spring MVC
HandlerMapping和HandlerAdapter
请求过来的时候首先通过HandlerMapping可以找到处理该请求的具体类 、具体方法。
这个映射关系可以简单理解成:http:xxx.xx.com/xxxHandler/xxMethod -- xxxHandler/xxMethod。
这里的映射只是一个关系映射,真正执行xxMethod时还要通过httpRequest中提取各种参数、解析等等很多逻辑,然后通过反射执行。
而Handler又有好多种类,比如Servlet和Controller他们都是handler,但是他们对于请求的处理各不相同,所以他们有各自对请求处理的代码。
所以执行解析参数的时候到底是用谁的代码解析?基于以上几点就需要适配器的登场。
HandlerMapping和HandlerAdapter是成对出现的,不同类型的HandlerMapping封装的Handler对象是不一样的,而不同类型的HandlerAdapter支持的Handler也不一样。
适配器的作用就是根据不同类型的HandlerMapping -- Handler对象 -- 具体哪种Handler。
HandlerMapping有三种实现:BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping、SimpleUrlHandlerMapping、RequestMappingHandlerMapping
HandlerAdapter有五种实现:HttpRequestHandlerAdapter、SimpleServletHandlerAdapter、SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter、AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter、RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping
看名字应该可以猜出来它是通过 bean 的 name 来确定请求所对应的处理器。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<!-- 配置处理器映射器 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping"></bean>
<!-- 配置处理器适配器 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter"></bean>
<!-- 配置视图解析器 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"></bean>
<!-- 注册我们实现的Controller -->
<bean name="/login.do" class="com.lyu.qjl.interview.controller.LoginController"></bean>
</beans>
SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter
如果使用这种处理器适配器来调用 Handler 的话,对应的 Handler 要求必须实现 Controller 接口,重写 handlerRequest 方法,并在配置文件中注册。
/**
* 类名称:用于处理登录请求的处理器
* 全限定性类名: com.lyu.qjl.interview.controller.LoginController
*/
public class LoginController implements Controller {
@Override
public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
if (username != null && password != null) {
if ("admin".equals(username) && "123".equals(password)) {
modelAndView.addObject("loginFlag", "登录成功");
modelAndView.setViewName("/main.jsp");
} else {
modelAndView.addObject("loginFlag", "用户名或密码错误");
modelAndView.setViewName("/login.jsp");
}
} else {
// 只是把模型放到request域里面,并没有真正的安排好
modelAndView.addObject("loginFlag", "用户名或密码错误");
modelAndView.setViewName("/login.jsp");
}
return modelAndView;
}
}
SimpleUrlHandlerMapping
这种映射器的一个特点是可以把请求以及所对应的处理器之间的映射关系放到一个 HashMap 中,统一进行管理。在映射器的 bean 标签内部定义 property 标签,其 name 属性值为 mappings,在 property 标签内部定义 props 标签,在 props 标签内部就可以定义 prop 标签用来存储对应的请求以及对应的在配置文件中注册的 handler 的 id 了。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<!-- 注册另一种映射器(面试表) -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping">
<property name="mappings">
<props>
<!-- key的值请求的名称,标签体内为对应的handler的id,可配置多个 -->
<prop key="/getUserList.do">userController</prop>
<prop key="/xxx.do">xxxController</prop>
<prop key="/yyy.do">yyyController</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 另一种HandlerAdapter(通知面试官来面试的小哥哥) -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter"></bean>
<!-- 配置视图解析器(面试评估人员) -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"></bean>
<!-- 注册handler(面试官) -->
<bean id="userController" class="com.lyu.qjl.interview.controller.UserController"></bean>
</beans>
HttpRequestHandlerAdapter
使用这种处理器适配器来调用 Handler 的话,对应的 Handler 要求必须实现 HttpRequestHandler 接口,重写 handlerRequest 方法,并在配置文件中注册。
public class UserController implements HttpRequestHandler {
@Override
public void handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("进入UserController");
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<User>();
User user1 = new User("arry", 18, "男");
User user2 = new User("cc", 28, "女");
User user3 = new User("dd", 38, "男");
userList.add(user1);
userList.add(user2);
userList.add(user3);
request.setAttribute("userList", userList);
request.getRequestDispatcher("/userList.jsp").forward(request, response);
}
}
RequestMappingHandlerMapping 与 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
前面的HandlerMapping与HandlerAdapter都是随意搭配的。而这两个必须成对出现,而且这两个使用也是最广泛的。
RequestMappingHandlerMapping:使用这种处理器映射器的话,只需要在编写的处理器的方法上加上 @RequestMapping("/xxx.do") 注解就可以完成请求到处理请求的方法上的映射,而且使用这种方式的话是一个方法对应一个请求,相比于上面两种映射器,高效许多。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<!-- 配置注解方式的处理器映射器 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping"></bean>
<!-- 配置注解方式的处理器适配器 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter"></bean>
<!-- 配置视图解析器 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"></bean>
</beans>
也可以在配置文件中用一个 <mvc:annotation-driven />来替代,配置文件就可以简化成下面这样:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<!-- 开启spring的组件扫描,自动扫描包,加载bean -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.lyu.qjl.interview.controller" />
<!-- 可以用mvc的注解驱动来代替 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 和 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter -->
<mvc:annotation-driven />
<!-- 配置视图解析器 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"></bean>
</beans>
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter:对应的 handler 只需要使用注解来标示即可,并且在配置文件中要开启注解扫描,便于 Spring 在初始化的时候就加载并实例化对应的 Handler。
handle方法继承于其父类AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter,自己没有重写。
@Controller
public class AnnoLoginController {
@RequestMapping("/loginAnno")
public ModelAndView login(String username, String password) {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
if (username != null && password != null) {
if ("admin".equals(username) && "123".equals(password)) {
modelAndView.addObject("loginFlag", "登录成功");
modelAndView.setViewName("main");
} else {
modelAndView.addObject("loginFlag", "用户名或密码错误");
modelAndView.setViewName("loginAnno");
}
} else {
// 只是把模型放到request域里面,并没有真正的安排好
modelAndView.addObject("loginFlag", "用户名或密码错误");
modelAndView.setViewName("loginAnno");
}
return modelAndView;
}
}
上下文
- 有三种上下文:
- web上下文(Servlet context):全局性
- spring上下文(WebApplication Context):spring ioc容器
- springmvc上下文(mlWebApplicationCont):servlet子上下文
- tomcat启动的时候,tomcat首先会初始化一个ServletContext,用来存放全局性上下文。
- 然后tomcat调用web.xml中配置的ContextLoaderListener来初始化webapplicationContext,初始化完毕后还要将webapplicationContext以key value形势保存在ServletContext中一份
- 接下来初始化web.xml中的servlet,初始化其自己的上下文-springmvc上下文,并且将webapplicationContext设置为其父类。

ServletContextListener
ServletContextListener:监听器,tomcat启动时会执行到该监听器的初始化方法。负责创建spring上下文。实现类是ContextLoaderListener。
public interface ServletContextListener extends EventListener {
void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent var1);
void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent var1);
}
MappingRegistry
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的内部类,即也是HandlerMapping的子类。用来存储映射关系。即HandlerMapping中可以通过它来获取映射关系。
class MappingRegistry {
//存储了所有的映射关系
private final Map<T, AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.MappingRegistration<T>> registry = new HashMap();
//url->mapping的映射
private final MultiValueMap<String, T> urlLookup = new LinkedMultiValueMap();
//mapping->HandlerMethod的映射
private final Map<T, HandlerMethod> mappingLookup = new LinkedHashMap();
private final Map<String, List<HandlerMethod>> nameLookup = new ConcurrentHashMap();
private final Map<HandlerMethod, CorsConfiguration> corsLookup = new ConcurrentHashMap();
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
HandlerExecutionChain
HandlerExecutionChain:controller中每个requestMapping方法对应一个HandlerExecutionChain
//HandlerExecutionChain
public class HandlerExecutionChain {
//实际处理该请求的对象(相当于controller方法)
private final Object handler;
//拦截器列表
private HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors;
private List<HandlerInterceptor> interceptorList;
public HandlerExecutionChain(Object handler) {
this(handler, null);
}
public HandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors) {
if (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain) {
HandlerExecutionChain originalChain = (HandlerExecutionChain) handler;
this.handler = originalChain.getHandler();
this.interceptorList = new ArrayList<HandlerInterceptor>();
CollectionUtils.mergeArrayIntoCollection(originalChain.getInterceptors(), this.interceptorList);
CollectionUtils.mergeArrayIntoCollection(interceptors, this.interceptorList);
}
else {
this.handler = handler;
this.interceptors = interceptors;
}
}
public Object getHandler() {
return this.handler;
}
public void addInterceptor(HandlerInterceptor interceptor) {
initInterceptorList();
this.interceptorList.add(interceptor);
}
public void addInterceptors(HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors) {
if (interceptors != null) {
initInterceptorList();
this.interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
private void initInterceptorList() {
if (this.interceptorList == null) {
this.interceptorList = new ArrayList<HandlerInterceptor>();
}
if (this.interceptors != null) {
this.interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(this.interceptors));
this.interceptors = null;
}
}
public HandlerInterceptor[] getInterceptors() {
if (this.interceptors == null && this.interceptorList != null) {
this.interceptors = this.interceptorList.toArray(new HandlerInterceptor[this.interceptorList.size()]);
}
return this.interceptors;
}
}
HandlerInterceptor:
1、前置处理preHandle,返回值为boolean。如果返回true,则执行下一个,如果返回false,则认为当前拦截器完成了请求,DispatcherServlet会直接返回,在返回前会调用所有拦截器的afterCompletion方法,完成清理工作。
2、afterCompletion方法在遇到任何情况时都需要被执行,无论是成功返回还是抛出异常。
3、可以理解成aop的通知,在目标方法执行前后执行相应的拦截器
public interface HandlerInterceptor {
// 在Handler找到后,执行前拦截
boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception;
// 在Handler执行后,视图渲染前拦截
void postHandle(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView)
throws Exception;
// 请求处理完成,视图渲染后执行资源清理等
void afterCompletion(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex)
throws Exception;
}
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!--suppress ALL -->
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"
version="3.1">
<!-- 声明spring上下文配置文件所在位置,可以使用通配符*等进行模糊匹配,
当有多个配置文件时,可以使用逗号间隔 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springConfig/applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!-- 配置上下文载入监听器,它会在web服务启动时,
根据contextConfigLocation中声明的spring配置文件位置载入配置信息 , -->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<filter>
<filter-name>Set Character Encoding</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>forceEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>Set Character Encoding</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<!-- spring MVC配置文件路径 -->
<param-value>classpath:springConfig/dispatcher-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<!-- 设置当前servlet在所有servlet中第一个启动 -->
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
</web-app>
上面的web.xml配置了两个容器,首先在web启动的时候,监听器ContextLoaderListener会根据
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springConfig/applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
这个文件加载一个父容器。
DispatcherServlet也会加载一个子容器。
父级容器的内容在子容器可见,子容器的内容在父容器不可见。
如果子容器配置了和父容器相同的内容,可能存在一个配置覆盖的问题。
一个web.xml可以根据我们的项目需求配置多个DispatcherServlet,通过对应的实现对不同逻辑的请求拦截。
父子容器分别加载不同的配置文件,互相隔离,一般子容器用来加载业务相关的bean,剩下的由父容器处理。
spring mvc配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.0.xsd
">
<!-- 扫描com.mvc.controller包下所有的类,使spring注解生效 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.mvc.controller"/>
<!-- 定义视图解析器 -->
<bean id="viewResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/views/"></property><!-- 前缀,在springMVC控制层处理好的请求后,转发配置目录下的视图文件 -->
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property><!-- 文件后缀,表示转发到的视图文件后缀为.jsp -->
</bean>
</beans>
控制器 Controller
@Controller//注解为控制器,通过spring容器扫描,会注册为一个Bean
@RequestMapping("/user")//一级访问路径,对类中所有方法生效
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")//二级访问路径
public String hello(){
//返回视图文件名,和servlet-context.xml,会将请求转发到/WEB-INF/views/hello.jsp文件中
return "hello";。
}
}
spring上下文初始化
web启动时,ContextLoaderListener的contextInitialized方法负责创建。
// ContextLoaderListener
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
// ContextLoader
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
} else {
if (this.context == null) {
//创建spring上下文
//private WebApplicationContext context;
//入口
this.context = this.createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
ApplicationContext parent = this.loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
// 加载并刷新上下文环境,也就是初始化Spring容器
// 绑定ServletContext到Spring根上下文
//入口2
this.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
// 将创建完的根上下文绑定到ServletContext
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
} else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
return this.context;
}
}
//ContextLoader
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
//获取class对象
Class<?> contextClass = this.determineContextClass(sc);//入口
//通过反射实例化对象
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter("contextClass");
if (contextClassName != null) {//可以在web.xml中配置contextClass
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var4) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", var4);
}
} else {
/***
* 没有配置的话取默认值XmlWebApplicationContext。
* 默认值在配置文件ContextLoader.properties中配置的。
* private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "ContextLoader.properties";
* private static final Properties defaultStrategies;
* org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext=org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
*/
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var5) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", var5);
}
}
}
// ContextLoader
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
String configLocationParam;
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter("contextId");
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setId(configLocationParam);
} else {
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX + ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
wac.setServletContext(sc);
//从配置文件中获取全局init参数“contextConfigLocation”,也就是spring.xml,并设置到父容器中
configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter("contextConfigLocation");
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment)env).initPropertySources(sc, (ServletConfig)null);
}
this.customizeContext(sc, wac);
//刷新父容器 ,就是spring ioc初始化的refresh方法
wac.refresh();
}
- 从web.xml中的context-param中找到contextClass属性,按照该配置通过反射创建spring上下文,如果没配置默认是XmlWebApplicationContext
- 通过spring ioc的refresh方法初始化spring容器
- 将spring上下文和全局上下文进行双向绑定
springMVC上下文初始化

DispatchServerlet默认是单例的,如果配置了load-on-startup参数,则在spring上下文初始化之后进行初始化。
否则当请求第一次过来的时候进行初始化。初始化就是执行其init方法。
它的作用是对后续所有请求进行转发,后续请求过来首先会进入其service方法。
public interface Servlet {
//负责初始化servlet
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException;
//执行客户端请求
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException;
public void destroy();
}
//HttpServletBean
public final void init() throws ServletException {
PropertyValues pvs = new HttpServletBean.ServletConfigPropertyValues(this.getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(this.getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, this.getEnvironment()));
this.initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
this.initServletBean();//入口
}
//FrameworkServlet
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
// 创建servlet子上下文 和创建根上下文挺相似
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();//入口
initFrameworkServlet();
}
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
// 从ServletContext获取SpringMVC根上下文
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {//正常应该进入这里
// 创建一个新的上下文对象并刷新
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);//入口
}
// DispatcherServlet中实现的,初始化各种组件,后面详细解析该方法
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
// 发布servlet子上下文到ServletContext
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +
"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) {
Class<?> contextClass = this.getContextClass();
//反射创建实例
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
wac.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
//设置父容器
wac.setParent(parent);
//设置容器启动XML:例如init-param的contextConfigLocation classpath*:spring-mvc.xml
wac.setConfigLocation(this.getContextConfigLocation());
//初始化新创建的子容器
this.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);//入口
return wac;
}
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
} else {
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX + ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(this.getServletContext().getContextPath()) + '/' + this.getServletName());
}
}
//将ServletContext和ServletConfig都绑定到servlet子上下文对象中
wac.setServletContext(this.getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(this.getServletConfig());
wac.setNamespace(this.getNamespace());
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new FrameworkServlet.ContextRefreshListener(null)));
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment)env).initPropertySources(this.getServletContext(), this.getServletConfig());
}
this.postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
this.applyInitializers(wac);
//最后初始化子容器,和上面根容器初始化一样
wac.refresh();
}
// DispatcherServlet
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
this.initStrategies(context);
}
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
// 文件上传解析器
initMultipartResolver(context);
// 本地化解析器
initLocaleResolver(context);
// 主题解析器
initThemeResolver(context);
// 处理器映射器(url和Controller方法的映射)
initHandlerMappings(context);
// 处理器适配器(实际执行Controller方法)
initHandlerAdapters(context);
// 处理器异常解析器
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
// RequestToViewName解析器
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
// 视图解析器(视图的匹配和渲染)
initViewResolvers(context);
// FlashMap管理者
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
- 通过反射创建springMVC上下文,并且设置和spring上下文的父子关系
- 根据springMVC配置文件对springMVC上下文进行初始化classpath*:spring-mvc.xml)
- 将springMVC上下文和全局上下文双向绑定
- 进行各个组件初始化
- initMultipartResolver
- initLocaleResolver
- initThemeResolver
- initHandlerMappings
- initHandlerAdapters
- initHandlerExceptionResolvers
- initRequestToViewNameTranslator
- initViewResolvers
- initFlashMapManager
HandlerMapping初始化
// DispatcherServlet
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
// 是否查找所有HandlerMapping标识
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) { //正常会进入这里
// 从上下文(包含所有父上下文)中查找HandlerMapping类型的Bean,是下文中的RequestMappingHandlerMapping,其中包含URL和Mapping的映射Map
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
//将从容器中查找出来的HandlerMapping加入到DispatcherServlet的handlerMappings属性中
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<HandlerMapping>(matchingBeans.values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {//根据指定名称查找
try {
// 根据指定名称获取HandlerMapping对象
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
/***
* 确保至少有一个HandlerMapping,如果没能找到
* 注册一个默认的,在spring jar包的配置配置文件中配置了默认值
* 所有的组件都以这种机制提供了默认实现
*/
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No HandlerMappings found in servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default");
}
}
}
- 从所有上下文中查找HandlerMapping类型的bean,如果找到了就将其封装到DispatcherServlet的handlerMappings属性上.
private List<HandlerMapping> handlerMappings;
上面从上下文中查找HandlerMapping类型的bean。但是spring容器中的HandlerMapping类型的bean是何时初始化进去的呢?
是在spring ioc初始化过程中。
<mvc:annotation-driven /> -- MvcNamespaceHandler -- AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser.parse。
parse方法中声明了RequestMappingHandlerMapping为HandlerMapping的实现类,并且初始化到spring容器中。
同时RequestMappingHandlerMapping实现了InitializingBean,所以在其实例化的时候还会调用它的afterPropertiesSet方法。在此方法中完成了Controller方法同请求url的映射表。
这系列代码略过,我们只要知道在springIOC初始化过程中,遇到 <mvc:annotation-driven /> 标签,就会执行下列方法来生成HandlerMapping到spring容器
//AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
// 默认只从当前上下文中查询所有beanName
String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ?
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(getApplicationContext(), Object.class) :
getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
beanType = getApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
}
// 如果类上有@Controller或@RequestMapping注解,则进行解析
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {//入口1
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);//入口2
}
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
//通过反射工具类判断类上是否有 Controller.class 或者 RequestMapping.class 注解
return AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) ||
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class);
}
//AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
protected void detectHandlerMethods(final Object handler) {
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
getApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
final Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
// 方法内省器,用于发现@RequestMapping注解的方法
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
new MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>() {
@Override
public T inspect(Method method) {
try {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
}
});
// 遍历所有有效方法,封装方法为可执行的Method,注册到URL-Controller方法映射表
for (Map.Entry<Method, T> entry : methods.entrySet()) {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(entry.getKey(), userType);
T mapping = entry.getValue();
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);//入口2
}
}
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {
this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method);
}
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
// 加锁,保证一致性
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
assertUniqueMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Mapped \"" + mapping + "\" onto " + handlerMethod);
}
// 添加mapping->HandlerMethod的映射
this.mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod);
List<String> directUrls = getDirectUrls(mapping);
for (String url : directUrls) {
// 添加url->mapping的映射
this.urlLookup.add(url, mapping);
}
String name = null;
if (getNamingStrategy() != null) {
name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping);
addMappingName(name, handlerMethod);
}
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);
if (corsConfig != null) {
this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig);
}
// 添加mapping->MappingRegistration的映射
this.registry.put(mapping, new MappingRegistration<T>(mapping, handlerMethod, directUrls, name));
}
finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
- 首先找到所有的bean,循环过滤留下类上有RequestMapping或者Controller注解的bean,所有bean进行遍历
- 添加映射关系:url->HandlerMapping , HandlerMapping->HandlerMethod。最后注册到MappingRegistry中。
doDispatch
请求发送到服务端,经过服务端处理,最终返回给客户端,springMVC如何控制这套流程。
整个流程可以被大致描述为:一个http请求到达服务器,被DispatcherServlet接收。DispatcherServlet将请求委派给合适的处理器Controller,此时处理控制权到达Controller对象。Controller内部完成请求的数据模型的创建和业务逻辑的处理,然后再将填充了数据后的模型即model和控制权一并交还给DispatcherServlet,委派DispatcherServlet来渲染响应。DispatcherServlet再将这些数据和适当的数据模版视图结合,向Response输出响应。
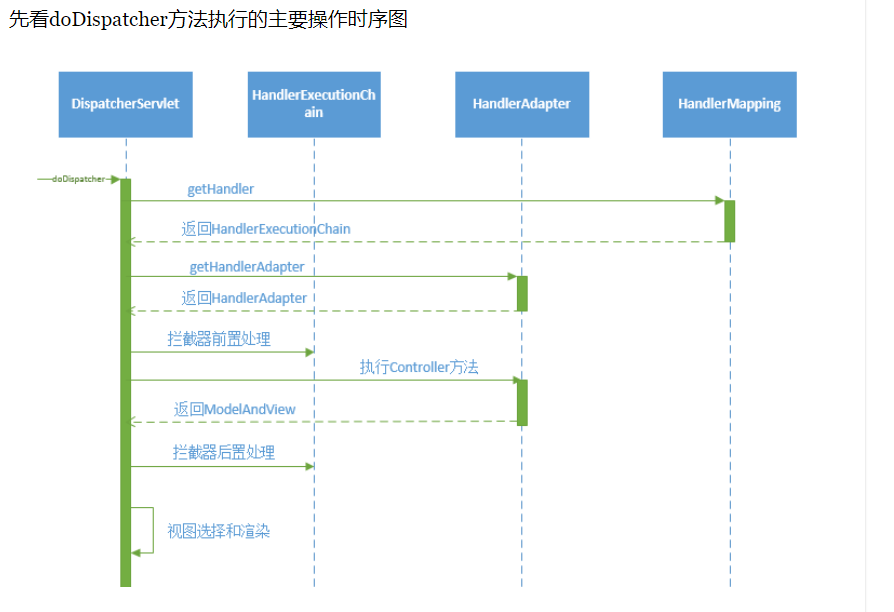
请求首先到达的是HttpServlet的service方法,然后经过几个转发最终到达我们开始关注的方法doDispatch
// DispatcherServlet
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 决定当前请求的Handler
//入口1
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// 决定当前请求的HandlerAdapter
//入口2
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// 拦截器的前置处理
//入口3
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Handler实际执行请求
//入口4
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
// 设置默认视图名
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
// 拦截器后置处理
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
// 选择视图并渲染视图
//入口5
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
}
该方法定义了整个请求流程:
- 获取handler(即handlerMethod,目标方法)
- 获取HandlerAdapter
- 拦截器的前置处理
- Handler实际执行请求
- 选择视图并渲染视图
获取handler
//DispatcherServlet
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);//入口
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
return null;
}
//AbstractHandlerMapping
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 由子类根据request获取Handler
//通过请求url,从registMapping的两个映射map中获取handlerMethod
//入口
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// 如果返回的Handler为String,则使用Spring容器实例化
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
// 查询匹配的拦截器,组装Handler生成HandlerExecutionChain
//入口
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.corsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(request);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 从request获取匹配url
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking up handler method for path " + lookupPath);
}
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
// 查询匹配的HandlerMethod
//通过mappingRegistry的两个映射map定位到handlerMethod
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
//通过构造函数直接构造HandlerExecutionChain对象,也就是handlerMethod可以直接转换成HandlerExecutionChain
HandlerExecutionChain chain = handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ? (HandlerExecutionChain)handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler);
String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request);
Iterator var5 = this.adaptedInterceptors.iterator();
//给HandlerExecutionChain添加拦截器
while(var5.hasNext()) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = (HandlerInterceptor)var5.next();
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor)interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
} else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return chain;
}
- 通过请求url从mappingRegistry中最终获取到了handlerMethod,handlerMethod即目标方法
- 将Handler转换成HandlerExecutionChain,HandlerExecutionChain持有目标发放所有属性,并且还有连接器链表
获取HandlerAdapter
这里是通过 <mvc:annotation-driven />开启的springMVC,所以使用的是默认的RequestMappingHandlerMapping 与 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter。
我们使用的RequestMappingHandlerMapping生成的对象是HandlerMethod对象,该对象能匹配到RequestMappingHandlerAdapter。
//DispatcherServlet
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
for (HandlerAdapter ha : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (ha.supports(handler)) {
return ha;
}
}
}
public final boolean supports(Object handler) {
return (handler instanceof HandlerMethod && supportsInternal((HandlerMethod) handler));
}
拦截器的前置处理
遍历执行所有拦截器的preHandle方法
boolean applyPreHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = this.getInterceptors();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) {
for(int i = 0; i < interceptors.length; this.interceptorIndex = i++) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
//遍历执行所有拦截器的preHandle方法
if (!interceptor.preHandle(request, response, this.handler)) {
this.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, (Exception)null);
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
Handler实际执行请求
handle方法实现在RequestMappingHandlerAdapter的父类AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter中
//AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter
public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
return this.handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod)handler);
}
//RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
this.checkRequest(request);
ModelAndView mav;
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized(mutex) {
mav = this.invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
} else {
mav = this.invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
} else {
mav = this.invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);//入口
}
if (!response.containsHeader("Cache-Control")) {
if (this.getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {
this.applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers);
} else {
this.prepareResponse(response);
}
}
return mav;
}
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
try {
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);
ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
// 封装HandlerMethod
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory);
invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request));
modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod);
mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect);
AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response);
asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor);
asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors);
asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors);
if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) {
Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult();
mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer) asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0];
asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Found concurrent result value [" + result + "]");
}
invocableMethod = invocableMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result);
}
// 执行处理
//入口
invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return null;
}
// 封装数据和视图
return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);
}
finally {
webRequest.requestCompleted();
}
}
public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
// 执行request
//入口
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
setResponseStatus(webRequest);
if (returnValue == null) {
if (isRequestNotModified(webRequest) || getResponseStatus() != null || mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
}
else if (StringUtils.hasText(getResponseStatusReason())) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false);
try {
// 对返回值进行处理
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(
returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(getReturnValueHandlingErrorMessage("Error handling return value", returnValue), ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
// 解析方法参数
Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);
Object returnValue = doInvoke(args);
return returnValue;
}
protected Object doInvoke(Object... args) throws Exception {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(getBridgedMethod());
return getBridgedMethod().invoke(getBean(), args);
}
- 最终通过反射执行目标方法
选择视图并渲染视图
当请求完成后,返回的ModelAndView需要渲染到浏览器进行显示。doDispatcher方法中processDispatchResult用来处理视图。
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, ModelAndView mv, Exception exception) throws Exception {
boolean errorView = false;
// 异常处理
if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
}
else {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
}
// Did the handler return a view to render?
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
// 渲染执行
//入口
render(mv, request, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Null ModelAndView returned to DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': assuming HandlerAdapter completed request handling");
}
}
if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Concurrent handling started during a forward
return;
}
// 完成后执行拦截器的afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
}
}
public void render(Map<String, ?> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Rendering view with name '" + this.beanName + "' with model " + model +
" and static attributes " + this.staticAttributes);
}
// 组装数据
//入口
Map<String, Object> mergedModel = createMergedOutputModel(model, request, response);
prepareResponse(request, response);
// 渲染输出
renderMergedOutputModel(mergedModel, getRequestToExpose(request), response);
}
以通用的InternalResourceView举例
protected void renderMergedOutputModel(
Map<String, Object> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// Expose the model object as request attributes.
exposeModelAsRequestAttributes(model, request);
// Expose helpers as request attributes, if any.
exposeHelpers(request);
// Determine the path for the request dispatcher.
String dispatcherPath = prepareForRendering(request, response);
// Obtain a RequestDispatcher for the target resource (typically a JSP).
RequestDispatcher rd = getRequestDispatcher(request, dispatcherPath);
if (rd == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not get RequestDispatcher for [" + getUrl() +
"]: Check that the corresponding file exists within your web application archive!");
}
// If already included or response already committed, perform include, else forward.
if (useInclude(request, response)) {
response.setContentType(getContentType());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Including resource [" + getUrl() + "] in InternalResourceView '" + getBeanName() + "'");
}
rd.include(request, response);
}
else {
// Note: The forwarded resource is supposed to determine the content type itself.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Forwarding to resource [" + getUrl() + "] in InternalResourceView '" + getBeanName() + "'");
}
rd.forward(request, response);
}
}
@RequestBody和@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/requestBody")
public void requestBody(@RequestBody String body, Writer writer) throws IOException{
writer.write(body);
}
@RequestMapping(value="/responseBody", produces="application/json")
@ResponseBody
public Map<String, Object> responseBody(){
Map<String, Object> retMap = new HashMap<>();
retMap.put("param1", "abc");
return retMap;
}
- 第一个requestBody请求,使用@RequestBody将HTTP请求体转换成String类型,第二个responseBody请求,将Map对象转换成json格式输出到HTTP响应中。
SpringMVC处理请求和响应时,支持多种类型的请求参数和返回类型,而此种功能的实现就需要对HTTP消息体和参数及返回值进行转换,为此SpringMVC提供了大量的转换类,所有转换类都实现了HttpMessageConverter接口。
public interface HttpMessageConverter<T> {
// 当前转换器是否能将HTTP报文转换为对象类型
boolean canRead(Class<?> clazz, MediaType mediaType);
// 当前转换器是否能将对象类型转换为HTTP报文
boolean canWrite(Class<?> clazz, MediaType mediaType);
// 转换器能支持的HTTP媒体类型
List<MediaType> getSupportedMediaTypes();
// 转换HTTP报文为特定类型
T read(Class<? extends T> clazz, HttpInputMessage inputMessage)
throws IOException, HttpMessageNotReadableException;
// 将特定类型对象转换为HTTP报文
void write(T t, MediaType contentType, HttpOutputMessage outputMessage)
throws IOException, HttpMessageNotWritableException;
}
SpringMVC定义了两个接口来操作这两个过程:参数解析器HandlerMethodArgumentResolver和返回值处理器HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler。
// 参数解析器接口
public interface HandlerMethodArgumentResolver {
// 解析器是否支持方法参数
boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter);
// 解析HTTP报文中对应的方法参数
Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
NativeWebRequest webRequest, WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception;
}
// 返回值处理器接口
public interface HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler {
// 处理器是否支持返回值类型
boolean supportsReturnType(MethodParameter returnType);
// 将返回值解析为HTTP响应报文
void handleReturnValue(Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception;
}
参数解析器和返回值处理器在底层处理时,都是通过HttpMessageConverter进行转换。流程如下:

SpringMVC为@RequestBody和@ResponseBody两个注解实现了统一处理类RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor,实现了HandlerMethodArgumentResolver和HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler两个接口。
在上面整个请求流程的过程,可以找到解析请求参数和封装返回结果的入口分别是getMethodArgumentValues和handleReturnValue方法
解析请求参数
//InvocableHandlerMethod
private Object[] getMethodArgumentValues(NativeWebRequest request, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
MethodParameter[] parameters = getMethodParameters();
Object[] args = new Object[parameters.length];
// 遍历所有参数,逐个解析
for (int i = 0; i < parameters.length; i++) {
MethodParameter parameter = parameters[i];
parameter.initParameterNameDiscovery(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
args[i] = resolveProvidedArgument(parameter, providedArgs);
if (args[i] != null) {
continue;
}
// 参数解析器解析HTTP报文到参数
if (this.argumentResolvers.supportsParameter(parameter)) {//入口1
args[i] = this.argumentResolvers.resolveArgument(
parameter, mavContainer, request, this.dataBinderFactory);//入口2
continue;
}
}
return args;
}
public boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter) {
return parameter.hasParameterAnnotation(RequestBody.class);
}
public Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
NativeWebRequest webRequest, WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception {
parameter = parameter.nestedIfOptional();
// 通过HttpMessageConverter读取HTTP报文
Object arg = readWithMessageConverters(webRequest, parameter, parameter.getNestedGenericParameterType());//入口
String name = Conventions.getVariableNameForParameter(parameter);
WebDataBinder binder = binderFactory.createBinder(webRequest, arg, name);
if (arg != null) {
validateIfApplicable(binder, parameter);
if (binder.getBindingResult().hasErrors() && isBindExceptionRequired(binder, parameter)) {
throw new MethodArgumentNotValidException(parameter, binder.getBindingResult());
}
}
mavContainer.addAttribute(BindingResult.MODEL_KEY_PREFIX + name, binder.getBindingResult());
return adaptArgumentIfNecessary(arg, parameter);
}
protected <T> Object readWithMessageConverters(HttpInputMessage inputMessage, MethodParameter parameter,
Type targetType) throws IOException, HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException, HttpMessageNotReadableException {
....
try {
inputMessage = new EmptyBodyCheckingHttpInputMessage(inputMessage);
for (HttpMessageConverter<?> converter : this.messageConverters) {
Class<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converterType = (Class<HttpMessageConverter<?>>) converter.getClass();
....
// 判断转换器是否支持参数类型
if (converter.canRead(targetClass, contentType)) {
if (inputMessage.getBody() != null) {
inputMessage = getAdvice().beforeBodyRead(inputMessage, parameter, targetType, converterType);
// read方法执行HTTP报文到参数的转换
body = ((HttpMessageConverter<T>) converter).read(targetClass, inputMessage);
body = getAdvice().afterBodyRead(body, inputMessage, parameter, targetType, converterType);
}
else {
body = getAdvice().handleEmptyBody(null, inputMessage, parameter, targetType, converterType);
}
break;
}
...
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new HttpMessageNotReadableException("I/O error while reading input message", ex);
}
....
return body;
}
- 遍历所有参数挨个解析
- 找到可以解析参数的HandlerMethodArgumentResolver,通过参数是否包含RequestBody注解来判断
- 通过HttpMessageConverter读取HTTP报文,HttpMessageConverter也是有多个实现类,挨个遍历找到一个可以解析的
- 通过canRead方法判断该类型HttpMessageConverter是否可以解析请求,如果可以,就通过该实现类的read方法获取请求body
接下来看返回值的处理
处理返回值
//HandlerMethodReturnValueHandlerComposite
public void handleReturnValue(Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception {
// 选择合适的HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler,如果没有用@ResposeBody注解和用了注解其返回值处理器肯定不同
HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler handler = selectHandler(returnValue, returnType);//入口1
if (handler == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown return value type: " + returnType.getParameterType().getName());
}
// 执行返回值处理
handler.handleReturnValue(returnValue, returnType, mavContainer, webRequest);//入口2
}
private HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler selectHandler(Object value, MethodParameter returnType) {
boolean isAsyncValue = this.isAsyncReturnValue(value, returnType);
Iterator var4 = this.returnValueHandlers.iterator();
HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler handler;
do {
do {
if (!var4.hasNext()) {
return null;
}
handler = (HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler)var4.next();
} while(isAsyncValue && !(handler instanceof AsyncHandlerMethodReturnValueHandler));
} while(!handler.supportsReturnType(returnType));
return handler;
}
public void handleReturnValue(Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest)
throws IOException, HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException, HttpMessageNotWritableException {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
ServletServerHttpRequest inputMessage = createInputMessage(webRequest);
ServletServerHttpResponse outputMessage = createOutputMessage(webRequest);//入口1
// 调用HttpMessageConverter执行
writeWithMessageConverters(returnValue, returnType, inputMessage, outputMessage);//入口2
}
protected <T> void writeWithMessageConverters(T value, MethodParameter returnType,
ServletServerHttpRequest inputMessage, ServletServerHttpResponse outputMessage)
throws IOException, HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException, HttpMessageNotWritableException {
....
if (selectedMediaType != null) {
selectedMediaType = selectedMediaType.removeQualityValue();
for (HttpMessageConverter<?> messageConverter : this.messageConverters) {
// 判断是否支持返回值类型,返回值类型很有可能不同,如String,Map,List等
if (messageConverter.canWrite(valueType, selectedMediaType)) {
outputValue = (T) getAdvice().beforeBodyWrite(outputValue, returnType, selectedMediaType,
(Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>>) messageConverter.getClass(),
inputMessage, outputMessage);
if (outputValue != null) {
addContentDispositionHeader(inputMessage, outputMessage);
// 执行返回值转换
((HttpMessageConverter) messageConverter).write(outputValue, selectedMediaType, outputMessage);//入口
...
}
return;
}
}
}
....
}
protected ServletServerHttpResponse createOutputMessage(NativeWebRequest webRequest) {
//获取HttpServletResponse
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse)webRequest.getNativeResponse(HttpServletResponse.class);
Assert.state(response != null, "No HttpServletResponse");
return new ServletServerHttpResponse(response);
}
public class ServletServerHttpResponse implements ServerHttpResponse {
private final HttpServletResponse servletResponse;
private final HttpHeaders headers;
private boolean headersWritten = false;
private boolean bodyUsed = false;
public ServletServerHttpResponse(HttpServletResponse servletResponse) {
Assert.notNull(servletResponse, "HttpServletResponse must not be null");
//将获取的HttpServletResponse作为ServletServerHttpResponse的属性值
this.servletResponse = servletResponse;
this.headers = new ServletServerHttpResponse.ServletResponseHttpHeaders();
}
}
public interface ServletResponse {
String getCharacterEncoding();
String getContentType();
//ServletResponse有一个输出流对象,保存需要相应客户端的字节流
ServletOutputStream getOutputStream() throws IOException;
PrintWriter getWriter() throws IOException;
void setCharacterEncoding(String var1);
void setContentLength(int var1);
void setContentLengthLong(long var1);
void setContentType(String var1);
void setBufferSize(int var1);
int getBufferSize();
void flushBuffer() throws IOException;
void resetBuffer();
boolean isCommitted();
void reset();
void setLocale(Locale var1);
Locale getLocale();
}
protected void writeInternal(Object obj, HttpOutputMessage outputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotWritableException {
HttpHeaders headers = outputMessage.getHeaders();
//创建一个数组字节流缓冲对象
ByteArrayOutputStream outnew = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
//将obj对象转换成JSON并写入ByteArrayOutputStream中
int len = JSON.writeJSONString(outnew, this.fastJsonConfig.getCharset(), obj, this.fastJsonConfig.getSerializeConfig(), this.fastJsonConfig.getSerializeFilters(), this.fastJsonConfig.getDateFormat(), JSON.DEFAULT_GENERATE_FEATURE, this.fastJsonConfig.getSerializerFeatures());
headers.setContentLength((long)len);
//获取ServletResponse的输出流对象
OutputStream out = outputMessage.getBody();
//将转换后的outnew写入ServletResponse的输出流对象,这样就可以给客户端响应数据了
outnew.writeTo(out);
outnew.close();
}
public OutputStream getBody() throws IOException {
this.bodyUsed = true;
this.writeHeaders();
//获取ServletResponse的输出流对象
//ServletOutputStream getOutputStream() throws IOException;
return this.servletResponse.getOutputStream();
}
- HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler也是有多种实现的,首先找到一个适合的HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler
- 是否是异步解析
- 返回必须有@ResponseBody注解
- 获取ServletServerHttpResponse
- handleReturnValue方法实际也是调用HttpMessageConverter来完成转换处理,也是在多个HttpMessageConverter实现中先找到一个适合的,然后调用其write方法
- 将返回结果通过字节流写入到ServletServerHttpResponse中



