第三节:Nginx的server参数配置、同一端口映射多项目、补充host配置、location详解
一. Server参数配置
1. 准备工作-编译安装echo
(1). 先去github上下载 https://github.com/openresty/echo-nginx-module 这个模块
(2). copy到nginx的安装目录下的modules文件夹下
(3). 解压,并删除原先的压缩包
【unzip echo-nginx-module-master】
【rm -rf echo-nginx-module-master】
(4)必须在nginx下载后解压出来的那个目录文件中执行下面命令(注意,不是安装目录哦!!), 该模块作用,使nginx可以直接输出“字符串”。
其中 【/usr/local/nginx】是安装目录,需要改成自己的安装目录(下面两个地方要改哦)
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --add-module=/usr/local/nginx/modules/echo-nginx-module-master
make && make install将目录改为【/root/mydevelop/nginx】后指令如下
./configure --prefix=/root/mydevelop/nginx --add-module=/root/mydevelop/nginx/modules/echo-nginx-module-master
make && make install
2. 虚拟主机
所谓虚拟主机,在 Web 服务里就是一个独立的网站站点,这个站点对应独立的域名(也可能是IP 或端口),具有独立的程序及资源,可以独立地对外提供服务供用户访问。
在 Nginx 中,使用一个 server{} 标签来标识一个虚拟主机,一个 Web 服务里可以有多个虚拟主机标签对,即可以同时支持多个虚拟主机站点。
虚拟主机有两种类型:基于域名的虚拟主机、基于IP+端口的虚拟主机。
3. 参数说明
分享配置文件如下:
server {
keepalive_requests 120; #单连接请求上限次数。 可省略
#listen 80 default; #default表示默认虚拟主机
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset utf8;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}配置说明
A. keepalive_requests :单连接请求上限次数。
B. listen:监听的端口。 (省略的话默认监听80端口)
listen后面可以加default,表示指定默认的虚拟主机,如果有多个访问的域名指向这台web服务器,但某个域名(或ip)未添加到nginx虚拟主机中,就会访问默认虚拟主机(泛解析)
注:如果不加default,则最上面的一个server为默认主机,可以手动添加default来指定默认主机。
C. server_name:监听的地址,后面可以跟多个地址,比如:
server_name *.com; 通配符在前 server_name www.abc.*; 通配符在后
4 完全匹配测试(同一个端口绑定多个域名映射不同的项目)
配置文件如下:
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80;
server_name test1.whales.com;
location / {
root html;
index index1.html;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name test2.whales.com;
location / {
root html;
index index2.html;
}
}
}结论:
访问: http://test1.whales.com 打开的是index1页面
访问:http://test1.whales.com 打开的是index2页面, 二者都使用的是80端口哦
5. 通配符匹配测试
匹配优先级:完全匹配 》 通配符在前 》通配符在后
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80;
server_name *.com;
charset utf8;
location / {
default_type text/html;
echo "通配符在前";
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name test2.whales.*;
charset utf8;
location / {
default_type text/html;
echo "通配符在后";
}
}
}经测试:
test1.whales.com 返回: 通配符在前
test2.whales.com 返回:通配符在前
test2.whales.cn 返回:通配符在后
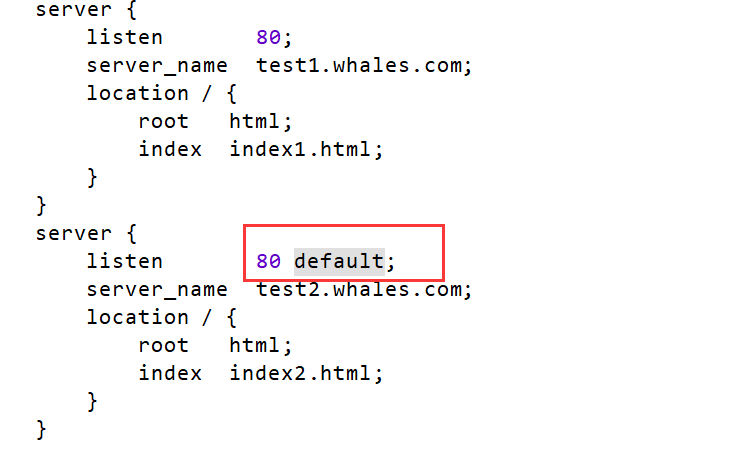
6. 默认主机测试
默认虚拟主机的作用就是:如果有多个访问的域名指向这台web服务器,但某个域名未添加到nginx虚拟主机中,就会访问默认虚拟主机(泛解析)
注:如果不加default,则最上面的一个server为默认主机,可以手动添加default来指定默认主机。
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80;
server_name test1.whales.com;
location / {
root html;
index index1.html;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name test2.whales.com;
location / {
root html;
index index2.html;
}
}
}如上述配置文件,访问 test1.whales.cn , 则默认访问的是 一个server,打开的是 index1页面。
如果在第二个server中加个deafult,访问 test1.whales.cn,打开的是index2页面
二. 同一端口绑定多个域名映射不同项目
1. 如果项目是静态页面的页面
详见上面的(一) 中的完全匹配测试,将上述index1.html 和 index2.html 换成具体的页面路径即可, 比如 /root/mydevelop/web/hello.html
2. 如果是两个完整的项目
用代理的方案即可,详见下面配置文件
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80;
server_name test1.whales.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://47.111.216.184:8001/;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name test2.whales.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://47.121.135.88:8095/;
}
}
}结论:
访问: http://test1.whales.com 打开的是 http://47.111.216.184:8001/ 对应项目,比如幼儿园项目。
访问:http://test1.whales.com 打开的是 http://47.111.216.184:8095/ 对应项目, 比如宜家宅配项目。
二者都使用的是80端口哦
三. 补充host配置说明
1.windows
(1). 进入该目录:C\Windows\System32\drivers\etc,打开host文件

(2). 修改如下: 将 test1.whales.com 和 test2.whales.com ,映射给192.168.137.101这个地址(虚拟机的地址),那么访问这个域名,实际访问的就是 192.168.137.101

补充:
我把 test1.whales.com 映射到 阿里云服务器 8.130.72.40, 但是我在本机配置了一下host,有把该域名映射到了 127.0.0.1 ,最终该域名访问的是哪个呢?
答案:访问这个域名,直接报错了。

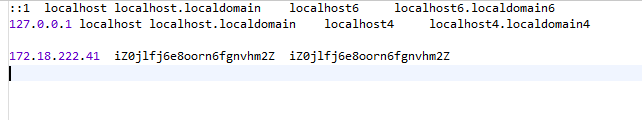
2. linux
修改 【/etc/hosts】文件即可
三. location详解
1. 配置文件详解
分享一个简单的配置文件
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index index.html main.html;
}
# root 的配置
location /static1/ {
root /webroot/mystatic1/;
}
# alias 的配置
location /static2/ {
alias /webroot/mystatic2/;
}
location /abc {
proxy_pass http://xxxx:8080/;
}
}参数说明
A. location:表示匹配的路径,这时配置了/表示所有请求都被匹配到这里
B. root:根路径,最终匹配路径: root路径+url中全路径 (和下面的alias不能在一个location中出现)
C. alias:别名路径, 最终匹配路径为:alias路径+url中移除location前缀后的路径
D. index:当没有指定主页时,默认会选择这个指定的文件,它可以有多个,并按顺序来加载,如果第一个不存在,则找第二个,依此类推。
E. proxy_pass:代理地址
举例区分root和alias的用法:
访问:http:xxxx/static1/ypf1.jpg 最终访问的路径为: http:xxxx/webroot/mystatic1/static1/ypf1.jpg
访问:http:xxxx/static2/ypf2.jpg 最终访问的路径为: http:xxxx/webroot/mystatic2/ypf2.jpg
2. 匹配规则详解
允许根据用户请求的URI来匹配定义的各location,匹配到时,此请求将被响应的location配置快中的配置所处理,例如做访问控制等功能
格式:
location 修饰符 pattern {
# .....
}
(1) 通用匹配
通用匹配使用一个 / 表示,可以匹配所有请求,一般nginx配置文件最后都会有一个通用匹配规则,当其他匹配规则均失效时,请求会被路由给通用匹配规则处理;如果没有配置通用匹配,并且其他所有匹配规则均失效时,nginx会返回 404 错误
server {
server_name test1.whales.com;
charset utf-8;
location /{
default_type text/html;
echo "通用匹配-default";
}
}(2) 前缀匹配
没有修饰符表示必须以指定模式开始,指定模式前面没有任何修饰符,直接在location后写需要匹配的uri,它的优先级次于正则匹配
server {
server_name test1.whales.com;
charset utf-8;
location /abc {
default_type text/html;
echo "前缀匹配-abc...";
}
}下面内容都可以正确匹配
test1.whales.com/abc
test1.whales.com/abc/
test1.whales.com/abc?
test1.whales.com/abcxxxxx
(3) 精确匹配
确匹配使用 = 表示,nginx进行路由匹配的时候,精确匹配具有最高的优先级,请求一旦精确匹配成功nginx会停止搜索其他到匹配项
server {
server_name test1.whales.com;
charset utf-8;
location = /abc {
default_type text/html;
echo "精确匹配-abc-accurate";
}
}下面内容都可以正确匹配
test1.whales.com/abc
test1.whales.com/abc?
下面内容不能匹配
test1.whales.com/abc/
test1.whales.com/abcxxx
(4) 精确前缀匹配
精确前缀匹配的优先级仅次于精确匹配,nginx对一个请求精确前缀匹配成功后,停止继续搜索其他到匹配项
server {
server_name test1.whales.com;
charset utf-8;
location ^~ /abc {
default_type text/html;
echo "精确前缀匹配-abc-prefix";
}
}下面内容都可以正确匹配
test1.whales.com/abc
test1.whales.com/abc?
test1.whales.com/abc/
test1.whales.com/abcxxx
(5) 正则表达式--区分大小写
正则匹配分为区分大小写和不区分大小写两种,分别用 ~ 和 ~* 表示;一个请求精确匹配和精确前缀匹配都失败后,如果配置有相关的正则匹配location,nginx会尝试对该请求进行正则匹配。需要说明的是正则匹配之间没有优先级一说,而是按照在配置文件中出现的顺序进行匹配,一旦匹配上一个,就会停止向下继续搜索
~:表示指定的正则表达式要区分大小写
server {
server_name test1.whales.com;
charset utf-8;
location ~ ^/abc$ {
default_type text/html;
echo "正则区分大小写-abc-regular-x";
}
}下面内容都可以正确匹配
test1.whales.com/abc
test1.whales.com/abc?
下面内容不能匹配
test1.whales.com/abc/
test1.whales.com/ABC/
test1.whales.com/abcxxx
(6) 正则表达式--不区分大小写
~*:表示指定的正则表达式不区分大小写,如:
server {
server_name test1.whales.com;
charset utf-8;
location ~* ^/abc$ {
default_type text/html;
echo "正则不区分大小写-abc-regular-Y";
}
}下面内容都可以正确匹配
test1.whales.com/abc
test1.whales.com/abc?
test1.whales.com/ABC/
下面内容不能匹配
test1.whales.com/abc/
test1.whales.com/abcxxx
3. 完整例子
server {
server_name test1.whales.com;
default_type text/html;
charset utf-8;
#精确匹配 (后面只有 /, 其后面什么也没有)
location = / {
echo "规则A";
}
#精确匹配
location = /login {
echo "规则B";
}
#精确前缀匹配
location ^~ /static/ {
echo "规则C";
}
#精确前缀匹配
location ^~ /static/files {
echo "规则X";
}
#正则匹配--区分大小写
location ~ \.(gif|jpg|png|js|css)$ {
echo "规则D";
}
#正则匹配--不区分大小写
location ~* \.js$ {
echo "规则E";
}
# 前缀匹配
location /img {
echo "规则Y";
}
#通用匹配
location / {
echo "规则F";
}
}答案:
4. 匹配顺序总结
匹配顺序和优先级,由高到底依次为:
- 带有“=”的精确匹配优先
- 正则表达式
- 没有修饰符的精确匹配
具体匹配规则如下:
- = 精准匹配命中时,停止location动作,直接走精准匹配,
- 一般匹配(含精确前缀匹配)命中时,先收集所有的普通匹配,最后对比出最长的那一条
- 如果最长的那一条普通匹配声明为精确前缀匹配,直接此条匹配,停止location
- 如果最长的那一条普通匹配不是精确前缀匹配,继续往下走正则location
- 按代码顺序执行正则匹配,当第一条正则location命中时,停止location
注:有多个正则表达式出现时,按照它们在配置文件中定义的顺序
5. 实际使用建议
至少有三个匹配规则定义,如下
#直接匹配网站根,通过域名访问网站首页比较频繁,使用这个会加速处理,官网如是说。
#这里是直接转发给后端应用服务器了,也可以是一个静态首页
# 第一个必选规则---精确匹配
location = / {
proxy_pass http://tomcat:8080/index
}
# 第二个必选规则是处理静态文件请求,这是nginx作为http服务器的强项
# 有两种配置模式,目录匹配或后缀匹配,任选其一或搭配使用
# 模式1--精确前缀匹配
location ^~ /static/ {
alias /webroot/static/;
}
# 模式2--正则匹配,不区分大小写
location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|css|js|ico)$ {
root /webroot/res/;
}
# 第三个规则就是通用规则,用来转发动态请求到后端应用服务器
# 非静态文件请求就默认是动态请求,自己根据实际把握
# 毕竟目前的一些框架的流行,带.php,.jsp后缀的情况很少了
# 通用匹配
location / {
proxy_pass http://tomcat:8080/
}特别说明:第一个必选规则非常重要,比如直接访问域名, test1.whales.com , 可以快速定位到这个地址!!!!
如果访问 test1.whales.com/xxx ,这个时候使用的是最后的通用匹配哦
6. path匹配过程 (了解)
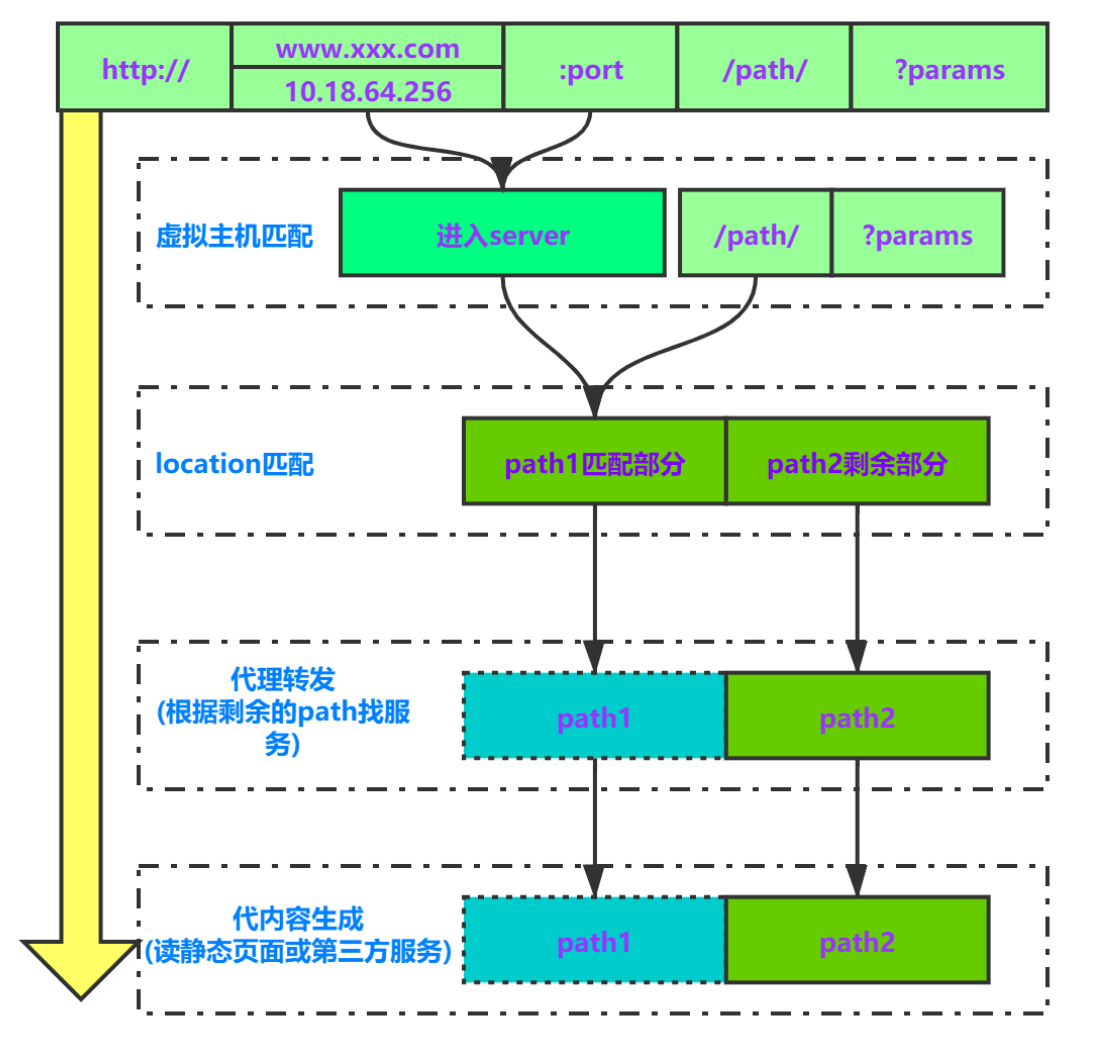
假设http请求路径为 http://192.168.123.101:8088/mvc/index?id=2 ,匹配过程如下:
- 将整个url拆解为域名/端口/path/params
- 先由域名/端口,对应到目标server虚拟主机
- path部分参与location匹配,path = path1匹配部分 + path2剩余部分
- 进入location方法体内部流程。
- 若是静态文件处理,则进入目标目录查找文件:root指令时找path1+path2对应的文件;alias指令时找path2对应的文件
- 若是proxy代理,则形如proxy_pass=ip:port时转发path1+path2路径到tomcat;形如proxy_pass=ip:port/xxx时转发path2路径到tomcat。params始终跟随转发。
!
- 作 者 : Yaopengfei(姚鹏飞)
- 博客地址 : http://www.cnblogs.com/yaopengfei/
- 声 明1 : 如有错误,欢迎讨论,请勿谩骂^_^。
- 声 明2 : 原创博客请在转载时保留原文链接或在文章开头加上本人博客地址,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。



