@SpringBootApplication注解详细解释
@SpringBootApplicayion = @Configuration + @EnableAutoConfiguration + @Componentscan
并具有三者的默认属性
一、@Configurantion
1. @Configuration启动spring容器
@Configuration标注在
类上,相当于xml配置文件中的<beans>一堆空间配置</beans>,作用为:配置Spring容器。
示例代码如下:
@Configuration
public class Application {
//无参构造器
public Application() {
System.out.println("应用启动");
}
}
public class myTest {
@Test
public void test01() {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Application.class);
}
}
运行结果如下:
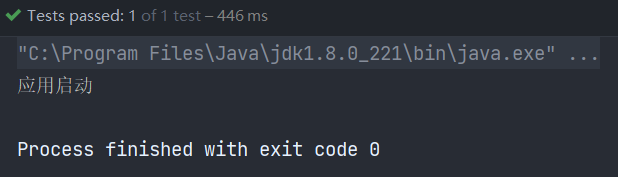
2. @Configuration配合@Bean注册Bean
@Bean标注在
方法上,该方法可以返回某个实例,相当于xml文件中的<bean></bean>,作用为:注册对象。
示例代码如下:
public class Dog {
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("hello...");
}
}
@Configuration
public class Application {
//无参构造器
public Application() {
System.out.println("应用启动");
}
//注册对象
@Bean
public Dog dog() {
return new Dog();
}
}
public class myTest {
@Test
public void test01() {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Application.class);
Dog dog = (Dog)context.getBean("dog");
dog.sayHello();
}
}
运行结果如下:
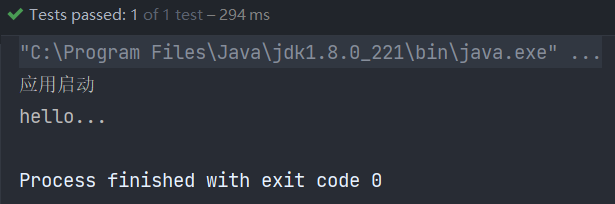
2.1 @Bean
- @Bean有name属性,若是不指定name属性,则默认是类名首字母小写。
- @Bean注册的对象一般使用@Autowired(@Autowired相当于setter)注入,用@Qualifier指定注入Bean的名称
3. @Configuration配合@Component注册Bean
使用步骤:
- 在类上添加@Component注解,交给Spring容器管理。
- @Configuratin和@ComponentScan(basePackages = "路径")就会扫描@Component注解的类
@Component和@Bean对比:
- @Bean在@Configuration注解类的内部,所以不需要扫描
- @Component在@Configuration注解类的外部,所以@ComponentScan扫描
二、@EnableAutoConfiguration
功能:根据定义在classpath下的类,自动的给你生成一些Bean,并加载到Spring的Context中。
classpath 等价于 main/java + main/resources + 第三方jar包的根目录。
三、@ComponentScan
功能:定义扫描路径,并从路径中找出标识了需要装配的类装配到spring的bean容器中。
扫描的类:@Component、@Service、@Controller、@Repository
环环无敌大可爱😋
本文作者:yanxioaguo
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/yanxiaoguo/p/16167561.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步