死锁-举例
首先回顾我们对死锁的定义,通俗易懂地说就是双方在占有自己手上的资源时,需要对方手上的资源才能继续下去,但是双方又不愿意主动放弃自己手上的资源
用一个生活中通俗易懂的例子就是:对方道歉我就道歉
这个模型用代码实现最简单的框架是这样
public class MustDeadLock implements Runnable{ public int flag; static final Object o1 = new Object(); static final Object o2 = new Object(); @Override public void run() { System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName() + "的flag为" + flag); if (flag == 1) { synchronized (o1) { try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } synchronized (o2) { System.out.println("线程1获得了两把锁"); } } } if (flag == 2) { synchronized (o2) { try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } synchronized (o1) { System.out.println("线程2获得了两把锁"); } } } } public static void main(String[] args) { TransferMoney r1 = new TransferMoney(); TransferMoney r2 = new TransferMoney(); r1.flag = 1; r2.flag = 2; Thread t1 = new Thread(r1, "t1"); Thread t2 = new Thread(r2, "t2"); t1.start(); t2.start(); } }
然后既然是举例我们需要对这个模型添加一点实际的情景,比如转账
public class TransferMoney implements Runnable { static class Account { int balance; public Account(int balance) { this.balance = balance; } } public int flag; static Account account1 = new Account(1000); static Account account2 = new Account(500); @Override public void run() { // 这里其实是两笔互相转账的操作导致的死锁 if (flag == 1) transferMoney(account1, account2, 500); if (flag == 2) transferMoney(account2, account1, 500); } private void transferMoney(Account from, Account to, int amount) { synchronized (from) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获取到第一把锁"); // 确保两把锁分别被不同的线程先拿到,发生死锁 try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } synchronized (to) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获取到第二把锁"); } if (from.balance - amount < 0) { System.out.println("余额不足,转账失败。"); return; } from.balance -= amount; to.balance += amount; System.out.println("成功转账" + amount + "元"); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { TransferMoney r1 = new TransferMoney(); TransferMoney r2 = new TransferMoney(); r1.flag = 1; r2.flag = 2; Thread t1 = new Thread(r1, "第一笔转账"); Thread t2 = new Thread(r2, "第二笔转账"); t1.start(); t2.start(); // 这里的两个join操作是为了保证下面打印余额前两笔转账完成 t1.join(); t2.join(); System.out.println("账户1的余额为:" + account1.balance); System.out.println("账户2的余额为:" + account2.balance); } }
死锁检测与避免
# 获取到Java进程的 pid jps # 检查线程死锁情况,以及各个线程具体持有的锁情况 jstack 8359
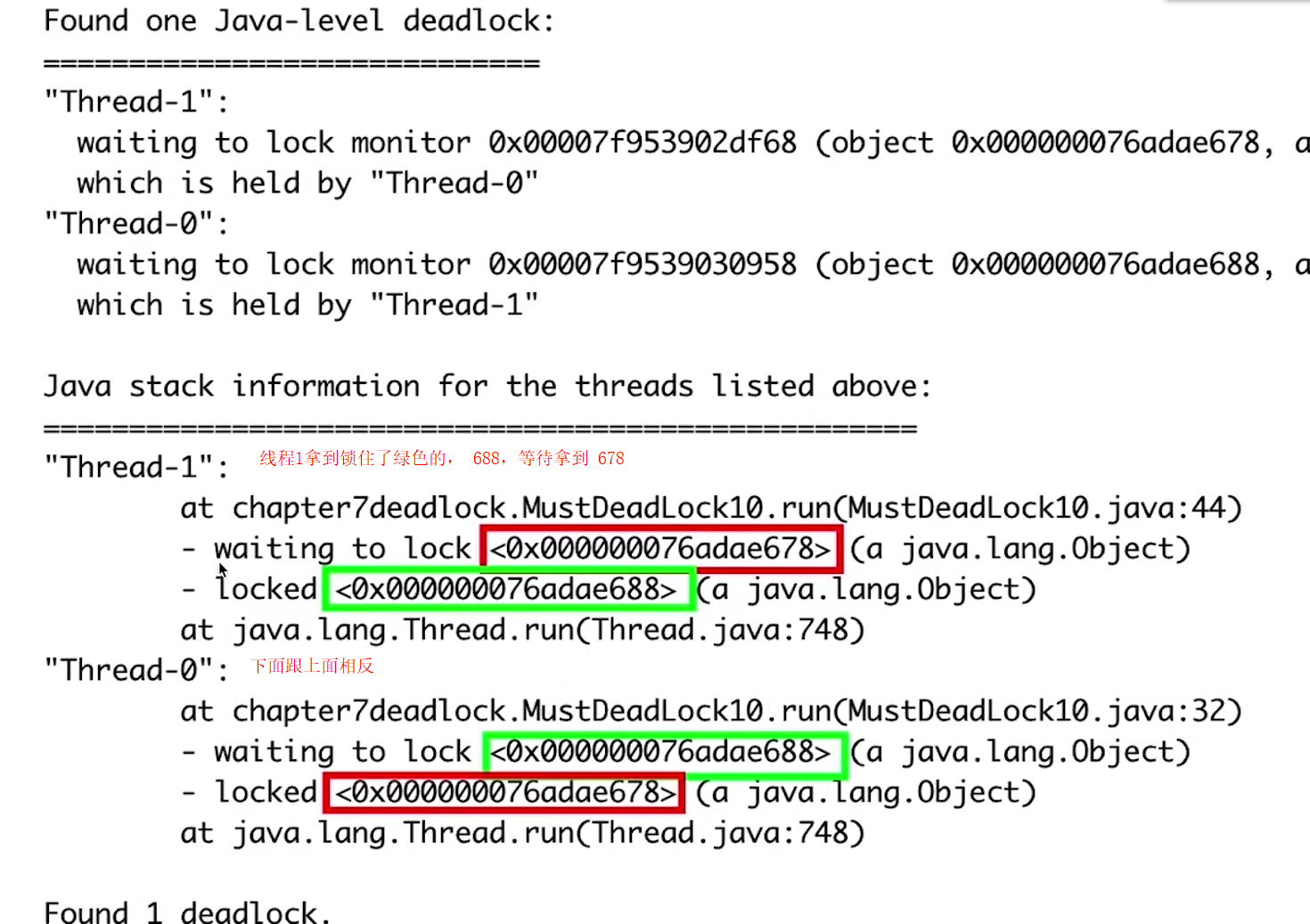
解决思路:
- 使用主键或者哈希,确保每次转账尝试获取锁时,尝试获取的都是主键或者哈希值最小的那个锁
引用:银行转账问题(死锁)
本文作者:YaosGHC
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/yaocy/p/18320977
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步