相似变换
相似变换:等距变换+均匀尺度缩放;
等距变换:平移+旋转,所谓平移旋转其实就是 wx+b,w 和 b 组成变换矩阵
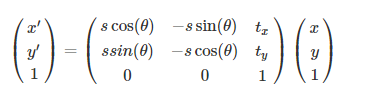
在等距变换中,角度、平行性、垂直性 不发生变换
SimilarityTransform 用法
这是一个类
class SimilarityTransform(EuclideanTransform): def __init__(self, matrix=None, scale=None, rotation=None, translation=None):
参数解释:
matrix:可选,(3,3)齐次变换矩阵,即 相似变换矩阵
Has the following form:: X = a0 * x - b0 * y + a1 = = s * x * cos(rotation) - s * y * sin(rotation) + a1 Y = b0 * x + a0 * y + b1 = = s * x * sin(rotation) + s * y * cos(rotation) + b1 where ``s`` is a scale factor and the homogeneous transformation matrix is:: [[a0 b0 a1] [b0 a0 b1] [0 0 1]]
scale:缩放因子
rotation:旋转角度,逆时针,以弧度表示角度
translation: 平移参数(tx, ty)
相关方法
def estimate(self, src, dst): """ Parameters ---------- src : (N, 2) array Source coordinates. dst : (N, 2) array Destination coordinates. Returns ------- success : bool True, if model estimation succeeds. """
从一组对应点(源点、目标点)估计变换矩阵
示例代码1
from skimage import transform as trans import numpy as np src = np.array([ [38.2946, 51.6963], [73.5318, 51.5014], [56.0252, 71.7366], [41.5493, 92.3655], [70.7299, 92.2041] ], dtype=np.float32) dst = np.array([ [38.2946, 51.6963], [73.5318, 51.5014], [56.0252, 71.7366], [41.5493, 92.3655], [70.7299, 92.2041] ], dtype=np.float32) tform = trans.SimilarityTransform() res =tform.estimate(dst, src) M = tform.params print(res) print(M)
获取变换矩阵用 params
[[ 1.00000004e+00 0.00000000e+00 -2.47753889e-06] [ 0.00000000e+00 1.00000004e+00 -3.17953211e-06] [ 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 1.00000000e+00]]
示例代码2
from skimage import io,data from skimage import transform as tf import matplotlib.pylab as plt ### 原图 img = data.camera() io.imshow(img) plt.show() ### 相似变换 tform = tf.SimilarityTransform(scale=1.5,rotation=np.deg2rad(10),translation=(10,12)) img1 = tf.warp(img,tform) io.imshow(img1) plt.show()

人脸对齐
在人脸识别时,有时候 检测到的人脸是 倾斜的,此时需要把脸扶正,这就叫人脸对齐;
人脸对齐有很多方法,相似变换只是最简单的一种;
大体思路
人脸检测时会识别到 人脸关键点,这是 相似变换的源点;
假设我们最后要截取一张(112,96)大小的正脸,那么人脸的五个关键点分别在什么位置才算是正脸呢?所以我们需要五个参考点,作为 目标点;
根据 N 组 源点、目标点得到变换矩阵;
把整张脸 乘以 变换矩阵 得到 变换后的 正脸;
import numpy as np import cv2 import matplotlib.pylab as plt from skimage import transform ################### 人脸关键点标注 ################### landmark = np.array([[153, 244, 215, 214, 292, 252, 196, 292, 346, 300]]) landmark = np.reshape(landmark, (2, 5)).T print(landmark) img = cv2.imread('wt.jpg') for point in landmark: cv2.circle(img, tuple(point), 2, (0, 0, 255)) cv2.imshow('img', img) cv2.waitKey(10000) ################### 标准脸的关键点 ################### REFERENCE_FACIAL_POINTS = np.array([ [30.29459953, 51.69630051], [65.53179932, 51.50139999], [48.02519989, 71.73660278], [33.54930115, 92.3655014], [62.72990036, 92.20410156] ], np.float32) # Lets create a empty image| empty_img = np.zeros((112,96,3), np.uint8) for point in REFERENCE_FACIAL_POINTS: cv2.circle(empty_img, tuple(point), 2, (0, 0, 255)) plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5)) plt.imshow(empty_img) plt.show() ################### 把人脸1和标准脸对齐 ################### #### 变换矩阵 trans = transform.SimilarityTransform() res = trans.estimate(landmark, REFERENCE_FACIAL_POINTS) M = trans.params print(res) # True print(M) # 变换矩阵 # [[ 0.29581306 -0.16732268 28.26420688] # [ 0.16732268 0.29581306 -47.51195016] # [ 0. 0. 1. ]] #### 人脸对齐 print(M[:2, :]) new_img = cv2.warpAffine(img, M[:2, :], dsize=(120, 120)) cv2.imshow('new_img', new_img) cv2.waitKey(1000000)


最后一张就是 对齐后 的人脸
参考资料:
https://blog.csdn.net/C_chuxin/article/details/100546657 skimage库的transform.SimilarityTransform()用法
https://www.jianshu.com/p/57c440af5760 人脸对齐
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/61343643 从零开始搭建人脸识别系统(二):人脸对齐





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人