利用bind搭建dns服务器
安装软件
yum install bind bind-chroot bind-utils
修改配置
vim /etc/named.conf
options {
listen-on port 53 { 192.168.72.131; }; #### 修改为本机的ip或者any
listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; };
directory "/var/named";
dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db";
statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt";
memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt";
recursing-file "/var/named/data/named.recursing";
secroots-file "/var/named/data/named.secroots";
allow-query { any; }; ##### 修改为本机ip或者any #############
/*
- If you are building an AUTHORITATIVE DNS server, do NOT enable recursion.
- If you are building a RECURSIVE (caching) DNS server, you need to enable
recursion.
- If your recursive DNS server has a public IP address, you MUST enable access
control to limit queries to your legitimate users. Failing to do so will
cause your server to become part of large scale DNS amplification
attacks. Implementing BCP38 within your network would greatly
reduce such attack surface
*/
recursion yes;
dnssec-enable yes;
dnssec-validation yes;
/* Path to ISC DLV key */
bindkeys-file "/etc/named.root.key";
managed-keys-directory "/var/named/dynamic";
pid-file "/run/named/named.pid";
session-keyfile "/run/named/session.key";
};
logging {
channel default_debug {
file "data/named.run";
severity dynamic;
};
};
zone "." IN {
type hint;
file "named.ca";
};
include "/etc/named.rfc1912.zones";
include "/etc/named.root.key";
vim /etc/named.rfc1912.zones
// named.rfc1912.zones:
//
// Provided by Red Hat caching-nameserver package
//
// ISC BIND named zone configuration for zones recommended by
// RFC 1912 section 4.1 : localhost TLDs and address zones
// and http://www.ietf.org/internet-drafts/draft-ietf-dnsop-default-local-zones-02.txt
// (c)2007 R W Franks
//
// See /usr/share/doc/bind*/sample/ for example named configuration files.
//
zone "localhost.localdomain" IN {
type master;
file "named.localhost";
allow-update { none; };
};
zone "localhost" IN {
type master;
file "named.localhost";
allow-update { none; };
};
zone "1.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.ip6.arpa" IN {
type master;
file "named.loopback";
allow-update { none; };
};
zone "1.0.0.127.in-addr.arpa" IN {
type master;
file "named.loopback";
allow-update { none; };
};
zone "0.in-addr.arpa" IN {
type master;
file "named.empty";
allow-update { none; };
};
zone "tets8099.com" IN {
type master;
file "test8099.com.zone";
};
zone "72.168.192.in-addr.arpa" IN {
type master;
file "192.168.72.arpa";
};
配置地址库文件
vim /var/named/huangshanyan888.com.zone
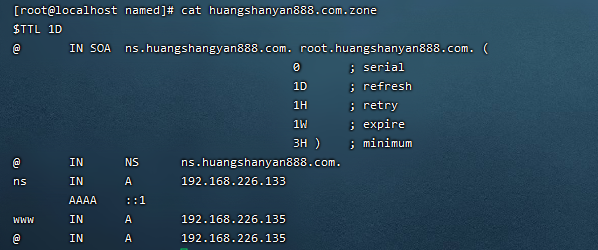
反向解析地址库文件
vim /var/named/192.168.226.arpa
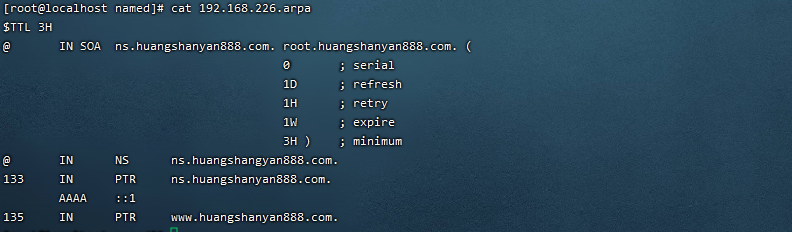
搭建dns实践
1 安装软件
yum install bind bind-devel bind-utils bind bind-chroot -y
2.修改配置文件
options {
listen-on port 53 { any; };
listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; };
directory "/var/named";
dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db";
statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt";
memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt";
recursing-file "/var/named/data/named.recursing";
secroots-file "/var/named/data/named.secroots";
allow-query { any; };
recursion yes;
dnssec-enable yes;
dnssec-validation yes;
bindkeys-file "/etc/named.iscdlv.key";
managed-keys-directory "/var/named/dynamic";
pid-file "/run/named/named.pid";
session-keyfile "/run/named/session.key";
forwarders { 202.96.128.166;8.8.8.8; };
};
logging {
channel default_debug {
file "data/named.run";
severity dynamic;
};
};
zone "." IN {
type hint;
file "named.ca";
};
include "/etc/named.rfc1912.zones";
include "/etc/named.root.key";
3. 追加域名解析入口配置:/etc/named.rfc1912.zones
zone "dylan.com" IN { # 测试用的域是 dylan.com
type master;
file "dylan.com.zone"; # 配置文件为 dylan.com.zone,该文件目录为 /var/named/ 下
};
4. 配置单独的解析文件:
/var/named/ cp named.localhost dylan.com.zone
chown named.named dylan.com.zone
修改配置:dylan.com.zone
$TTL 1D ;TTL 修改配置生效时间,默认为一天
@ IN SOA @ rname.invalid. (
0 ; serial,配置编号,每次改完配置 +1,这样从服务器就知道更新配置
1D ; refresh,从服务器刷新时间,默认一天刷新一次
1H ; retry,如果刷新失败,默认1小时重试一次
1W ; expire,缓存过期时间,一周
3H ) ; minimum
NS @
A 127.0.0.1
AAAA ::1
www IN A 192.168.100.112
添加ww.dylan.com 的 A 记录。
4. 启动服务测试:
systemctl start named
systemctl enable named
查看端口:
netstat -tlunp | grep 53
dig @127.0.0.1 www.dylan.com 测试域名解析
注明:修改文件属主属组 chown -R named:named /var/named
How To Configure DNS (BIND) Server on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7
 Configure DNS (BIND) Server on CentOS 7
Configure DNS (BIND) Server on CentOS 7
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical distributed naming system for computers, services, or any resource connected to the Internet or a private network. It associates various information with domain names assigned to each of the participating entities.
Most importantly, it translates domain names meaningful to humans into the numerical identifiers associated with networking equipment for the purpose of locating and addressing these devices worldwide.
This guide will help you to set up DNS server on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7.
Environment
Server Name: ns1itzgeek.local
IP Address: 192.168.0.10
Install DNS (BIND)
BIND stands for Berkeley Internet Name Domain, a software that provides an ability to perform name to ip conversion.
yum -y install bind bind-utils
Configure DNS (BIND)
By default, BIND listens on the localhost. So, we will configure the DNS server to listen on the system IP address to let clients can reach to DNS server for resolving domain names.
vi /etc/named.conf
Listen on all IP address:
Configure BIND to listen on all IP addresses.
// listen-on port 53 { 127.0.0.1; };
// listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; };
Listen on particular IP address:
Configure BIND to listen to a particular IP address.
listen-on port 53 { 127.0.0.1; 192.168.0.10; };
Add your network in the following line. This setting will allow clients from the mentioned network can query the DNS for the name to ip translation.
I’ve added 192.168.0.0/24 for this demo.
allow-query { localhost; 192.168.0.0/24; };
Create Zones
Edit /etc/named.conf.
vi /etc/named.conf
Forward Zone
The following zone is the forward zone entry for the itzgeek.local domain.
zone "itzgeek.local" IN {
type master;
file "/var/named/itzgeek.local.db";
allow-update { none; };
};
itzgeek.local – Domain name
master – Primary DNS
fwd.itzgeek.local.db – Forward lookup file
allow-update – Since this is the primary DNS, it should be none
Reverse Zone
The following zone is the reverse zone entry.
zone "0.168.192.in-addr.arpa" IN {
type master;
file "/var/named/192.168.0.db";
allow-update { none; };
};
0.168.192.in-addr.arpa – Reverse lookup name
master – Primary DNS
192.168.0.db – Reverse lookup file
allow-update – Since this is the primary DNS, it should be none
Create Zone Files
By default, zone lookup files are placed under /var/named directory. Create a zone file called fwd.itzgeek.local.db for forward lookup under /var/named directory. All domain names should end with a dot (.).
vi /var/named/itzgeek.local.db
There are some special keywords for Zone Files
A – A record
NS – Name Server
MX – Mail for Exchange
CNAME – Canonical Name
@ IN SOA ns1.itzgeek.local. root.itzgeek.local. (
1001 ;Serial
3H ;Refresh
15M ;Retry
1W ;Expire
1D ;Minimum TTL
)
;Name Server Information
@ IN NS ns1.itzgeek.local.
;IP address of Name Server
ns1 IN A 192.168.0.10
;Mail exchanger
itzgeek.local. IN MX 10 mail.itzgeek.local.
;A - Record HostName To IP Address
www IN A 192.168.0.100
mail IN A 192.168.0.150
;CNAME record
ftp IN CNAME www.itgeek.local.
Create a zone file called 192.168.0.db for the reverse zone under /var/named directory.
vi /var/named/192.168.0.db
Create a reverse pointer for the forward zone entries we created earlier.
PTR – Pointer
SOA – Start of Authority
@ IN SOA ns1.itzgeek.local. root.itzgeek.local. (
1001 ;Serial
3H ;Refresh
15M ;Retry
1W ;Expire
1D ;Minimum TTL
)
;Name Server Information
@ IN NS ns1.itzgeek.local.
;Reverse lookup for Name Server
10 IN PTR ns1.itzgeek.local.
;PTR Record IP address to HostName
100 IN PTR www.itzgeek.local.
150 IN PTR mail.itzgeek.local.
Once zone files are created, restart bind service.
systemctl restart named
Enable it on system startup.
systemctl enable named
Firewall
Add a allow rule in the firewall to let clients can connect to the DNS server for name resolution.
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=53/udp firewall-cmd --reload
Verify Zones
Visit any client machine and add a DNS server ip address in /etc/resolv.conf.
nameserver 192.168.0.10
If Network Manager manages the networking then place the following entry in /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eXX file.
DNS1=192.168.0.10
Restart network service.
systemctl restart NetworkManager
Use the following command to verify the forward lookup.
dig www.itzgeek.local
Output: The DNS server should give 192.168.0.100 as ip for www.itzgeek.local.
; <<>> DiG 9.9.4-RedHat-9.9.4-74.el7_6.1 <<>> www.itzgeek.local ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 35563 ;; flags: qr aa rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 1, ADDITIONAL: 2 ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;www.itzgeek.local. IN A ;; ANSWER SECTION: www.itzgeek.local. 86400 IN A 192.168.0.100 ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: itzgeek.local. 86400 IN NS primary.itzgeek.local. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: ns1.itzgeek.local. 86400 IN A 192.168.0.10 ;; Query time: 0 msec ;; SERVER: 192.168.0.10#53(192.168.0.10) ;; WHEN: Wed Jul 03 02:00:40 EDT 2019 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 100
Confirm the reverse lookup.
dig -x 192.168.0.100
Output: The DNS server gives www.itzgeek.local as a name for 192.168.0.100.
; <<>> DiG 9.9.4-RedHat-9.9.4-74.el7_6.1 <<>> -x 192.168.0.100 ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 4807 ;; flags: qr aa rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 1, ADDITIONAL: 2 ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;100.0.168.192.in-addr.arpa. IN PTR ;; ANSWER SECTION: 100.0.168.192.in-addr.arpa. 86400 IN PTR www.itzgeek.local. ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: 0.168.192.in-addr.arpa. 86400 IN NS ns1.itzgeek.local. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: ns1.itzgeek.local. 86400 IN A 192.168.0.10 ;; Query time: 0 msec ;; SERVER: 192.168.0.10#53(192.168.0.10) ;; WHEN: Wed Jul 03 02:02:47 EDT 2019 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 124
It is now confirmed that both forward and reverse lookups are working fine.
参考地址 https://www.itzgeek.com/how-tos/linux/centos-how-tos/configure-dns-bind-server-on-centos-7-rhel-7.html

