24暑假集训day2上午
上午
内容:基础数据结构
1. 链表
分类:单向和双向
单向:当前链表只指向下一个元素
双向:对于每个元素,记录其前面一个元素,也记录其后面一个元素。
注意:链表不建议使用 STL 的某些元素进行替代,手写链表更为方便。
1. 单向链表
做法:维护每个元素编号,然后维护 nx 指针,表示当前元素的下一个元素是谁加入和删除都是方便的。
手写的单向链表:
void ins(int x,int y){
int to=nx[x];
nx[x]=y,nx[y]=to;
}
void erase(int x){
int to=nx[x];
nx[x]=nx[to];
}
问题简述:如题
思路:我谔谔, 直接模拟
std:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1e6 + 10;
int nx[MAXN];
int main(){
int q;
cin >> q;
for(int i = 1;i <= q;i++){
int op;
cin >> op;
if(op == 1){
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
int a;
a = nx[x];
nx[x] = y;
nx[y] = a;
}else if(op == 2){
int x;
cin >> x;
cout << nx[x] << '\n';
}else{
int x;
cin >> x;
int a = nx[x];
nx[x] = nx[a];
}
}
return 0;
}
前项星
本质:多个单项链表组成,维护链头数组,然后可以支持每个点加边。
struct nod{
int next,to;
}e[xx*2];
int cnt,h[xx];
void add(int x,int y){
cnt++;
e[cnt]={h[x],y};
h[x]=cnt;
}
void dfs(int x,int y){
for(int i=h[x];i;i=e[i].next){
dfs(e[i].to,x);
}
}
思路:直接复制上述程序
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN=100005;
struct Node{
int next,to;
}e[MAXN*2];
int n,m,cnt,h[MAXN];
void add(int x,int y){
cnt++;
e[cnt]={h[x],y};
h[x]=cnt;
}
int ans[MAXN],id;
void dfs(int x){
if(!ans[x])ans[x]=id;
else return;
for(int i=h[x];i;i=e[i].next)dfs(e[i].to);
}
int main(){
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
add(b,a);
}
for(int i=n;i>=1;i--)id=i,dfs(i);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cout<<ans[i]<<' ';
return 0;
}
2. 双向链表
做法:每个元素维护前驱
手写的双向链表:
void ins(int x,int y){
int to=nx[x];
nx[x]=y,pr[to]=y;
pr[y]=x,nx[y]=to;
}
void era(int x){
int L=pr[x],R=nx[x];
nx[L]=R,pr[R]=L;
}
2. 栈
做法:维护一个序列,每次从末端加入元素,然后末端弹出元素
具体维护:使用一个数组,维护一个
手写的栈:
int stk[xx],tp;
void push(int x){
stk[++tp]=x;
}
int top(){
return stk[tp];
}
void pop(){
--tp;
}
STL 的栈:
stack<int>stk;
stk.push(1);
stk.pop();
cout<<stk.top()<<"\n";
cout<<stk.size()<<"\n";
模板题直接用 STL。
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
#define int unsigned long long
stack<int>stk;
void a(int n){
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++){
string op;
cin >> op;
if(op == "push"){
int x;
cin >> x;
stk.push(x);
} else if(op == "pop"){
if(!stk.empty()){
stk.pop();
} else {
cout << "Empty" << '\n';
}
} else if(op == "query"){
if(!stk.empty()){
cout << stk.top() << '\n';
} else {
cout << "Anguei!" << '\n';
}
} else if(op == "size"){
cout << stk.size() << '\n';
}
}
}
int t, n;
signed main(){
cin >> t;
for(int i = 1;i <= t;i++){
int n;
cin >> n;
a(n);
while(!stk.empty()){
stk.pop();
}
}
/*
stack<int>stk;
stk.top();
stk.pop();
cout << stk.top() << '\n';
cout << stk.size() << '\n';
*/
return 0;
}
单调栈
实质:用栈维护了单调的结构
问题简述:给定一个长度为
方法:从后往前枚举,栈内维护单调的下标,满足这些下标的值是递减的
关键:保留对当前状态最优的信息。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,a[3000005];
int top,ans[3000005],maxn;
struct node{
int val,i;
};
stack<node>sta;
stack<int>p;
int main(){
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
}
for(int i=n;i>=1;i--){
int vis=0;
while(!sta.empty()){
if(a[i]<sta.top().val){
p.push(sta.top().i);
vis=1;
break;
}
else sta.pop();
}
if(!vis)p.push(0);
sta.push((node){a[i],i});
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cout<<p.top()<<' ';
p.pop();
}
}
3. 队列
方法:后进先出
手写的队列:
int q[xx],l,r;
void push(int x){
q[++r]=x;
}
int front(){
return q[l];
}
void pop(){
l++;
}
STL 队列:
queue<int>q;
q.push(1);
q.pop();
cout<<q.front()<<"\n";
cout<<q.size()<<"\n";
模板题直接用 STL。
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
queue<int> q;
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++){
int op;
cin >> op;
if(op == 1){
int x;
cin >> x;
q.push(x);
} else if(op == 2){
if(!q.empty()){
q.pop();
} else {
cout << "ERR_CANNOT_POP" << '\n';
}
} else if(op == 3){
if(!q.empty()){
cout << q.front() << '\n';
} else {
cout << "ERR_CANNOT_QUERY" << '\n';
}
} else {
cout << q.size() << '\n';
}
}
return 0;
}
单调队列
定义:权值是递减的(求目前最大值),但是
关键:保留对于当前而言更优的一个信息。
方法:
-
判断队首元素是否超出范围,如果是,则队首元素出队;
-
判断队尾元素是否满足要求(例如求区间最大值,要求则为队尾元素小于插入的元素),如果是,则队尾元素出队,返回步骤
-
将元素插入队尾。
std:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a[1000005];
int q[1000005];
int l, r;
int read() {
char c;
int w = 1;
while ((c = getchar()) > '9' || c < '0')
if (c == '-')
w = -1;
int ans = c - '0';
while ((c = getchar()) >= '0' && c <= '9')
ans = (ans << 1) + (ans << 3) + c - '0';
return ans * w;
}
int m;
int main() {
int n;
n = read();
m = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
a[i] = read();
}
l = r = 1;
q[1] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n + 1; i++) {
while (l <= r && q[l] < i - m)
l++;
if (i > m)
printf("%d ", a[q[l]]);
while (l <= r && a[q[r]] >= a[i])
r--;
q[++r] = i;
}
l = r = 1;
q[1] = 1;
cout << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= n + 1; i++) {
while (l <= r && q[l] < i - m)
l++;
if (i > m)
printf("%d ", a[q[l]]);
while (l <= r && a[q[r]] <= a[i])
r--;
q[++r] = i;
}
return 0;
}
4. 队列
方法:维护一个序列,每次加入一个元素,询问当前序列中最小的元素,然后删除最小元素。
具体维护:一般维护的称为二叉堆,即维护一个结构,支持上述处理过程。
每个节点
手写的堆:
int hp[xx],sz;
void push(int val){
int id=++sz;
hp[id]=val;
while(id!=1){
int to=id/2;
if(hp[id]<hp[to])swap(hp[id],hp[to]);
id=to;
}
}
void pop(){
hp[1]=hp[sz],--sz;
int id=1;
while((id*2)<=sz){
int L=id*2,R=id*2+1,ty=L;
if(R<=sz&&hp[R]<hp[ty])ty=R;
if(hp[ty]<hp[id])swap(hp[ty],hp[id])
id=ty;
}
}
STL 堆:
priority_queue<int>q;//大根堆!
q.push(1),q.pop();
cout<<g.top()<<"\n";
cout<<q,size()<<\n";
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>>q;//小根堆!
q.push(1),q.pop();
cout<<g.top()<<"\n";
cout<<q.size()<<"\n";
思路:模板是小根堆,直接用STL
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN=1000005;
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,less<int> > h;
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int op;
cin>>op;
if(op==1){
int x;
cin>>x;
h.push(-x);
}else if(op==2)cout<<-h.top()<<'\n';
else h.pop();
}
return 0;
}
对顶堆
问题简述:一个序列,我们每次加入一个元素,或者进行询问。
维护一个初始指针
思路:使用两个堆,把序列分为前半和后半,分界点位置就是我们尝试输出的值。
std:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 200010;
priority_queue<int>q1, q2;
int a[MAXN], u[MAXN];
int main(){
int n,m;
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>a[i];
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
cin>>u[i];
for(int l=u[i-1]+1;l<=u[i];l++){
q2.push(a[l]);
}
while(q1.size()&&q2.size()&&-q1.top()<q2.top()){
q1.push(-q2.top());
q2.pop();
}
while(q2.size()<i){
q2.push(-q1.top());
q1.pop();
}
while(q2.size()>i){
q1.push(-q2.top());
q2.pop();
}
cout<<q2.top()<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
5. 哈夫曼树
本质:在堆的基础上的一点点贪心的扩展
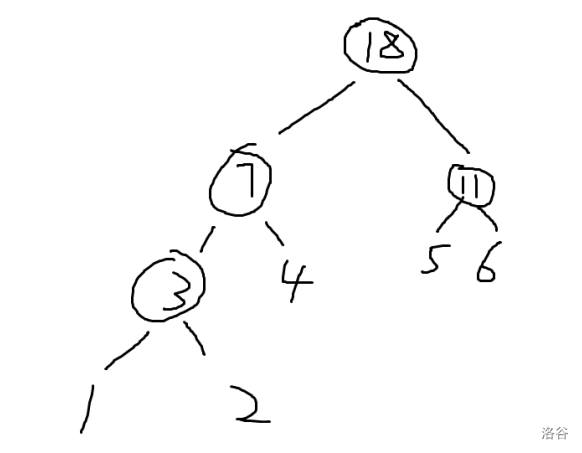
性质:
每个数贡献的次数是他到根的边数。
数大的贡献较少,即经过的边数较少。
如果把边顺次标号为
问题简述:有
每次选择两堆果子,将其合并为一堆,
即删除原来两堆
std:
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int n, x, ans;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> >q;
int main(){
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++){
cin >> x;
q.push(x);
}
while(q.size() >= 2){
int a = q.top();
q.pop();
int b = q.top();
q.pop();
ans += a + b;
q.push(a + b);
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
哈夫曼树扩展
思路:选择最小的两堆合并,并一直执行这个过程
多叉的哈夫曼树同样涉及到一个补
具体的,补其
问题简述:给定
思路:注意到,没有前缀包含关系完全对应了哈夫曼编码,而我们最优化次数正好是哈夫曼树的最小的贡献!
所以我们建立扩展的
std:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int read()
{
char c;
int w=1;
while((c=getchar())>'9'||c<'0')if(c=='-')w=-1;
int ans=c-'0';
while((c=getchar())>='0'&&c<='9')ans=(ans<<1)+(ans<<3)+c-'0';
return ans*w;
}
priority_queue<pair<int,int> >q;
int a[5000005];
int n;
int k;
signed main(){
n=read();
k=read();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
a[i]=read();
q.push(make_pair(-a[i],-1));
}
while((n-1)%(k-1))n++,q.push(make_pair(0,-1));
int anss=0;
for(int i=1;i<=(n-1)/(k-1);i++)
{
int ans=0;
int maxx=0;
for(int j=1;j<=k;j++)
{
ans+=(-q.top().first);
maxx=max(maxx,-q.top().second);
q.pop();
}
anss+=ans;
q.push(make_pair(-ans,-maxx-1));
}
cout<<anss<<endl<<-q.top().second-1<<endl;
return 0;
}




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现