Hook
## 钩子 函数 def module_hook(module: nn.Module, input: Tensor, output: Tensor): # For nn.Module objects only. def tensor_hook(grad: Tensor): # For Tensor objects only. # Only executed during the *backward* pass! ## 将 钩子 注册到 主体上 torch.tensor.register_hook(tensor_hook) # 主体是 tensor torch.nn.Module.register_forward_hook(module_hook) # 主题是 module torch.nn.Module.register_forward_pre_hook(module_hook) # 主题是 module torch.nn.Module.register_backward_hook(module_hook) # 主题是 module
钩子函数的 输入 输出 相对固定
torch.tensor.register_hook
PyTorch采用动态图的设计理念,在计算过程中,除叶子节点外,其他节点在计算完毕后会被释放,无法获取计算结果,此时可以用 hook 获取非叶子节点;
也可以用 hook 改变 叶子节点的值;
import torch from torch import nn hook_list = [] def tensor_hook(grad): hook_list.append(grad) def tensor_hook2(grad): # 改变叶子节点梯度的值 grad *= 1000000 x = torch.tensor([2.], requires_grad=True) w = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True) a = torch.add(x, w) b = w + 1 y = torch.mul(a, b) print(y) # tensor([6.], grad_fn=<MulBackward0>) print(a.requires_grad, b.requires_grad, y.requires_grad) # True True True ##### 不加hook,除了叶子节点,其他节点的梯度全部释放 # y.backward() # print(x.grad, w.grad, a.grad, b.grad, y.grad) # tensor([2.]) tensor([5.]) None None None ##### 加上hook,除了叶子节点,被加上hook的节点梯度被保存在我们指定的地方,list中 handle = a.register_hook(tensor_hook) # handle2 = a.register_hook(tensor_hook2) y.backward(retain_graph=True) print(x.grad, w.grad, a.grad, b.grad, y.grad) # tensor([2.]) tensor([5.]) None None None print('hook_list: ', hook_list) # hook_list: [tensor([2.])] #### 删除hook handle.remove() print('hook_list: ', hook_list)
torch.nn.Module.register_forward_hook
示例,用 hook 获取最终的 feature map
import torch import torchvision import cv2 as cv from torch import nn import numpy as np from PIL import Image test_transforms = torchvision.transforms.Compose([ torchvision.transforms.Resize(size=224), torchvision.transforms.CenterCrop(size=224), torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), torchvision.transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.485, 0.456, 0.406), std=(0.229, 0.224, 0.225)) ]) conv_hook_list = [] class MyModule(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(MyModule, self).__init__() model = torchvision.models.vgg16(pretrained=True) print(list(model.named_children())) self.feature = model.features self.feature.register_forward_hook(self.conv_hook) # 在moudle上注册 hook self.pool = model.avgpool self.classifier_middle = model.classifier[:-1] self.classifier_fc = model.classifier[-1] def conv_hook(self, module, input, output): conv_hook_list.append(output) def forward(self, x): feat = self.feature(x) print('feat.shape: ', feat.shape) x = self.pool(feat) x = x.view(1, -1) x = self.classifier_middle(x) y = self.classifier_fc(x) return y model = MyModule() model.eval() img = Image.open('desk.png').convert('RGB') x = test_transforms(img) x = torch.unsqueeze(x, 0) print('x.shape: ', x.shape) y = model(x) print('conv_hook_list[0].shape: ', conv_hook_list[0].shape) features = conv_hook_list[0]
剩下的hook不太常用,可自行研究,大同小异
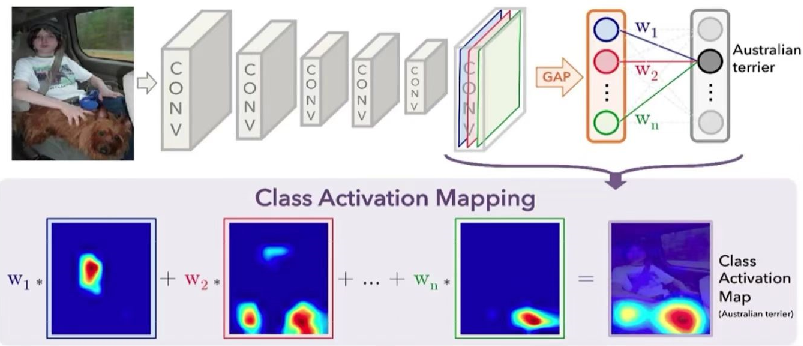
CAM
CAM的全称是Class Activation Mapping或Class Activation Map,即类激活映射或类激活图。
论文《Learning Deep Features for Discriminative Localization》发现了CNN分类模型的一个有趣的现象:
CNN的最后一层卷积输出的特征图,对其通道进行加权叠加后,其激活值(ReLU激活后的非零值)所在的区域,即为图像中的物体所在区域。
而将这一叠加后的单通道特征图覆盖到输入图像上,即可高亮图像中物体所在位置区域。
该文章作者将实现这一现象的方法命名为类激活映射,并将特征图叠加在原始输入图像上生成的新图片命名为类激活图。

Hook注册实现CAM
使用pytorch的hook注册, 取出网络某中间层feature map
(为啥用hook? 因为pytorch是动态图结构, 计算后的节点会被释放. 想要取出某中间结构, 需手动注册获取),
结合weighted_softmax, 点乘得到CAM(Class Activation Mapping)和heatmap.
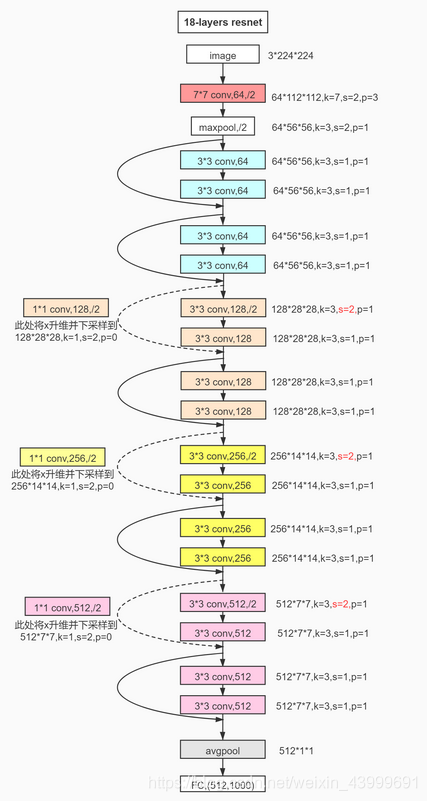
以 resnet18 为例
import numpy as np import cv2 import torch from PIL import Image from torchvision import models, transforms from torch.autograd import Variable from torch.nn import functional as F def hook_feature(module, input, output): # hook注册, 响应图提取 print("hook input", input[0].shape) features_blobs.append(output.data.cpu().numpy()) def returnCAM(feature_conv, weight_softmax, class_idx, size_upsample): # 生成CAM图: 输入是feature_conv和weight_softmax bz, nc, h, w = feature_conv.shape # feature_conv和weight_softmax 点乘(.dot)得到cam print(weight_softmax[class_idx].shape, feature_conv.reshape((nc, h * w)).shape) # (512,) (512, 49) cam = weight_softmax[class_idx].dot(feature_conv.reshape((nc, h * w))) cam = cam.reshape(h, w) cam = cam - np.min(cam) cam_img = cam / np.max(cam) cam_img = np.uint8(255 * cam_img) output_cam = cv2.resize(cam_img, size_upsample) return output_cam if __name__ == '__main__': size_upsample = (224, 224) # 1. imput image process normalize = transforms.Normalize( mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) preprocess = transforms.Compose([ transforms.Resize(size_upsample), transforms.ToTensor(), normalize]) img_name = 'car.png' img_pil = Image.open(img_name).convert('RGB') img = cv2.imread(img_name) img_tensor = preprocess(img_pil) img_variable = Variable(img_tensor.unsqueeze(0)) # 2. 导入res18 pretrain, 也可自行定义net结构然后导入.pth net = models.resnet18(pretrained=True) # net = models.resnet18(pretrained=False) # net.load_state_dict(torch.load('./resnet18-f37072fd.pth'), strict=True) net.eval() # print(net) # 3. 获取特定层的feature map # 3.1. hook the feature extractor features_blobs = [] finalconv_name = 'layer4' # 最后一个卷积模块 # 对layer4层注册, 把layer4层的输出加入features net._modules.get(finalconv_name).register_forward_hook(hook_feature) print(net._modules) # 3.2. 得到weight_softmax params = list(net.parameters()) # 将参数变换为列表 按照weights bias 排列 池化无参数 print(params) weight_softmax = np.squeeze(params[-2].data.numpy()) # 提取softmax 层的参数 (weights,-1是bias) print('weight_softmax.shape', weight_softmax.shape) # (1000, 512) # 4. imput img inference logit = net(img_variable) h_x = F.softmax(logit, dim=1).data.squeeze() probs, idx = h_x.sort(0, True) probs = probs.numpy() idx = idx.numpy() print(idx.shape) # (1000,) # features_blobs[0], weight_softmax点乘得到CAM # CAMs = returnCAM(features_blobs[0], weight_softmax, [idx[2], idx[3]], size_upsample) CAMs = returnCAM(features_blobs[0], weight_softmax, idx[0], size_upsample) # CAMs = returnCAM(features_blobs[0], weight_softmax, [idx[-2], idx[-1]], size_upsample) # 将图片和CAM拼接在一起展示定位结果结果 img = cv2.resize(img, size_upsample) height, width, _ = img.shape # 生成热度图 heatmap = cv2.applyColorMap(cv2.resize(CAMs, (width, height)), cv2.COLORMAP_JET) cv2.imwrite('./heatmap.jpg', heatmap) result = heatmap * 0.3 + img * 0.5 cv2.imwrite('./CAM.jpg', result)

CAM的缺点
注意,上面的代码我用 resnet18 举例,那其他模型是否可以呢,很遗憾,不行;
因为 CAM 需要在 feature map 后 接 global avg pooling,然后接1层全连接,否则就不太好计算CAM了
Grad-CAM
解决了CAM的缺点
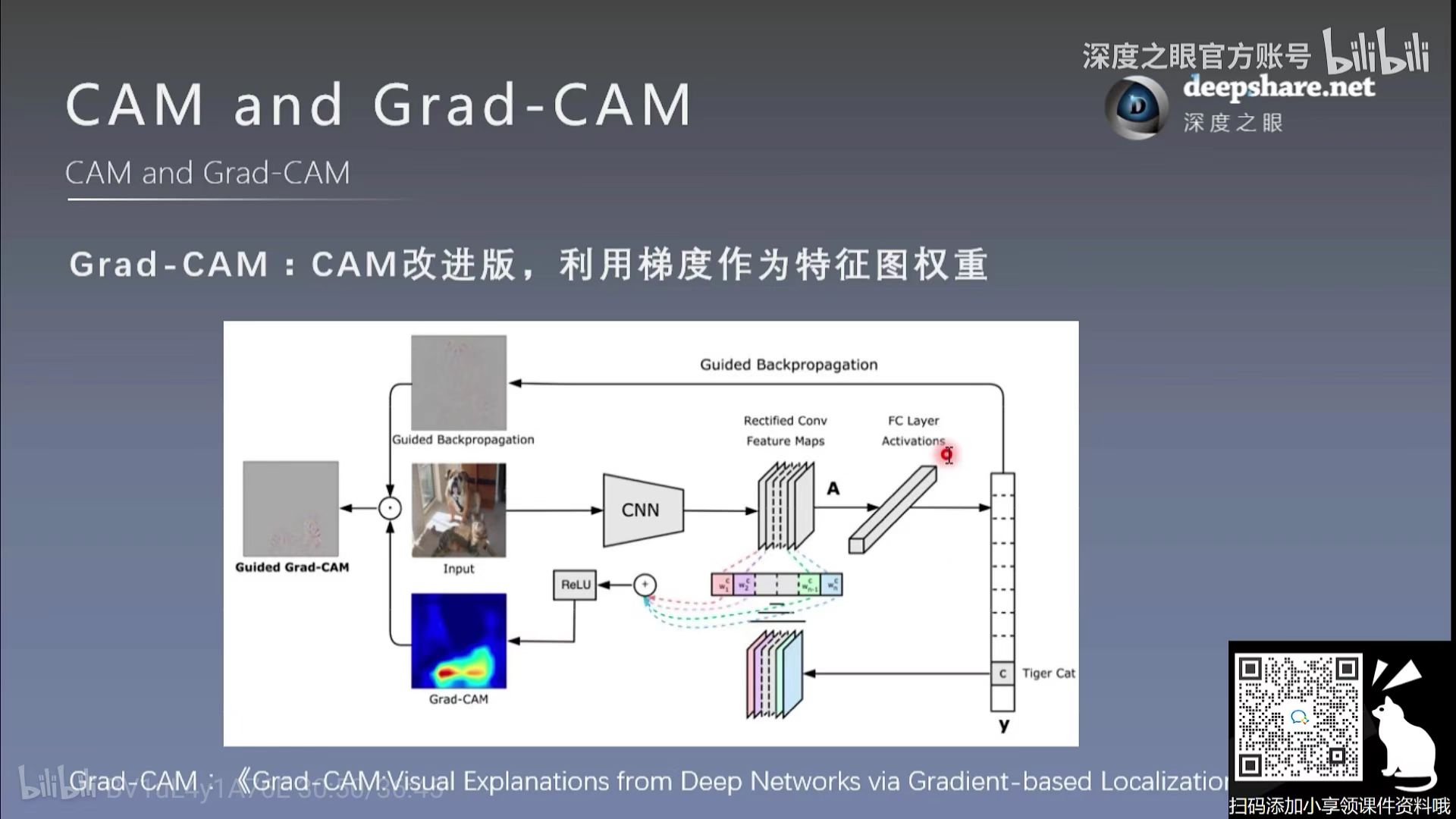
CAM分析
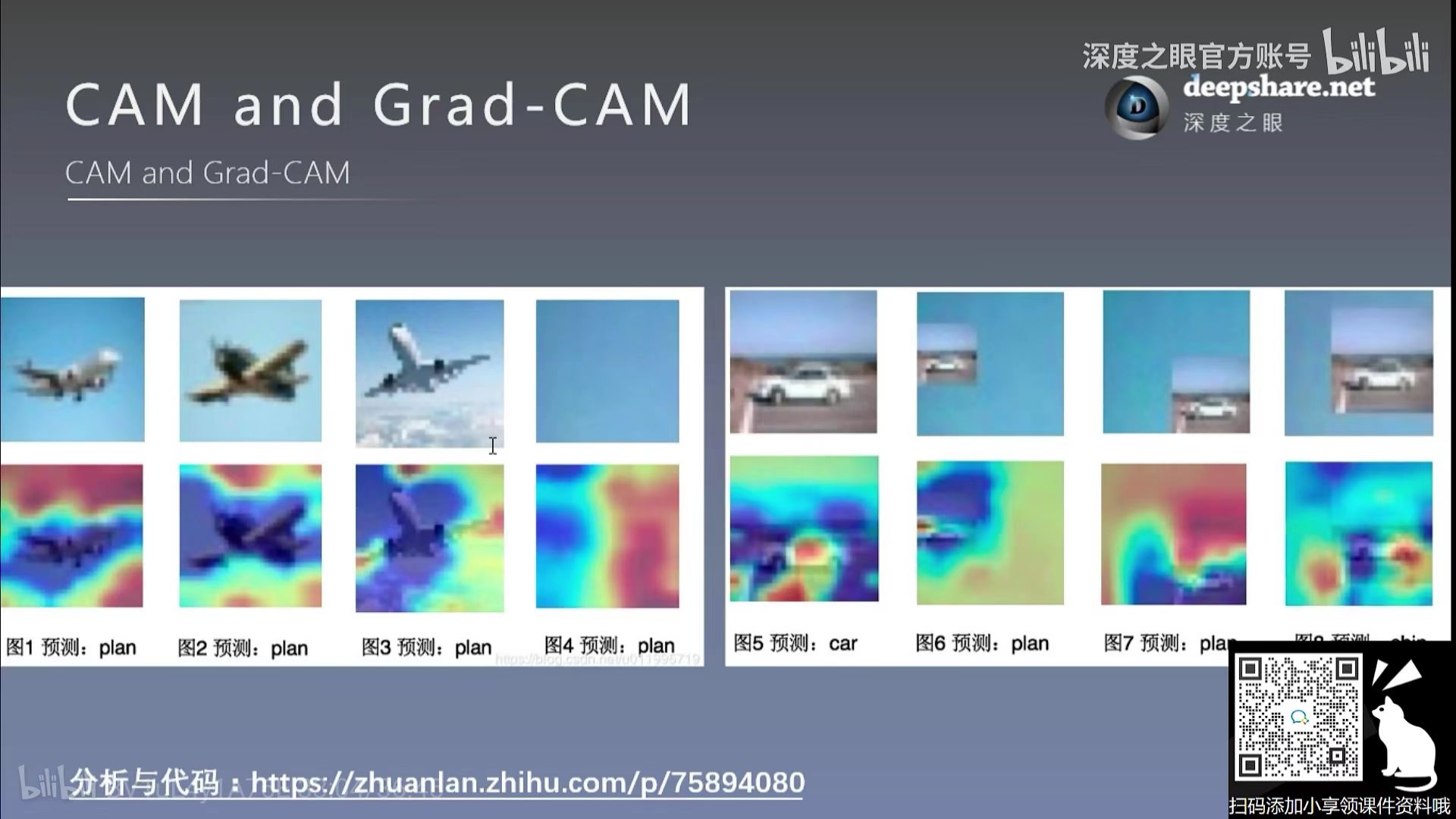
通过CAM分析,我们发现一些有意思的东西,比如 模型在识别飞机时,并没有关注 飞机本身,二是关注到了蓝天,因为飞机常常与天空是一起的
参考资料:
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/3mz7RyfBdOmY8WyZtr739w pytorch-hook注册: 生成feature map可视化热力图
https://www.jianshu.com/p/fd2f09dc3cc9 CAM系列(一)之CAM(原理讲解和PyTorch代码实现)
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/267800207 PyTorch中Hook的简单使用
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/339718510 Python函数进阶: Hook 钩子函数
https://www.jianshu.com/p/69e57e3526b3 PyTorch之HOOK——获取神经网络特征和梯度的有效工具





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 全程不用写代码,我用AI程序员写了一个飞机大战
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· MongoDB 8.0这个新功能碉堡了,比商业数据库还牛
· .NET10 - 预览版1新功能体验(一)
2022-03-25 模型加速【1】入门篇