Robot Framework - 常用断言讲解
RobotFramework带有丰富的系统关键,使用时无需导入,直接使用,为写自动化用例带来了极大的方便;不能停留在知道或者是会得程度,只有熟练使用各关键字,才能提升自动化用例的写作效率。
下面将逐个举例介绍:为方便讲解,首先创建三个list变量:list_a、list_b、list_c;以及两个scalar变量:string和name。
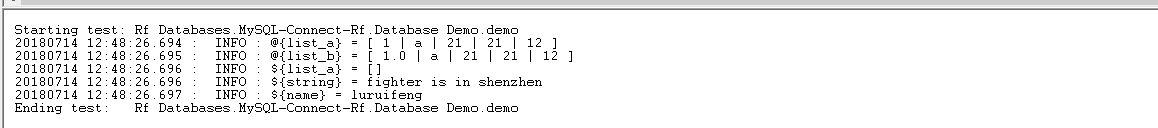
@{list_a} create list 1 a ${21} 21 12
@{list_b} set variable 1.0 a ${21} 21 21
@{list_c} create list
${string} set variable fighter is in shenzhen
${name} set variable luruifeng

备注:以下提供的用例都是断言成功。
01、should contain 、 should not contain 与should contain x times
should contain ${list_b} 1.0
should not contain ${list_b} 1
should contain x times ${list_b} 21 2
说明:变量${list_b}包含对象1.0而不包含对象1,且对象21在变量${list_b}出现了两次。
02、should be empty 与 should not be empty
should be empty ${list_c}
should not be empty ${list_a}
说明:变量${list_c}没有赋值,所以为空;相反,变量${list_a}有赋初始值,故为非空。
03、should be equal 与 should not be equal
should be equal ${list_a[1]} ${list_b[1]}
should not be equal ${list_a} ${list_b}
说明:${list_a[1]}=a,${list_b[1]}=a故两个对象相等;而${list_a}和${list_b}有元素不一致,这两个对象不相等。
04、Should Be Equal As Numbers 与 Should not Be Equal As Numbers
Should Be Equal As Numbers ${list_b[0]} 1.0000
Should not Be Equal As Numbers ${list_b[0]} 1.1
说明:${list_b[0]}=1,忽略精度,故与1.0000相等;而即使是忽略精度,1与1.1还是不相等的;
05、Should Be Equal As Integers与Should not Be Equal As Integers
Should Be Equal As Integers ${list_a[3]} ${list_b[3]}
Should not Be Equal As Integers ${list_a[4]} ${list_b[4]}
说明:${list_a[3]}=21,${list_b[3]}=21,而系统默认为字符串格式的“21”,故需要转化为整数类型,转化为整数后两个对象相等;
${list_a[4]}=12,${list_b[4]}=21,即使转化为整数后两个对象依旧是不相等;
06、Should Be Equal As Strings与Should not Be Equal As Strings
Should Be Equal As Strings ${list_a[2]} ${list_b[2]}
Should not Be Equal As Strings ${list_a[0]} ${list_b[0]}
说明:${list_a[2]}=${21},${list_b[2]}=${21},而均为数值型的21,故需要转化为字符串类型,转化为字符串后两个对象相等;

