GAN 简介
GAN,Generative Adversarial Networks,生成对抗网络;
GAN 被认为是 AI 领域 最有趣的 idea,一句话,历史地位很高,很火;
GAN 是由 Goodfellow 大神在 2014 年提出来的,当时的 G 神还只是个蒙特利尔大学的博士生;
paper:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1406.2661.pdf
GAN 原理
在 GAN 被提出后,迅速衍生了各种各样的变种,本文旨在讲述原始 GAN 的思想;
GAN 的核心就是 两大护法:G 和 D
G:generator,生成器,负责 凭空 捏造 数据
D:discriminator,判别器,负责判断数据是真是假
GAN 是一个 博弈的过程,生成器 负责 生成数据,判别器负责 识别 数据 是 真实存在的还是 生成器生成的,判别器 尽量做到 识别正确,生成器 尽量做到 让 判别器 识别不出来;
GAN 的训练过程很像我们打假的过程,刚开始,我们对某些事物不够了解,以致于别人拿很假的东西(随机生成),我们也无法辨别真假,于是我们努力提高认知,把那些很假的东西和真实的东西区分开了,但是造假者永不死心,他们提高了造假技术,于是我们又无法辨别了,只好继续提高认知,然后造假者继续提高造假技术,最终 GAN 希望达成的效果是,造假者造出来的东西,专家都无法辨别真假;
这个过程用两幅图来表示 【我找了很多图,都不是特别好,大家将就着看吧】
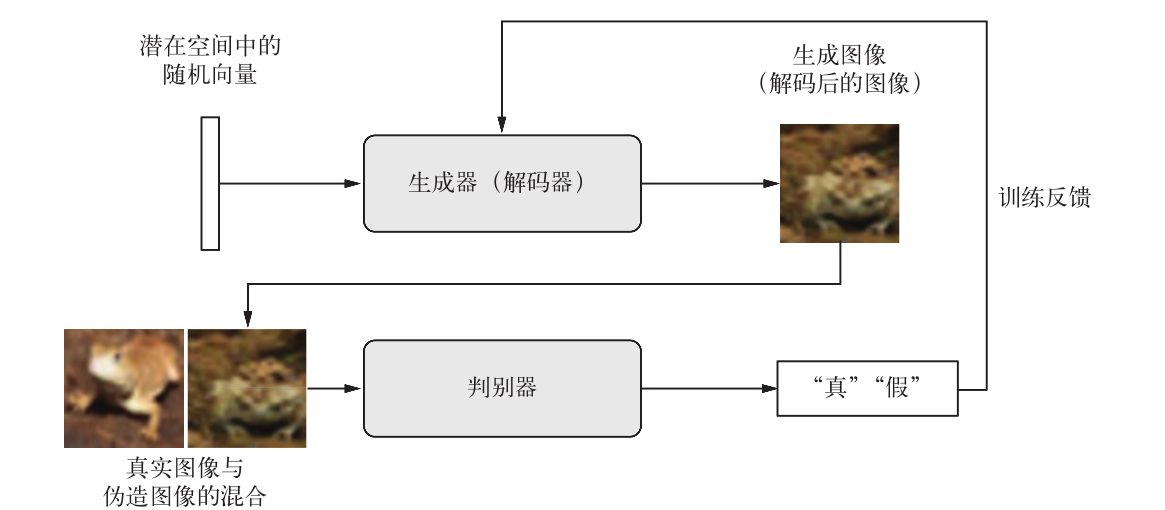
图1 很生动,形象,容易理解,但是不能够很好的反应 GAN 的网络结构,所以还需下面这张图
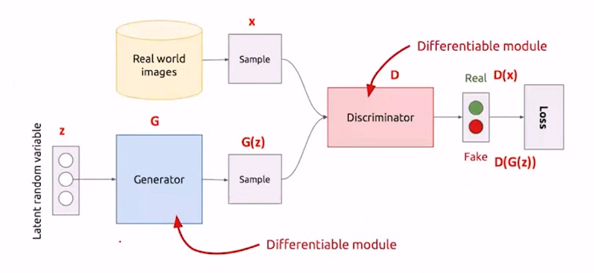
我主要是想让大家看到,生成器网络 和 判别器网络 都 有 判别器结构,这对于理解网络训练很有帮助
GAN 训练
GAN 的训练是 G 和 D 同步成长的过程,所以 G 和 D 需要交替训练;
在每一轮迭代 中,我们需要做两件事:
先训练 D,在训练 D 时,G 不动;
首先我们生成一些随机数 z;
然后 用 当前 G 把 z 解码成图片; 【最初的 G 就是瞎鸡巴解码,每轮训练后,G 的参数被更新,解码能力逐渐变强】
然后 把 真实图片 和 生成的图片 混合,真实图片 label 为 1, 生成的图片 label 为 0;
喂给 判别器,训练得到一个 二分类 的分类器;
再训练 G,在训练 G 时,D 不动;
此时我们已经拥有一个 看起来 像那么回事的 专家 D,训练 G 就是 先把这个专家给 蒙骗过去,即 让 D 对 G 生成的图片 输出 1;
首先还是生成随机数 z;
然后用 G 解码成图片;
然后 把 label 设为 1,喂给 判别器;
此时 判别器的输出 肯定不是 1,因为这个判别器我们已经训练过了,还算靠谱,对于 假的对象输出肯定 小于 1,记为 score;
然后 1-score 就是 loss,调整 G 的参数,得到一个 更好的 解码器;
下面是作者原话
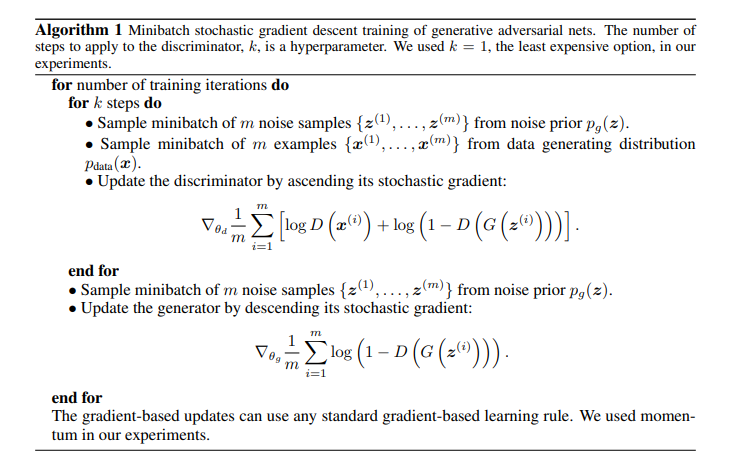
最后强调一下:GAN 是一种思路,GAN 网络不一定是 深度网络,也不只是用于 图像;
GAN 代码
说得再多,不如看代码
from __future__ import print_function, division from keras.datasets import mnist from keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout from keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, ZeroPadding2D from keras.layers.advanced_activations import LeakyReLU from keras.layers.convolutional import UpSampling2D, Conv2D from keras.models import Sequential, Model from keras.optimizers import Adam import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import sys import numpy as np class GAN(): def __init__(self): self.img_rows = 28 self.img_cols = 28 self.channels = 1 self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels) self.latent_dim = 100 optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5) # Build and compile the discriminator self.discriminator = self.build_discriminator() self.discriminator.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer=optimizer, metrics=['accuracy']) # Build the generator self.generator = self.build_generator() # The generator takes noise as input and generates imgs z = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,)) img = self.generator(z) # For the combined model we will only train the generator self.discriminator.trainable = False # The discriminator takes generated images as input and determines validity validity = self.discriminator(img) # The combined model (stacked generator and discriminator) # Trains the generator to fool the discriminator self.combined = Model(z, validity) self.combined.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer=optimizer) def build_generator(self): model = Sequential() model.add(Dense(256, input_dim=self.latent_dim)) model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)) model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)) model.add(Dense(512)) model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)) model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)) model.add(Dense(1024)) model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)) model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)) model.add(Dense(np.prod(self.img_shape), activation='tanh')) model.add(Reshape(self.img_shape)) model.summary() noise = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,)) img = model(noise) return Model(noise, img) def build_discriminator(self): model = Sequential() model.add(Flatten(input_shape=self.img_shape)) model.add(Dense(512)) model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)) model.add(Dense(256)) model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)) model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) model.summary() img = Input(shape=self.img_shape) validity = model(img) return Model(img, validity) def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50): # Load the dataset (X_train, _), (_, _) = mnist.load_data() # Rescale -1 to 1 X_train = X_train / 127.5 - 1. X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=3) # Adversarial ground truths valid = np.ones((batch_size, 1)) fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 1)) for epoch in range(epochs): # --------------------- # Train Discriminator # --------------------- # Select a random batch of images idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], batch_size) imgs = X_train[idx] noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, self.latent_dim)) # Generate a batch of new images gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(noise) # Train the discriminator d_loss_real = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(imgs, valid) d_loss_fake = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(gen_imgs, fake) d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake) # --------------------- # Train Generator # --------------------- noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, self.latent_dim)) # Train the generator (to have the discriminator label samples as valid) g_loss = self.combined.train_on_batch(noise, valid) # Plot the progress print ("%d [D loss: %f, acc.: %.2f%%] [G loss: %f]" % (epoch, d_loss[0], 100*d_loss[1], g_loss)) # If at save interval => save generated image samples if epoch % sample_interval == 0: self.sample_images(epoch) def sample_images(self, epoch): r, c = 5, 5 noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (r * c, self.latent_dim)) gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(noise) # Rescale images 0 - 1 gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5 fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c) cnt = 0 for i in range(r): for j in range(c): axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt, :,:,0], cmap='gray') axs[i,j].axis('off') cnt += 1 fig.savefig("images/%d.png" % epoch) plt.close() if __name__ == '__main__': gan = GAN() gan.train(epochs=30000, batch_size=32, sample_interval=200)
下面是生成器 生成的第一张图片和最后一张图片
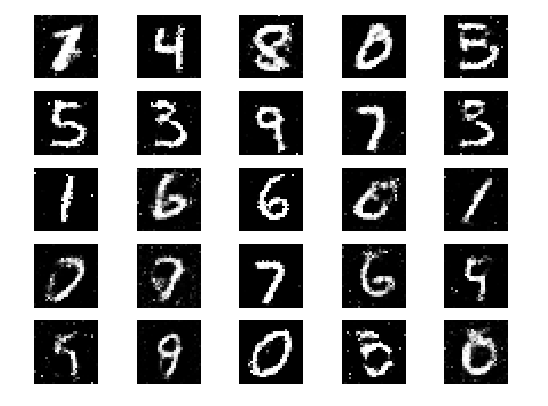
补充
GAN 的训练十分困难,有人总结了一些 trick,由于我并没有验证,仅截图做个记录

参考资料:





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
2019-04-15 数据编码
2019-04-15 缺失值处理