红黑树
1.红黑树
1.1概述【理解】
-
红黑树的特点
-
平衡二叉B树
-
每一个节点可以是红或者黑
-
红黑树不是高度平衡的,它的平衡是通过"自己的红黑规则"进行实现的
-
-
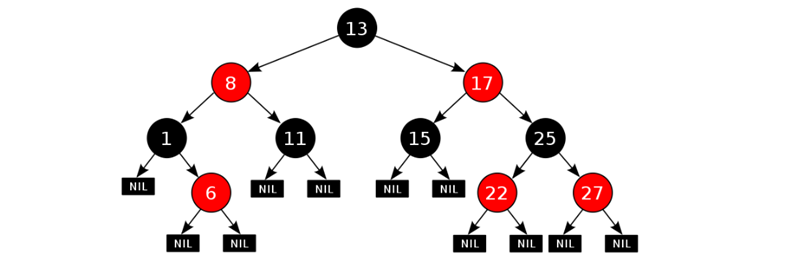
红黑树的红黑规则有哪些
-
每一个节点或是红色的,或者是黑色的
-
根节点必须是黑色
-
如果一个节点没有子节点或者父节点,则该节点相应的指针属性值为Nil,这些Nil视为叶节点,每个叶节点(Nil)是黑色的
-
如果某一个节点是红色,那么它的子节点必须是黑色(不能出现两个红色节点相连 的情况)
-
对每一个节点,从该节点到其所有后代叶节点的简单路径上,均包含相同数目的黑色节点
-
-
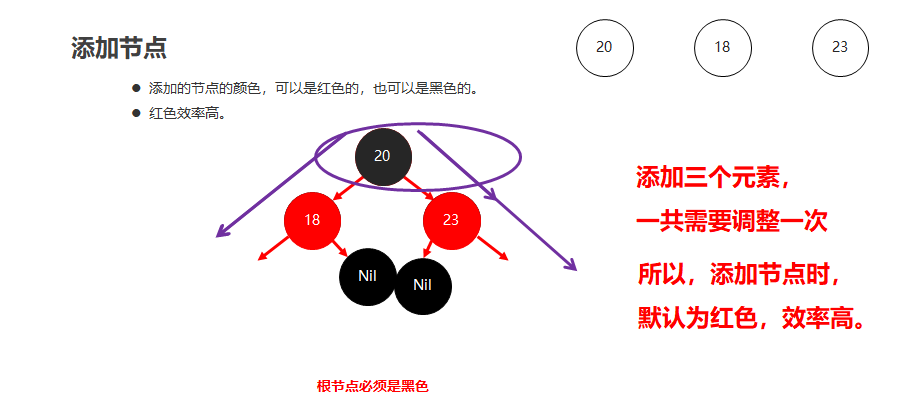
红黑树添加节点的默认颜色
-
添加节点时,默认为红色,效率高
-
-
红黑树添加节点后如何保持红黑规则
-
根节点位置
-
直接变为黑色
-
-
非根节点位置
-
父节点为黑色
-
不需要任何操作,默认红色即可
-
-
父节点为红色
-
叔叔节点为红色
-
将"父节点"设为黑色,将"叔叔节点"设为黑色
-
将"祖父节点"设为红色
-
如果"祖父节点"为根节点,则将根节点再次变成黑色
-
-
叔叔节点为黑色
-
将"父节点"设为黑色
-
将"祖父节点"设为红色
-
以"祖父节点"为支点进行旋转
-
-
-
-
1.2成绩排序案例【应用】
-
案例需求
-
用TreeSet集合存储多个学生信息(姓名,语文成绩,数学成绩,英语成绩),并遍历该集合
-
要求: 按照总分从高到低出现
-
-
代码实现
学生类
public class Student implements Comparable<Student> { private String name; private int chinese; private int math; private int english; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int chinese, int math, int english) { this.name = name; this.chinese = chinese; this.math = math; this.english = english; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getChinese() { return chinese; } public void setChinese(int chinese) { this.chinese = chinese; } public int getMath() { return math; } public void setMath(int math) { this.math = math; } public int getEnglish() { return english; } public void setEnglish(int english) { this.english = english; } public int getSum() { return this.chinese + this.math + this.english; } @Override public int compareTo(Student o) { // 主要条件: 按照总分进行排序 int result = o.getSum() - this.getSum(); // 次要条件: 如果总分一样,就按照语文成绩排序 result = result == 0 ? o.getChinese() - this.getChinese() : result; // 如果语文成绩也一样,就按照数学成绩排序 result = result == 0 ? o.getMath() - this.getMath() : result; // 如果总分一样,各科成绩也都一样,就按照姓名排序 result = result == 0 ? o.getName().compareTo(this.getName()) : result; return result; } }
测试类
public class TreeSetDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建TreeSet集合对象,通过比较器排序进行排序 TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<Student>(); //创建学生对象 Student s1 = new Student("jack", 98, 100, 95); Student s2 = new Student("rose", 95, 95, 95); Student s3 = new Student("sam", 100, 93, 98); //把学生对象添加到集合 ts.add(s1); ts.add(s2); ts.add(s3); //遍历集合 for (Student s : ts) { System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getChinese() + "," + s.getMath() + "," + s.getEnglish() + "," + s.getSum()); } } }
资源来源 : 黑马程序员
