删除出队元素 this._head = (this._head + 1) % this._array.Length; //循环队列 处理机制,保证下标是循环的 this._size--; return obj; } //入队 public void Enqueue(T item) { if (this._size == this._array.Length) { //计算新的容量 int capacity = (int)(this._array.Length * this._growfactor / 100f); if (capacity < this._array.Length + _MinimumGrow) { //最少要增长四个元素 capacity = this._array.Length + _MinimumGrow; } //调整容量 SetCapacity(capacity); } this._array[_tail] = item; //入队 this._tail = (this._tail + 1) % this._array.Length; //移动尾巴指针 this._size++; } private void SetCapacity(int capacity) { //内存搬家 T[] destinationArray = new T[capacity]; if (this._head < this._tail) { //头指针在尾指针的前面 Array.Copy(this._array, this._head, destinationArray, 0, this._size); } else { //头指针在尾指针的后面 Array.Copy(this._array, this._head, destinationArray, 0, this._array.Length - this._head); Array.Copy(this._array, 0, destinationArray, this._array.Length - this._head, this._tail); } this._array = destinationArray; this._head = 0; this._tail = (this._size == capacity) ? 0 : this._size; } public bool IsEmpty() { return this._size == 0; } //获取队头元素,不删除 public T Peek() { if (this._size == 0) { throw new InvalidOperationException("队列下溢,队里里没有数据"); } T obj = this._array[_head]; //出队数据 return obj; } }
测试
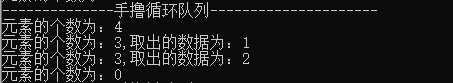
{ Console.WriteLine("--------------手撸循环队列---------------------"); IQueue<int> s1 = new SeqQueue<int>(); s1.Enqueue(1); s1.Enqueue(2); s1.Enqueue(3); s1.Enqueue(4); Console.WriteLine($"元素的个数为:{s1.Count}"); int p1 = s1.Dequeue(); //取出并删除 Console.WriteLine($"元素的个数为:{s1.Count},取出的数据为:{p1}"); int p2 = s1.Peek(); //取出不删除 Console.WriteLine($"元素的个数为:{s1.Count},取出的数据为:{p2}"); s1.Clear(); Console.WriteLine($"元素的个数为:{s1.Count}"); }
运行结果
三. 链队列
1. 含义
队列的另外一种存储方式是链式存储,这样的队列称为链队列(Linked Queue)。同链栈一样,链队列通常用单链表来表示,它的实现是单链表的简化。
2. 手撸链队列
接口
/// <summary> /// 声明队列接口 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam> public interface IQueue<T> { int Count { get; }//获取元素个数 bool IsEmpty(); //是否为空队列 void Clear(); //清空队列 void Enqueue(T item); //入队 T Dequeue(); //出队 T Peek(); //取队头元素 }
代码

/// <summary> /// 链队列 /// (队尾tail入队,队头front出队) /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam> public class LinkedQueue<T> : IQueue<T> { public QueueNode<T> front; //队头节点 public QueueNode<T> tail; //队尾节点 public int count; //元素个数 public LinkedQueue() { Clear(); } public int Count { get { return count; } } /// <summary> /// 清空所有元素 /// </summary> public void Clear() { front = null; tail = null; count = 0; } /// <summary> /// 判空 /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> public bool IsEmpty() { return count == 0; } /// <summary> /// 出队(不删除元素) /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> public T Peek() { if (front == null) { throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("队列下溢,队列中没有元素"); } T data = front.data; return data; } /// <summary> /// 出队(删除元素) /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> public T Dequeue() { if (front == null) { throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("队列下溢,队列中没有元素"); } T data = front.data; if (count == 1) { front = null; tail = null; } else { front = front.next; } count--; return data; } /// <summary> /// 入队 /// </summary> /// <param name="item"></param> public void Enqueue(T item) { QueueNode<T> newNode = new QueueNode<T>(item); if (count == 0) { front = newNode; tail = newNode; } else { tail.next = newNode; tail = newNode; } count++; } }
测试
{ Console.WriteLine("--------------手撸链队列---------------------"); IQueue<int> s1 = new LinkedQueue<int>(); s1.Enqueue(1); s1.Enqueue(2); s1.Enqueue(3); s1.Enqueue(4); Console.WriteLine($"元素的个数为:{s1.Count}"); int p1 = s1.Dequeue(); //取出并删除 Console.WriteLine($"元素的个数为:{s1.Count},取出的数据为:{p1}"); int p2 = s1.Peek(); //取出不删除 Console.WriteLine($"元素的个数为:{s1.Count},取出的数据为:{p2}"); s1.Clear(); Console.WriteLine($"元素的个数为:{s1.Count}"); }
运行结果

四. 应用
1. 流量削峰
高并发场景,比如秒杀,可以把下单请求存放到队列中,然后消费者从队列中依次取出来进行实际下单业务。
2. 应用解耦(异步)
比如登录成功后,要增加积分或者发送邮件,可以引入消息队列进行解耦,异步处理增加积分 或者 发送邮件的请求。
!
- 作 者 : Yaopengfei(姚鹏飞)
- 博客地址 : http://www.cnblogs.com/yaopengfei/
- 声 明1 : 如有错误,欢迎讨论,请勿谩骂^_^。
- 声 明2 : 原创博客请在转载时保留原文链接或在文章开头加上本人博客地址,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· DeepSeek如何颠覆传统软件测试?测试工程师会被淘汰吗?